Abstract
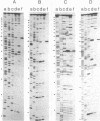
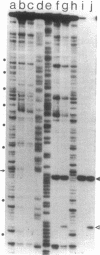
DNA gyrase, in the presence of the inhibitor oxolinic acid, can induce double-strand DNA breakage at specific sites. The sequences at several sites have been determined. In addition, the structure of complexes formed between DNA gyrase and restriction fragments containing an oxolinic acid-promoted cleavage site has been examined by DNase protection methods. DNA gyrase protects more than 120 base pairs of DNA against pancreatic DNase in a region surrounding the cleavage site. Protection is observed both in the presence and absence of oxolinic acid. Protected DNA flanking the cleavage site contains DNase I-sensitive sites spaced on the average 10 or 11 base pairs apart. This result supports the view that, in the DNA gyrase--DNA complex, the DNA is largely wrapped on the outside of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown P. O., Cozzarelli N. R. A sign inversion mechanism for enzymatic supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1979 Nov 30;206(4422):1081–1083. doi: 10.1126/science.227059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. DNA gyrase and DNA supercoiling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Wang J. C. Mapping the topography of DNA wrapped around gyrase by nucleolytic and chemical probing of complexes of unique DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevan L., Wang J. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase-deoxyribonucleic acid complex containing 140 base pairs of deoxyribonucleic acid and an alpha 2 beta 2 protein core. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5229–5234. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Formation and resolution of DNA catenanes by DNA gyrase. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Liu C. C., Alberts B. M. Type II DNA topoisomerases: enzymes that can unknot a topologically knotted DNA molecule via a reversible double-strand break. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):697–707. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. DNA-DNA gyrase complex: the wrapping of the DNA duplex outside the enzyme. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):979–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Micrococcus luteus DNA gyrase: active components and a model for its supercoiling of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2098–2102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Fisher L. M., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. DNA gyrase action involves the introduction of transient double-strand breaks into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1847–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P. Structures and mechanisms of DNA restriction and modification enzymes. Q Rev Biophys. 1979 Aug;12(3):315–369. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Cozzarelli N. R. Contacts between DNA gyrase and its binding site on DNA: features of symmetry and asymmetry revealed by protection from nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1416–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Cozzarelli N. R. Site-specific cleavage of DNA by E. coli DNA gyrase. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Higgins N. P., Cozzarelli N. R. Interaction between DNA gyrase and its cleavage site on DNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2211–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Higgins N. P., Cozzarelli N. R. DNA gyrase subunit stoichiometry and the covalent attachment of subunit A to DNA during DNA cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3865–3874. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J. I., Ohmori H., Bird R. E. Origin of replication of colicin E1 plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse Y. C., Kirkegaard K., Wang J. C. Covalent bonds between protein and DNA. Formation of phosphotyrosine linkage between certain DNA topoisomerases and DNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5560–5565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]