Abstract
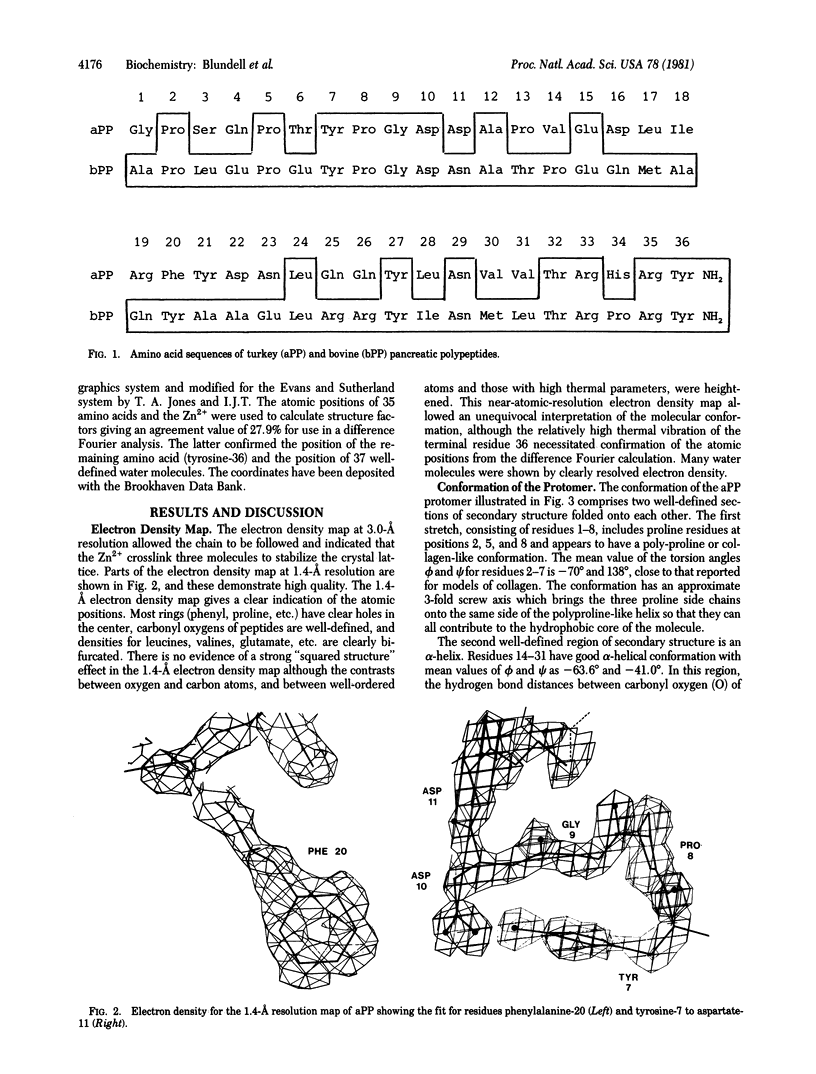
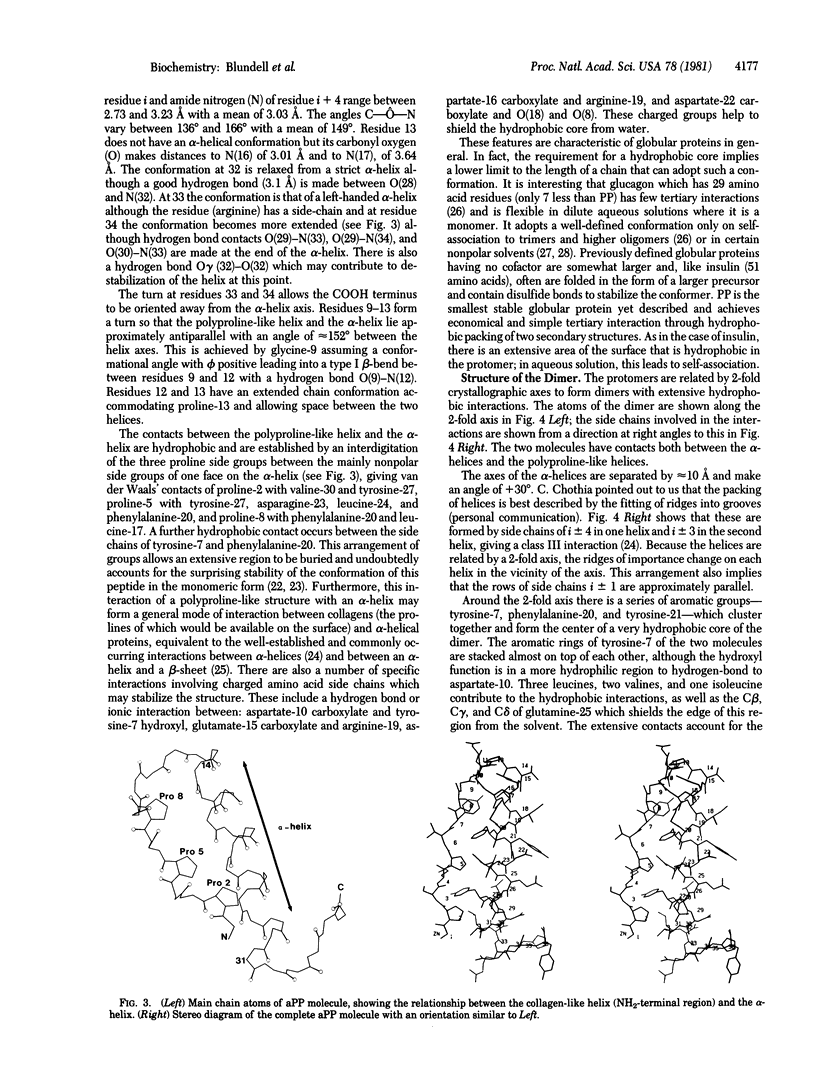
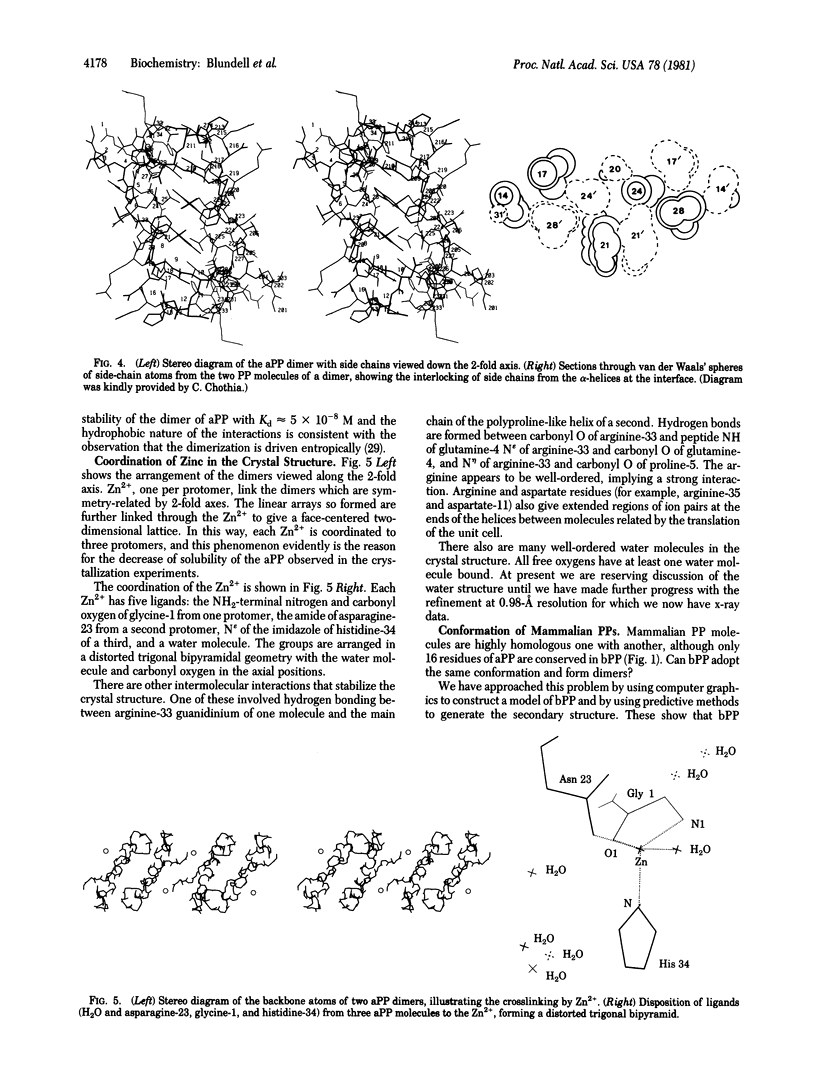
The crystal structure of avian pancreatic polypeptide (aPP), a 36-residue polypeptide with some hormonal properties, has been determined by using single isomorphous replacement and anomalous scattering to 2.1-Å resolution. The phases were extended to 1.4-Å resolution by using a modified tangent formula. The molecule contains two regions of secondary structure—an extended polyproline-like helix (residues 1-8) and an α-helix (residues 14-31)—that run roughly antiparallel. The packing together of nonpolar groups from these regions gives the molecule a hydrophobic core in spite of its small size. The aPP molecules form a symmetrical dimer in the crystal stabilized principally by interlocking of nonpolar groups from the α-helices. The aPP dimers are crosslinked by coordination of Zn2+; three aPP molecules contribute ligands to each zinc. The coordination geometry is a distorted trigonal bipyramid. The properties of the aPP molecule in solution are consistent with expectations based on the crystal structure. The aPP molecule has several general features in common with the pancreatic hormones insulin and glucagon. All three hormones have complex mechanisms for self-association. Like insulin, aPP seems to have a stable monomeric structure but its biological activity seems to depend on the more flexible COOH-terminal region analogous to the flexible NH2-terminal region of glucagon.
Keywords: satiety factor, graphics, zinc, insulin, glucagon
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björnsson O. G., Adrian T. E., Dawson J., McCloy R. F., Greenberg G. R., Bloom S. R., Chadwick V. S. Effects of gastrointestinal hormones on fasting gallbladder storage patterns in man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;9(4):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Dockerill S., Sasaki K., Tickle I. J., Wood S. P. The relation of structure to storage and receptor binding of glucagon. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1331–1336. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. J., Noelken M. E., Kimmel J. R. Reversible dimerization of avian pancreatic polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1844–1849. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. J., Noelken M. E., Kimmel J. R. Reversible dimerization of avian pancreatic polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1844–1849. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Levitt M., Richardson D. Structure of proteins: packing of alpha-helices and pleated sheets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4130–4134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contaxis C. C., Epand R. M. A study of the conformational properties of glucagon in the presence of glycols. Can J Biochem. 1974 Jun;52(6):456–468. doi: 10.1139/o74-070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd J. C., Jr, Fajans S. S., Pek S., Chance R. E. A newly recognized pancreatic polypeptide; plasma levels in health and disease. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;33:519–570. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571133-3.50019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates R. J., Lazarus N. R. The ability of pancreatic polypeptides (APP and BPP) to return to normal the hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinaemia and weight gain of New Zealand obese mice. Horm Res. 1977;8(4):189–202. doi: 10.1159/000178800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel J. R., Hayden L. J., Pollock H. G. Isolation and characterization of a new pancreatic polypeptide hormone. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9369–9376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel J. R., Pollock H. G., Hazelwood R. L. Isolation and characterization of chicken insulin. Endocrinology. 1968 Dec;83(6):1323–1330. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-6-1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Sundler F., Håkanson R., Pollock H. G., Kimmel J. R. Localization of APP, a postulated new hormone, to a pancreatic endocrine cell type. Histochemistry. 1974;42(4):377–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00492685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Evans D. C., Chance R. E., Spray G. F. Bovine pancreatic peptide: action on gastric and pancreatic secretion in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1977 Mar;232(3):E311–E315. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.232.3.E311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Carpentier J. L., Patel Y. C., Malaisse W. J., Orci L. Pancreatic polypeptide: a possible role in the regulation of food intake in the mouse. Hypothesis. Experientia. 1977 Jul 15;33(7):915–917. doi: 10.1007/BF01951279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Baetens D., Ravazzola M., Stefan Y., Malaisse-Lagae F. Pancreatic polypeptide and glucagon : non-random distribution in pancreatic islets. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 15;19(12):1811–1815. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen R. A., Lindsay D. G., Wood S. P., Tickle I. J., Blundell T. L., Wollmer A., Krail G., Brandenburg D., Zahn H., Gliemann J. Receptor-binding region of insulin. Nature. 1976 Feb 5;259(5542):369–373. doi: 10.1038/259369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Dockerill S., Adamiak D. A., Tickle I. J., Blundell T. X-ray analysis of glucagon and its relationship to receptor binding. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):751–757. doi: 10.1038/257751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A. B., Edelhoch H. Polypeptide hormone interaction. II. Glucagon binding to lysolecithin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):4986–4991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. W., Gingerich R. L., Tager H. S. Biosynthesis of pancreatic polypeptide. Identification of a precursor and a co-synthesized product. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11494–11498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. W., Stenquist B., Olbe L., Stadil F. Synchronous oscillations in the basal secretion of pancreatic-polypeptide and gastric acid. Depression by cholinergic blockade of pancreatic-polypeptide concentrations in plasma. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jan;76(1):14–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg M. J., Thornton J. M. On the conformation of proteins: an analysis of beta-pleated sheets. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 25;110(2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Mutt V. Isolation of two novel candidate hormones using a chemical method for finding naturally occurring polypeptides. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):417–418. doi: 10.1038/285417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. L., Solomon T. E., Walsh J. H., Grossman M. I. Pancreatic polypeptide. Metabolism and effect on pancreatic secretion in dogs. Gastroenterology. 1979 Mar;76(3):524–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Noorden S., Falkmer S. Gut-islet endocrinology-some evolutionary aspects. Invest Cell Pathol. 1980 Jan-Mar;3(1):21–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. P., Pitts J. E., Blundell T. L., Tickle I. J., Jenkins J. A. Purification, crystallisation and preliminary X-ray studies on avian pancreatic polypeptide. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



