Abstract
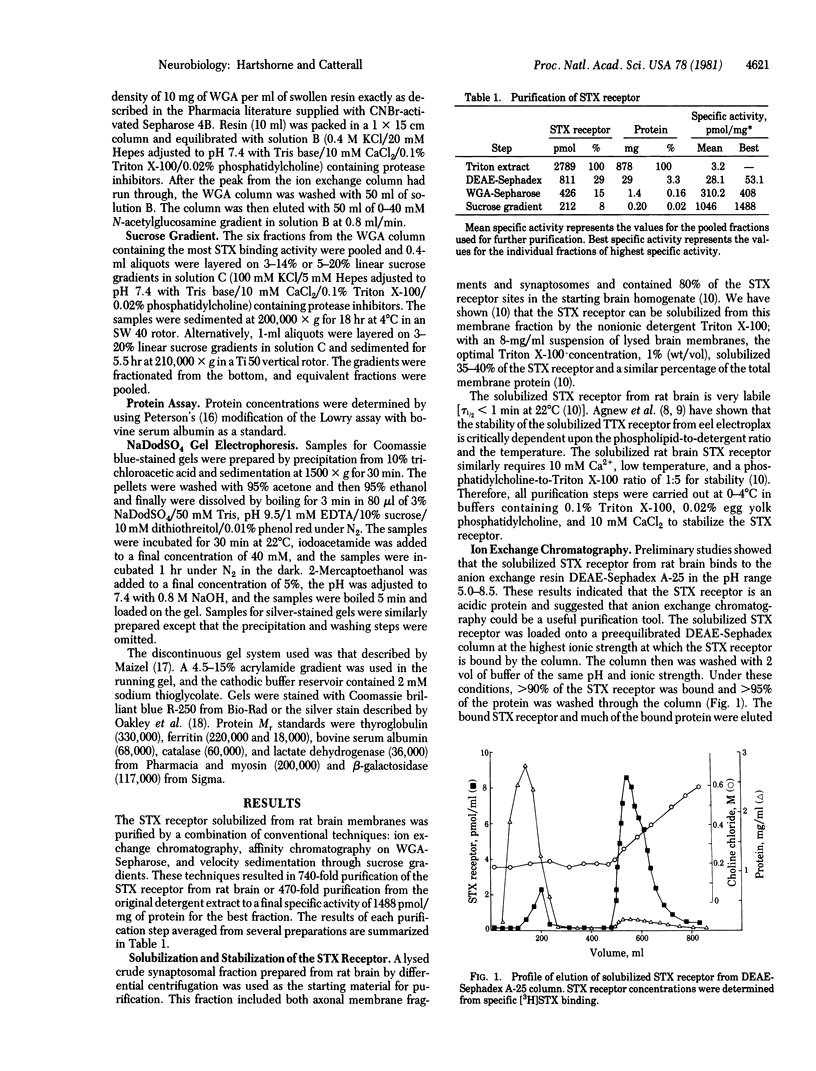
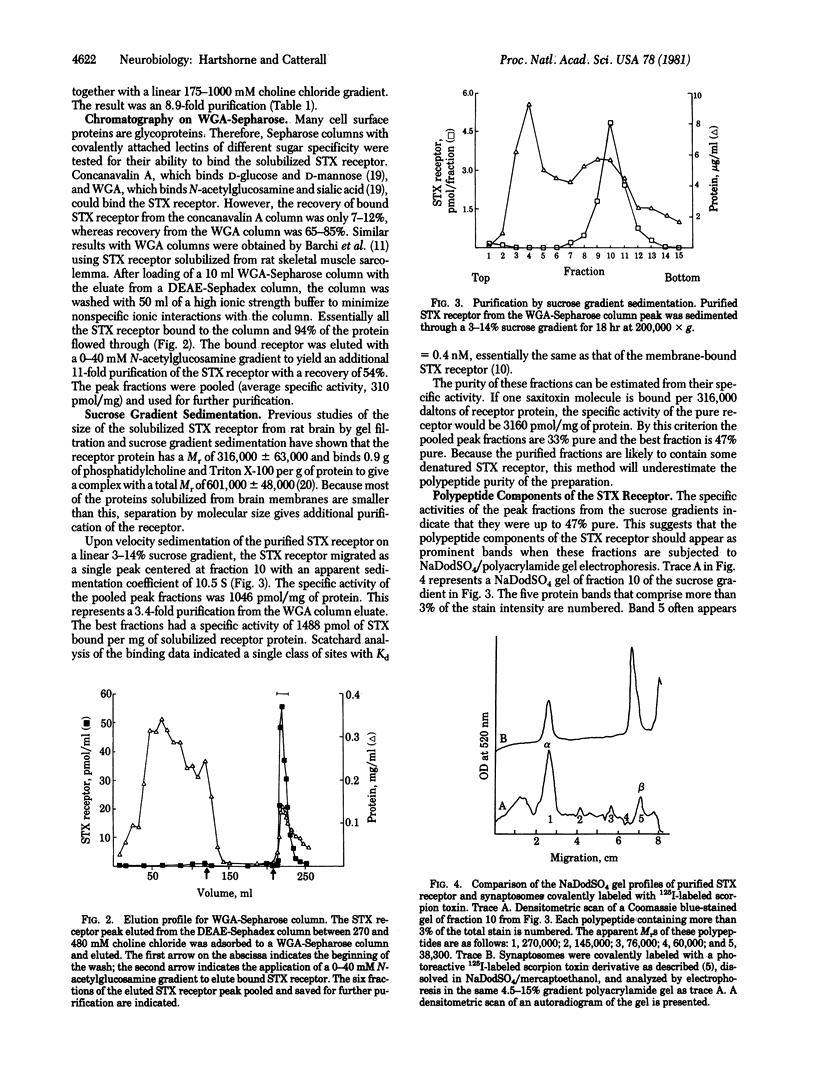
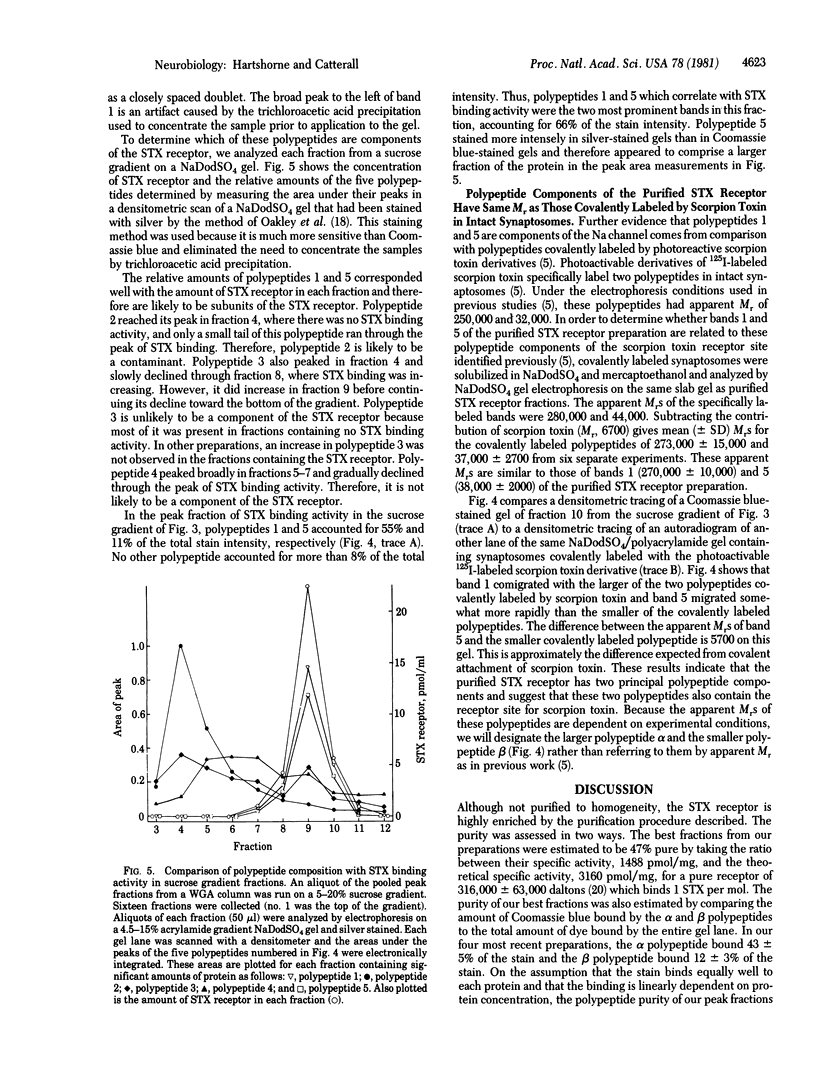
The saxitoxin (STX) receptor has been purified 740-fold from rat brain by a combination of ion exchange chromatography, wheat germ agglutinin chromatography, and sedimentation on sucrose gradients to a specific activity of 1488 pmol/mg of protein. The best fractions were estimated to be 47% pure from their specific activity or 66% pure on the basis of NaDodSO4 gel electrophoresis. Two polypeptides, alpha (Mr approximately equal to 270,000 +/- 10,000) and beta (Mr approximately equal to 38,300 +/- 2000) (mean +/- SD) copurify with STX binding activity. Two polypeptides of the same apparent Mr are specifically covalently labeled by photoreactive derivatives of 125I-labeled scorpion toxin in rat brain synaptosomes and are likely to be identical to alpha and beta. The solubilized STX receptor has a Mr of 316,000 +/- 63,000, limiting its composition to one alpha polypeptide and one or more beta polypeptides per soluble receptor. Our results suggest that the alpha and beta polypeptides contain both the STX binding site and the scorpion toxin binding site of the mammalian sodium channel.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R., Brabson J. S., Raftery M. A. Purification of the tetrodotoxin-binding component associated with the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from Electrophorus electricus electroplax membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnew W. S., Moore A. C., Levinson S. R., Raftery M. A. Identification of a large molecular weight peptide associated with a tetrodotoxin binding protein from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):860–866. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90782-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnew W. S., Raftery M. A. Solubilized tetrodotoxin binding component from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Stability as a function of mixed lipid-detergent micelle composition. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1912–1919. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Cohen S. A., Murphy L. E. Purification from rat sarcolemma of the saxitoxin-binding component of the excitable membrane sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1306–1310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beneski D. A., Catterall W. A. Covalent labeling of protein components of the sodium channel with a photoactivable derivative of scorpion toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):639–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer T. I., Raftery M. A. Solubilization and partial characterization of the tetrodotoxin binding component from nerve axons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):939–944. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Binding of scorpion toxin to receptor sites associated with sodium channels in frog muscle. Correlation of voltage-dependent binding with activation. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Sep;74(3):375–391. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Morrow C. S., Hartshorne R. P. Neurotoxin binding to receptor sites associated with voltage-sensitive sodium channels in intact, lysed, and detergent-solubilized brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11379–11387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Coppersmith J., Catterall W. A. Size characteristics of the solubilized saxitoxin receptor of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10572–10575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Wang J. H. Solubilization of a specific tetrodotoxin-binding component from garfish olfactory nerve membrane. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4565–4569. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The receptor for tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. A structural hypothesis. Biophys J. 1975 Jun;15(6):615–619. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85842-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y., Nishiyama A. Actions of saxitoxin on peripheral neuromuscular systems. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(1):50–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W. Sodium channels in presynaptic nerve terminals. Regulation by neurotoxins. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Sep;76(3):287–313. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B., Strichartz G. R. A new method for labelling saxitoxin and its binding to non-myelinated fibres of the rabbit vagus, lobster walking leg, and garfish olfactory nerves. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):477–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B. The binding of saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin to excitable tissue. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;79:1–50. doi: 10.1007/BFb0037088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun M. M., Catterall W. A. Ion flux studies of voltage-sensitive sodium channels in synaptic nerve-ending particles. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;19(1):78–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



