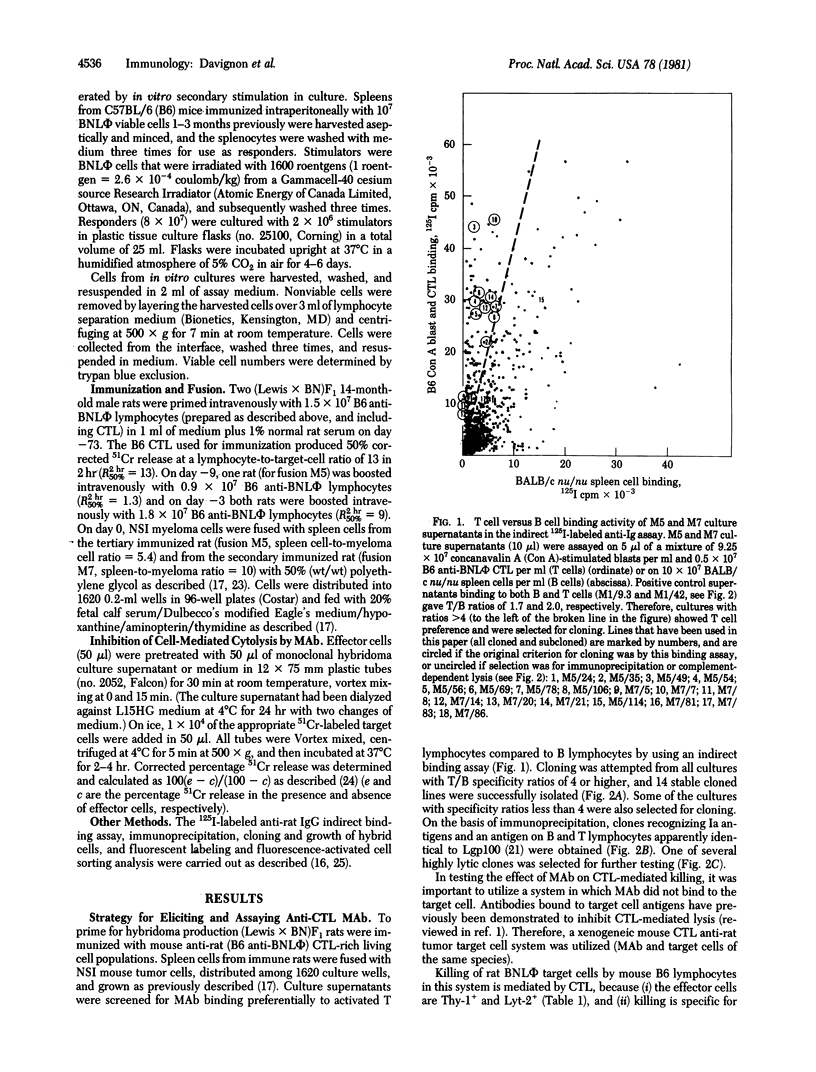
Abstract
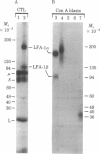
Monoclonal antibodies (MAb) have been used to probe the relationship of cytolytic T lymphocyte (CTL) surface molecules to CTL function. Rat MAb to mouse CTL were generated. Twelve MAb so obtained gave preferential binding to T cells as compared to B cells, and three of these recognized previously undescribed surface polypeptides. These Mab and more broadly reactive and previously obtained MAb were tested for their ability to block CTL-mediated killing in the absence of complement. To ensure that any observed blocking was due to binding of MAb to the effector cell rather than the target cell, a xenogeneic mouse CTL anti-rat BN lymphoma target cell system was utilized (MAb and target cells both of rat origin). Of 24 MAb tested here, 21 had little or no effect on CTL function, including those to H-2, Thy-1, Lyt-1, Ly 5, Ly 6, Lgp 100, and at least six other defined antigens. We confirmed inhibition of killing with two MAb to Lyt-2,3. Another MAb, M7/14, gave profound and consistent blockade of CTL function. It was confirmed that M7/14 MAb blocks killing by binding to the mouse CTL and does not bind to the rat lymphoma target cells used for the CTL assay. The findings suggest that the antigen defined by M7/14, termed a lymphocyte function-associated antigen, LFA-1, participates in or is closely associated with the mechanism of CTL-mediated killing. LFA-1 contains two polypeptide chains of 180,000 and 95,000 Mr and is distinct from other described lymphocyte glycoproteins. LFA-1 thus represents both a previously undescribed lymphocyte surface antigen and molecular site for blockade of CTL-mediated killing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berke G. Interaction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and target cells. Prog Allergy. 1980;27:69–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke G., Sullivan K. A., Amos B. Rejection of ascites tumor allografts. I. Isolation, characterization, and in vitro reactivity of peritoneal lymphoid effector cells from BALB-c mice immune to EL4 leukosis. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1334–1350. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz H., Wigzell H. Antigen-binding, idiotypic T-lymphocyte receptors. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;7:113–177. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3054-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M., Saal F. The T-cell receptor and cytotoxicity An anti=idiotype antiserum that inhibits a graft-versus-host reaction does not inhibit cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Cell Immunol. 1977 May;30(2):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Celis E., Eisen H. N., Solomon F. Crawling movements of lymphocytes on and beneath fibroblasts in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2917–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S. L., Ozato K., Sachs D. H. Blocking of allogeneic cell-mediated lympholysis by monoclonal antibodies to H-2 antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J., Ahmed A., Bonavida B. Studies on the induction and expression of T cell-mediated immunity. X. Inhibition by Lyt 2,3 antisera of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated antigen-specific and -nonspecific cytotoxicity: evidence for the blocking of the binding between T lymphocytes and target cells and not the post-binding cytolytic steps. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2444–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gately M. K., Martz E. Early steps in specific tumor cell lysis by sensitized mouse T lymphocytes. III. Resolution of two distinct roles for calcium in the cytolytic process. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):482–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gately M. K., Martz E. T11: a new protein marker on activated murine T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):709–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gately M. K., Wechter W. J., Martz E. Early steps in specific tumor cell lysis by sensitized mouse T lymphocytes. IV. Inhibition of programming for lysis by pharmacologic agents. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):783–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golstein P., Smith E. T. The lethal hit stage of mouse T and non-T cell-mediated cytolysis: differences in cation requirements and characterization of an analytical "cation pulse" method. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jan;6(1):31–37. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S. T cell mediated cytolysis: consideration of the role of a soluble mediator. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Apr;17(4):231–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S. T-Cell-mediated cytolysis: an overview of some current issues. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;7:245–272. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3054-7_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander N., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Blocking effect of lyt-2 antibodies on T cell functions. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):674–687. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A. K., Wigzell H. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte membrane components: an analysis of structures related to function. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1977;6:209–244. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2841-4_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Wigzell H., Holmquist G., Ersson B., Carlsson P. Selective affinity fractionation of murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). Unique lectin specific binding of the CTL associated surface glycoprotein, T 145. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):473–484. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppers R. C., Henney C. S. Studies on the mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. IX. Relationships between antigen recognition and lytic expression in killer T cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightbody J. J., Urbani L., Poulik M. D. Effect of beta 2 microglobulin antibody on effector function of T-cell mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):227–228. doi: 10.1038/250227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl K. F. Antisera against recognition sites. Lack of effect on the mixed leukocyte culture interaction. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Dec;2(6):501–504. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl K. F., Lemke H. Inhibition of killer-target cell interaction by monoclonal anti-H-2 antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jul;9(7):526–536. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Fink P., Gridley T., Raulet D. H., Bevan M. J., Gefter M. L. Properties and applications of monoclonal antibodies directed against determinants of the Thy-1 locus. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2491–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E., Benacerraf B. An effector-cell independent step in target cell lysis by sensitized mouse lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1538–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E. Immune T lymphocyte to tumor cell adhesion. Magnesium sufficient, calcium insufficient. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):584–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E. Mechanism of specific tumor-cell lysis by alloimmune T lymphocytes: resolution and characterization of discrete steps in the cellular interaction. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;7:301–361. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3054-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama E., Shiku H., Stockert E., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cytotoxic T cells: Lyt phenotype and blocking of killing activity by Lyt antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Trowbridge I. S., Scheid M. P. T200 cell surface glycoprotein of the mouse. Polymorphism defined by the Ly-5 system of alloantigens. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1311–1316. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker W. L., Martz E. Lectin-induced nonlethal adhesions between cytolytic T lymphocytes and antigenically unrecognizable tumor cells and nonspecific "triggering" of cytolysis. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):25–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein T. L., Mage M. G., Mond J., McHugh L. L. Guinea pig antiserum to mouse cytotoxic T lymphocytes and their precursors. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):209–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein T. L., Mage M., Jones G., McHugh L. L. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte sequential killing of immobilized allogeneic tumor target cells measured by time-lapse microcinematography. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1652–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B., Golstein P., Nordfang O., Hertel-Wulff B. Generation of H-2-reactive T cell lines that bear the 5936 idiotype(s). J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):161–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J. The mechanism of T cell mediated cytotoxicity. II. Morphological studies of cell death by time-lapse microcinematography. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Jan 20;192(1107):241–255. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Burakoff S. J., Benacerraf B. The induction of cytolytic T lymphocytes with specificity for p-azophenylarsonate coupled syngeneic cells. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1432–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara N., Hämmerling U., Sachs D. H. Mouse alloantibodies capable of blocking cytotoxic T cell function. II. Further study on the relationship between the blocking antibodies and the products of the Lyt-2 locus. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):589–594. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara N., Sachs D. H. Mouse alloantibodies capable of blocking cytotoxic T-cell function. I. Relationship between the antigen reactive with blocking antibodies and the Lyt-2 locus. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):432–444. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K., Golstein P. Target cell recognition by cytolytic T cells: different requirements for the formation of strong conjugates or for proceeding to lysis. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):833–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Identification of Ly-5 and T200 antigens on identical cell surface proteins. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1400–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfrè G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Monoclonal xenogeneic antibodies to murine cell surface antigens: identification of novel leukocyte differentiation antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):539–551. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfré G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):301–306. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. A., Berke G., Amos D. B. An antigenic determinant of cytotoxic lymphocytes. Transplantation. 1973 Oct;16(4):388–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S. Interspecies spleen-myeloma hybrid producing monoclonal antibodies against mouse lymphocyte surface glycoprotein, T200. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):313–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Martz E. Simultaneous suppression of allogeneic cytolytic activity and stimulation of lectin-dependent cytolytic activity by con A. Cell Immunol. 1978 Sep 15;40(1):103–116. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]