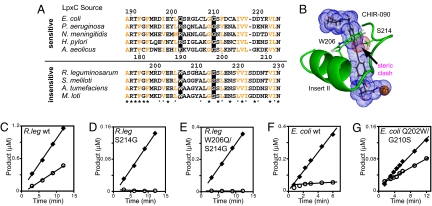
BIOCHEMISTRY. For the article “Structure of the deacetylase LpxC bound to the antibiotic CHIR-090: Time-dependent inhibition and specificity in ligand binding,” by Adam W. Barb, Ling Jiang, Christian R. H. Raetz, and Pei Zhou, which appeared in issue 47, November 20, 2007, of Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (104:18433–18438; first published November 19, 2007; 10.1073/pnas.0709412104, the authors note that Fig. 4 appeared incorrectly. In Fig. 4A, in the E. coli LpxC sequence, the residues “QSTGLCLGG” should instead appear as “QSRGLCLGG.” Additionally, Fig. 4G was mislabeled. These errors do not affect the conclusions of the article. The corrected figure and its legend appear below.
Fig. 4.
LpxC Insert II residues in the hydrophobic passage are critical for CHIR-090 resistance and time-dependent inhibition. (A) Sequence alignment of LpxC orthologs from CHIR-090-sensitive and -insensitive bacteria. Conserved hydrophobic residues are colored in orange. The amino acids tested in this work are highlighted with a black background. Residue numbers for A. aeolicus, E. coli, and R. leguminosarum LpxC are included. (B) Homology model of R. leguminosarum LpxC Insert II with CHIR-090. CHIR-090 and the Ser and Trp side chains are shown as stick models. The vdW surfaces of CHIR-090 and the Ser 214 hydroxyl group are shown as blue and red dots, respectively. (C–G) Sensitivity of mutant LpxC enzymes to CHIR-090. The wild-type R. leguminosarum enzyme (C) and the mutant enzymes S214G (D) and W206Q/S214G (E) were assayed with 0 μM CHIR-090 (◆) or 0.5 μM CHIR-090 (○). The wild-type E. coli enzyme (F) and the mutant enzyme Q202W/G210S (G) were assayed with 0 nM CHIR-090 (◆) or 4 nM CHIR-090 (○). The linear portion of the reaction velocity is depicted with a line.