Abstract
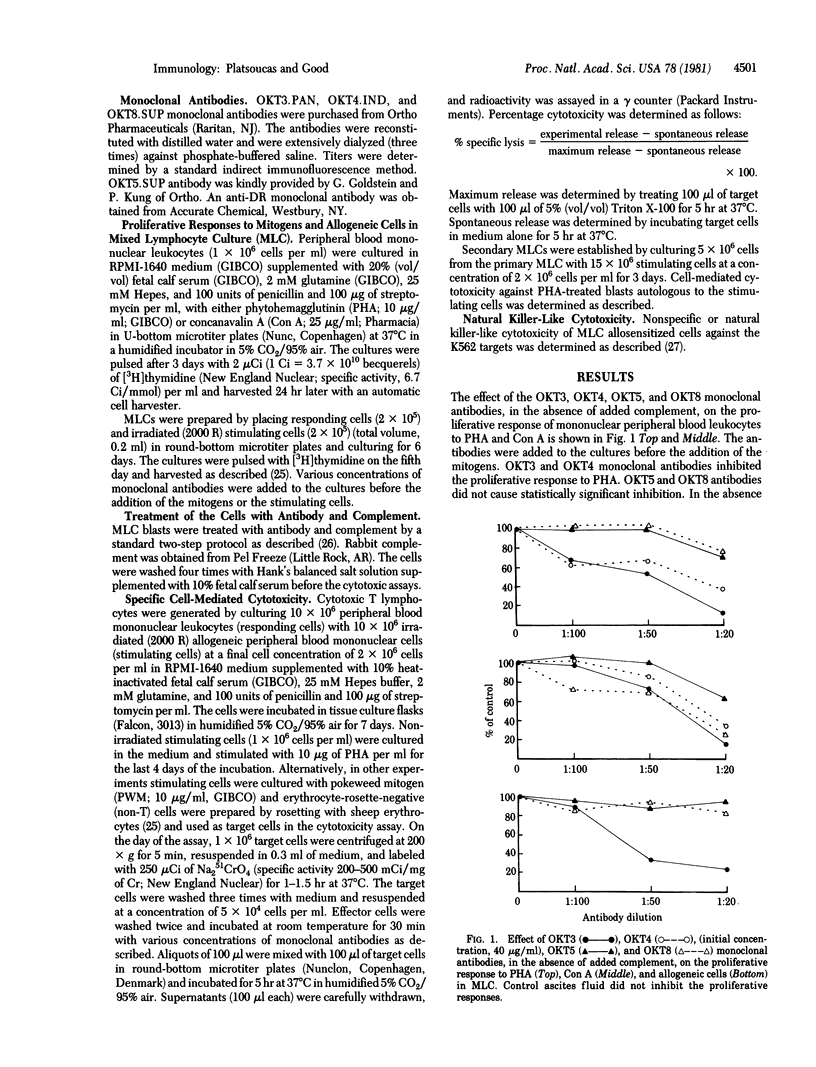
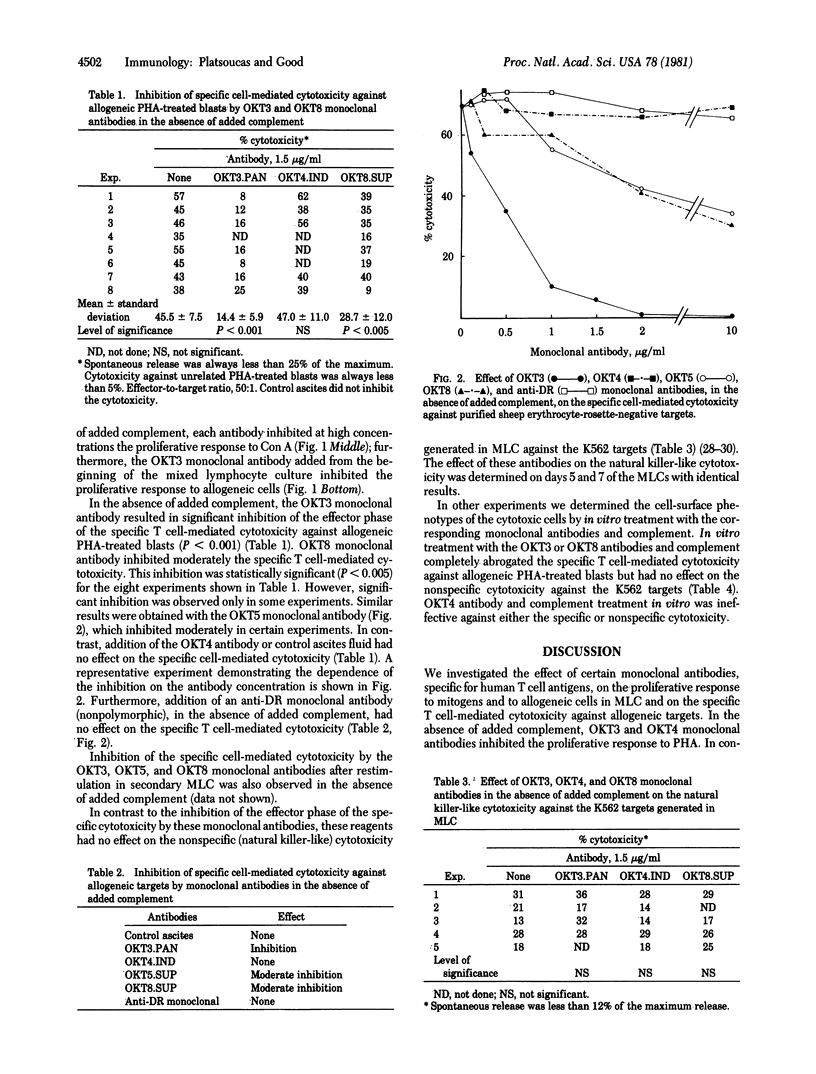
Human T lymphocyte subpopulations recently have been defined by monoclonal antibodies that recognize cell-surface antigens selectively expressed on functionally distinct T cell subsets. The majority (approximately 90%) of the peripheral blood sheep erythrocyte-rosette-forming cells carry the OKT3 antigen. Helper cells are OKT4+, whereas cytotoxic/suppressor cells are OKT5+ and OKT8+. We investigated the effect of several monoclonal antibodies recognizing T cell antigens on certain proliferative responses of T cells and on the effector phase of the specific T cell-mediated cytotoxicity generated in mixed lymphocyte culture (MLC). In the absence of added complement, (i) OKT3 and OKT4 monoclonal antibodies inhibited the proliferative response to phytohemagglutinin (PHA), (ii) OKT3 monoclonal antibody inhibited the proliferative response to allogeneic cells in MLC, and (iii) OKT3 monoclonal antibody significantly and regularly inhibited the effector phase of the specific T cell-mediated cytotoxicity against allogeneic targets (P < 0.001) in a concentration-dependent manner. The OKT5 and OKT8 monoclonal antibodies, again in the absence of complement, inhibited moderately the specific cell-mediated cytotoxicity. This inhibition was observed in some experiments only. Inhibition of the specific cytotoxicity by these antibodies also was observed in secondary responses. In contrast, again in the absence of added complement, none of these antibodies had an effect on the nonspecific cytotoxicity generated in MLC against the K562 targets. The OKT4 antibody in the absence of added complement had no effect on either the specific or nonspecific cytotoxicity. Furthermore, treatment with OKT3 or OKT8 antibody and complement completely abrogated the specific T cell-mediated cytotoxicity but had no effect on the natural killer-like cytotoxicity against the K562 cells. Treatment with the OKT4 antibody and complement had no effect. These results suggest that (i) the T5/T8 and T3 antigens, present on cytotoxic T lymphocytes, may be involved directly or indirectly in the antigen recognition step(s) or the lytic mechanism of T cell-mediated lympholysis; and (ii) nonspecific cytotoxicity against the K562 targets generated in MLC is mediated by cells phenotypically different than those that mediate specific cytotoxicity.
Keywords: thymus-dependent antigens, mixed lymphocyte culture, cytotoxic T cells, natural killer-like cytotoxicity
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callewaert D. M., Lightbody J. J., Kaplan J., Jaroszewski J., Peterson W. D., Jr, Rosenberg J. C. Cytotoxicity of human peripheral lymphocytes in cell-mediated lympholysis; antibody-dependent cell-mediated lympholysis and natural cytotoxicity assays after mixed lymphocyte culture. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clagett J. A., Wilson C. B., Weigle W. O. Interstitial immune complex thyroiditis in mice: the role of autoantibody to thyroglobulin. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1439–1456. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. L., Faldetta T. J., Humphreys R. E., Pratt D. M., Yunis E. J., Schlossman S. F. Peripheral human T cells sensitized in mixed leukocyte culture synthesize and express Ia-like antigens. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1440–1445. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. L., Lazarus H., Penta A. C., Schlossman S. F. Two functionally distinct subpopulations of human T cells that collaborate in the generation of cytotoxic cells responsible for cell-mediated lympholysis. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1423–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. L., Wall D. W., Platsoucas C. D., Siegal F. P., Fikrig S. M., Testa C. M., Good R. A. Thymus-dependent membrane antigens in man: inhibition of cell-mediated lympholysis by monoclonal antibodies to TH2 antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):544–548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu S. M., Chiorazzi N., Wang C. Y., Montrazeri G., Kunkel H. G., Ko H. S., Gottlieb A. B. Ia-bearing T lymphocytes in man. Their identification and role in the generation of allogeneic helper activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1423–1428. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. M., Taylor B. A., Cherry M. Evidence for close linkage of a mouse light chain marker with the Ly-2,3 locus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1585–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander N., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Blocking effect of lyt-2 antibodies on T cell functions. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):674–687. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A. K., Wigzell H. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte membrane components: an analysis of structures related to function. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1977;6:209–244. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2841-4_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fu S. M., Winchester R. J., Yu D. T., Kunkel H. G. Ia determinants on stimulated human T lymphocytes. Occurrence on mitogen- and antigen-activated T cells. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):246–255. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung P. C., Goldstein G. Functional and developmental compartments of human T lymphocytes. Vox Sang. 1980 Sep;39(3):121–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1980.tb01846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung P., Goldstein G., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Monoclonal antibodies defining distinctive human T cell surface antigens. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):347–349. doi: 10.1126/science.314668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Evans R. L., Lipinski M., Cunningham-Rundles C., Good R. A., Herzenberg L. A. Evolutionary conservation of surface molecules that distinguish T lymphocyte helper/inducer and cytotoxic/suppressor subpopulations in mouse and man. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):310–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama E., Shiku H., Stockert E., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cytotoxic T cells: Lyt phenotype and blocking of killing activity by Lyt antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platsoucas C. D., Catsimpoolas N. Separation of rat T and B lymphocytes by density gradient electrophoresis. J Immunol Methods. 1979;26(3):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platsoucas C. D., Fernandes G., Gupta S. L., Kempin S., Clarkson B., Good R. A., Gupta S. Defective spontaneous and antibody-dependent cytotoxicity mediated by E-rosette-positive and E-rosette-negative cells in untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: augmentation by in vitro treatment with interferon. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1216–1223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platsoucas C. D., Good R. A., Gupta S. Separation of human T lymphocyte subpopulations (Tmu, Tgamma) by density gradient electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1972–1976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with the human cytotoxic/suppressor T cell subset previously defined by a heteroantiserum termed TH2. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1301–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Further characterization of the human inducer T cell subset defined by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2894–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Separation of functional subsets of human T cells by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Con A-inducible suppression of MLC: evidence for mediation by the TH2 + T cell subset in man. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1335–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. The differentiation and function of human T lymphocytes. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):821–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J. K., Golub S. H. Studies on cytotoxicity generated in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. I. Time course and target spectrum of several distinct concomitant cytotoxic activities. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1415–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J. K., Masucci G., Poros A., Klein E., Golub S. H. Studies on cytotoxicity generated in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. II. Anti-K562 effectors are distinct from allospecific CTL and can be generated from NK-depleted T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1303–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiku H., Kisielow P., Bean M. A., Takahashi T., Boyse E. A., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Expression of T-cell differentiation antigens on effector cells in cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Evidence for functional heterogeneity related to the surface phenotype of T cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):227–241. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara N., Sachs D. H. Mouse alloantibodies capable of blocking cytotoxic T-cell function. I. Relationship between the antigen reactive with blocking antibodies and the Lyt-2 locus. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):432–444. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhorst C., van Agthoven A., Reinherz E., Schlossman S. Biochemical analysis of human T lymphocyte differentiation antigens T4 and T5. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):520–521. doi: 10.1126/science.6967228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Good R. A., Ammirati P., Dymbort G., Evans R. L. Identification of a p69,71 complex expressed on human T cells sharing determinants with B-type chronic lymphatic leukemic cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1539–1544. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettstein P. J., Bailey D. W., Mobraaten L. E., Klein J., Frelinger J. A. T lymphocyte response to H-2 mutants: cytotoxic effectors are Ly-1+2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



