Abstract
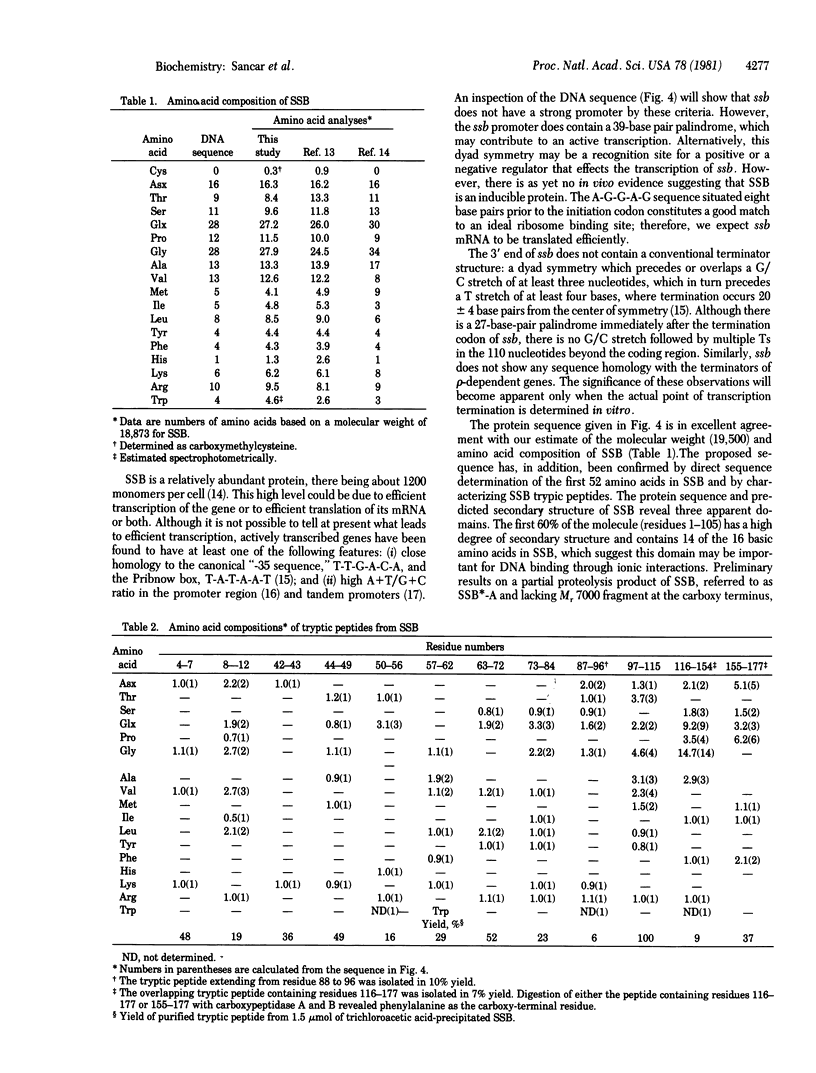
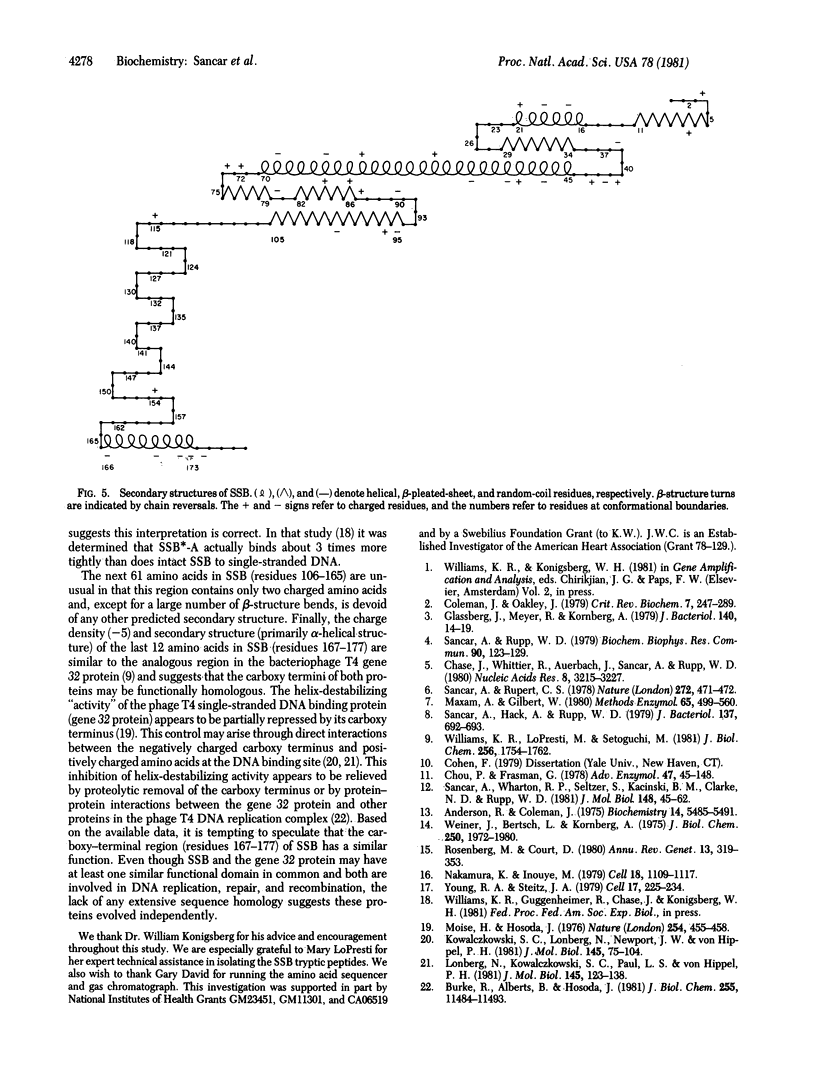
We have determined the sequences of the ssb gene and protein of Escherichia coli. The coding region of ssb is 534 base pairs and is preceeded and followed by dyad symmetries of 39 base pairs and 27 base pairs, respectively. The promoter for ssb is close to that for uvrA and these two genes are transcribed in opposite directions: ssb clockwise and uvrA counterclockwise on the standard E. coli genetic map. The DNA helix-destabilizing protein encoded by the ssb gene (single-strand binding protein) contains 177 amino acids and has a calculated molecular weight of 18,873. Although there is no extensive sequence homology among the three helix-destabilizing proteins whose sequences are now known, both the E. coli and bacteriophage T4 DNA helix-destabilizing proteins do contain an acidic, alpha-helical region at their carboxy termini that may be functionally homologous. The remainder of the E. coli helix-destabilizing protein can be divided into two apparent domains on the basis of its amino acid sequence. The amino-terminal region (residues 1-105) contains 79% of the charged residues (27 out of 34 total) in the protein and is predicted to have a high degree of secondary structure (alpha helix and beta pleated sheet). In contrast, the region including residues 106-165 contains only two charged amino acids and is devoid of alpha helix or beta pleated sheet.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Coleman J. E. Physiochemical properties of DNA binding proteins: gene 32 protein of T4 and Escherichia coli unwinding protein. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5485–5491. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Alberts B. M., Hosoda J. Proteolytic removal of the COOH terminus of the T4 gene 32 helix-destabilizing protein alters the T4 in vitro replication complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11484–11493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. W., Whittier R. F., Auerbach J., Sancar A., Rupp W. D. Amplification of single-strand DNA binding protein in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3215–3227. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. E., Oakley J. L. Physical chemical studies of the structure and function of DNA binding (helix-destabilizing) proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980 Jan;7(3):247–289. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassberg J., Meyer R. R., Kornberg A. Mutant single-strand binding protein of Escherichia coli: genetic and physiological characterization. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):14–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.14-19.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Lonberg N., Newport J. W., von Hippel P. H. Interactions of bacteriophage T4-coded gene 32 protein with nucleic acids. I. Characterization of the binding interactions. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):75–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg N., Kowalczykowski S. C., Paul L. S., von Hippel P. H. Interactions of bacteriophage T4-coded gene 32 protein with nucleic acids. III. Binding properties of two specific proteolytic digestion products of the protein (G32P*I and G32P*III). J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):123–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moise H., Hosoda J. T4 gene 32 protein model for control of activity at replication fork. Nature. 1976 Feb 12;259(5543):455–458. doi: 10.1038/259455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Inouye M. DNA sequence of the gene for the outer membrane lipoprotein of E. coli: an extremely AT-rich promoter. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1109–1117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupert C. S. Determination of plasmid molecular weights from ultraviolet sensitivities. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):471–472. doi: 10.1038/272471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupp W. D. Cloning of uvrA, lexC and ssb genes of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91598-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Wharton R. P., Seltzer S., Kacinski B. M., Clarke N. D., Rupp W. D. Identification of the uvrA gene product. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 5;148(1):45–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner J. H., Bertsch L. L., Kornberg A. The deoxyribonucleic acid unwinding protein of Escherichia coli. Properties and functions in replication. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):1972–1980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. R., LoPresti M. B., Setoguchi M. Primary structure of the bacteriophage T4 DNA helix-destabilizing protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1754–1762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Tandem promoters direct E. coli ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]