Abstract
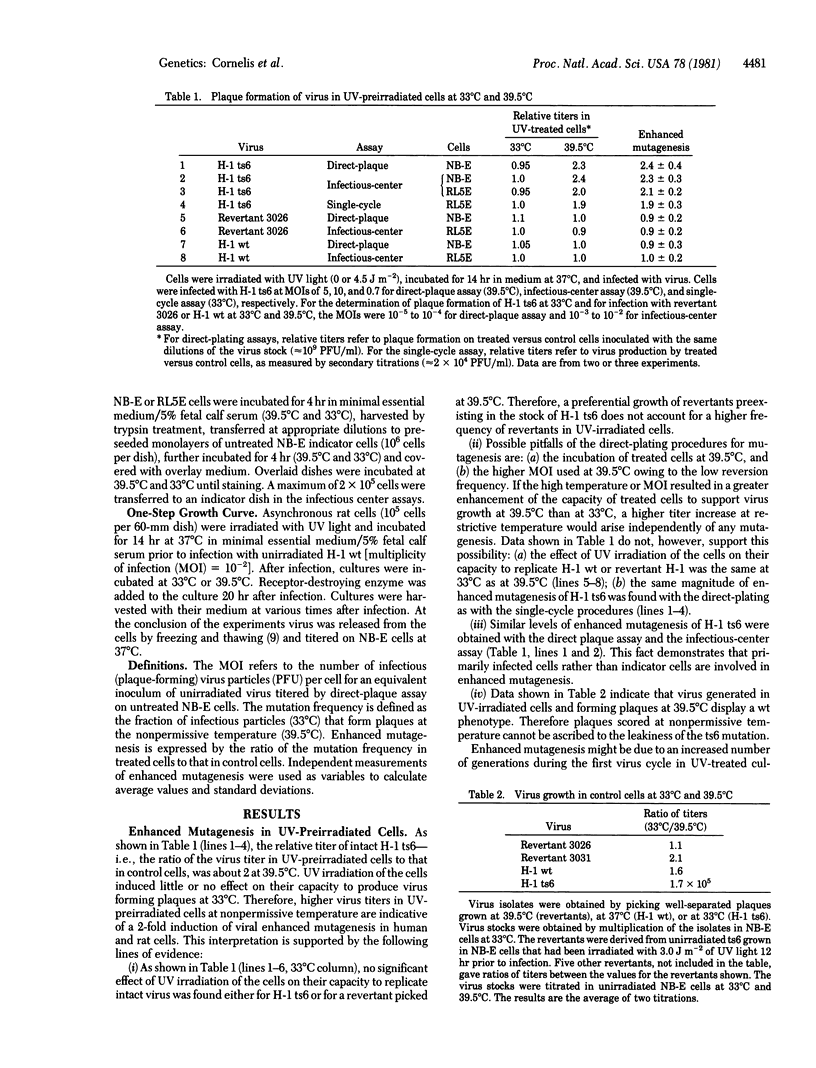
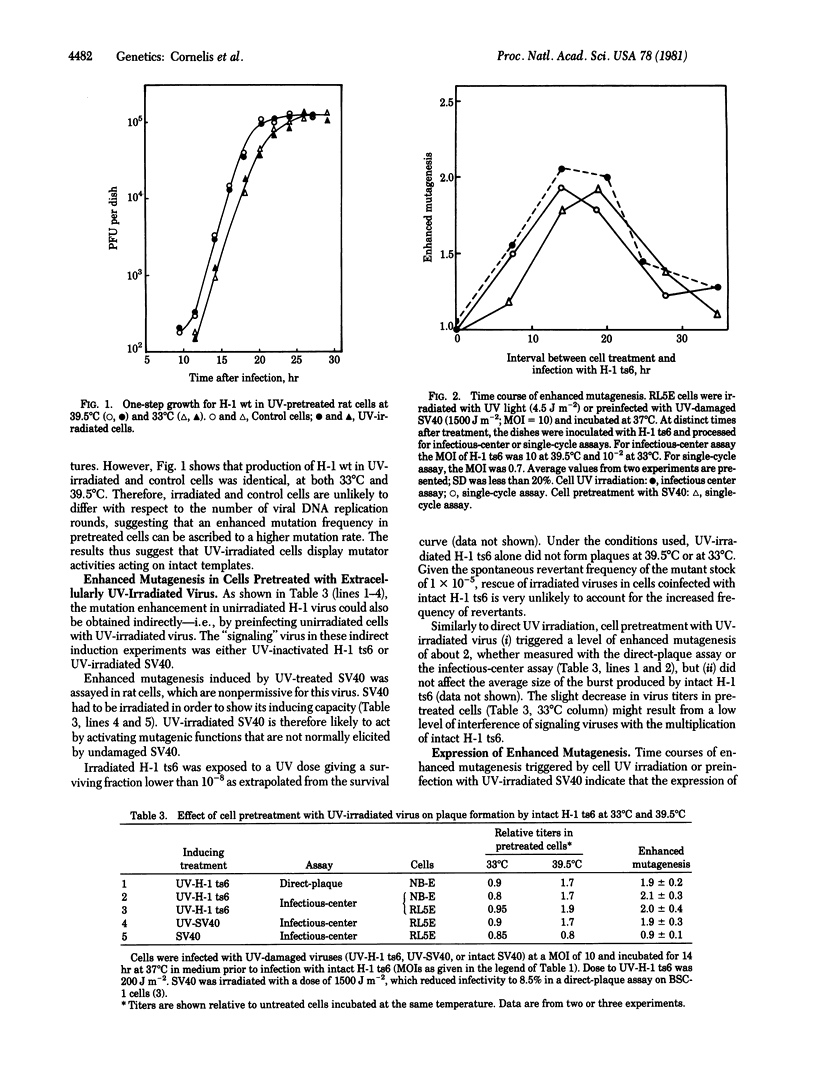
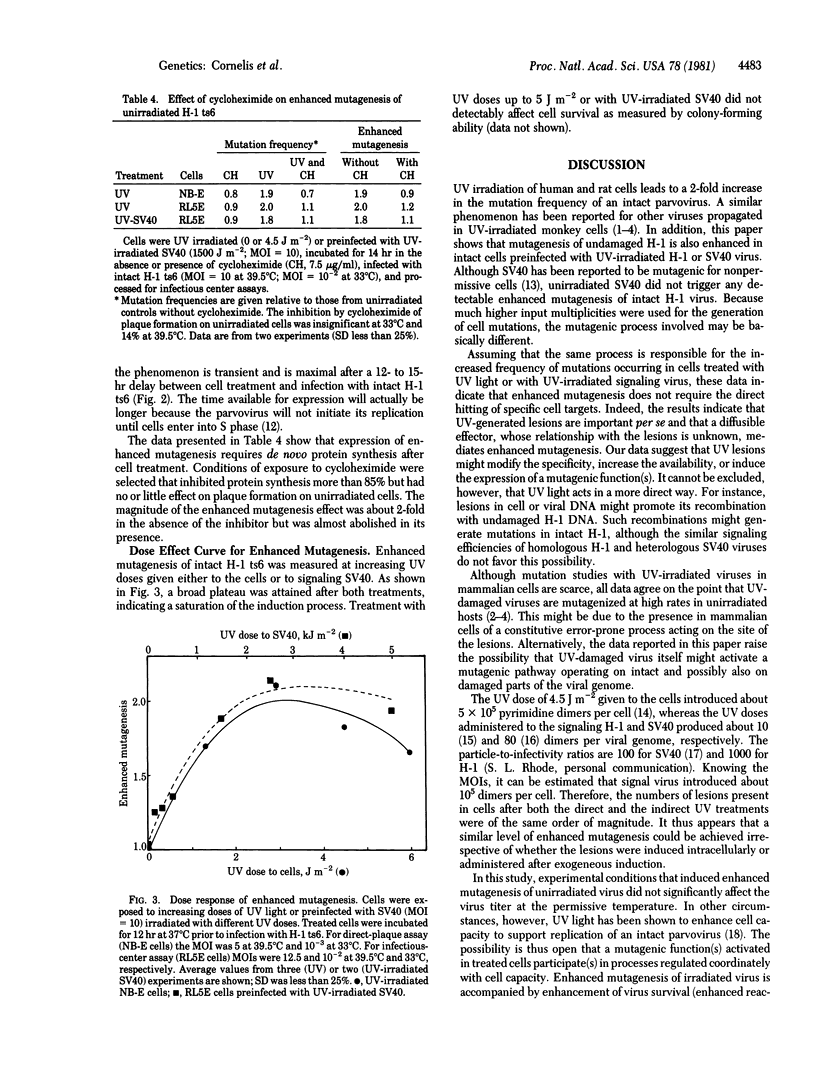
The frequency of mutants among the descendants of intact parvovirus H-1 was increased when cells of human and rat origin were exposed to UV light prior to infection. An enhanced mutagenesis of intact H-1 could be induced to almost the same extent in unirradiated cells by preinfecting them with H-1 or simian virus 40 that had been irradiated with UV light. The expression of an enhanced mutagenesis of unirradiated H-1 after cell treatment with UV light or UV-irradiated virus was delayed, transient, and dose-dependent, and it was dependent on de novo protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bomford R., Weinstein I. B. Transformation of a rat epithelial-like cell line by murine sarcoma virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Aug;49(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis J. J., Lupker J. H., van der Eb A. J. UV-reactivation, virus production and mutagenesis of SV40 in VU-irradiated monkey kidney cells. Mutat Res. 1980 Jun;71(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta U. B., Summers W. C. Ultraviolet reactivation of herpes simplex virus is mutagenic and inducible in mammlian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2378–2381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J., Devoret R., Radman M. Indirect ultraviolet-reactivation of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):144–147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House W. A simple method for the production of neuraminidase. Lab Pract. 1967 Mar;16(3):321–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledinko N., Hopkins S., Toolan H. Relationship between potentiation of H-1 growth by human adenovirus 12 and inhibition of the 'helper' adenovirus by H-1. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jul;5(1):19–31. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytle C. D., Goddard J. G., Lin C. H. Repair and mutagenesis of herpes simplex virus in UV-irradiated monkey cells. Mutat Res. 1980 Apr;70(2):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor W. R., Cook J. S., Tennant R. W. Ultraviolet photobiology of Kilham rat virus and the absolute ultraviolet photosensitivities of other animal viruses: influence of DNA strandedness, molecular weight, and host-cell repair. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):368–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90489-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Replication process of the parvovirus H-1 V. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive H-1 mutants. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):659–667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.659-667.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarasin A., Benoit A. Induction of an error-prone mode of DNA repair in UV-irradiated monkey kidney cells. Mutat Res. 1980 Mar;70(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Cawte P. J., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Three structural polypeptides coded for by minite virus of mice, a parvovirus. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.273-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theile M., Strauss M., Luebbe L., Scherneck S., Krause H., Geissler E. SV40-induced somatic mutations: possible relevance to viral transformation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):377–382. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



