Abstract
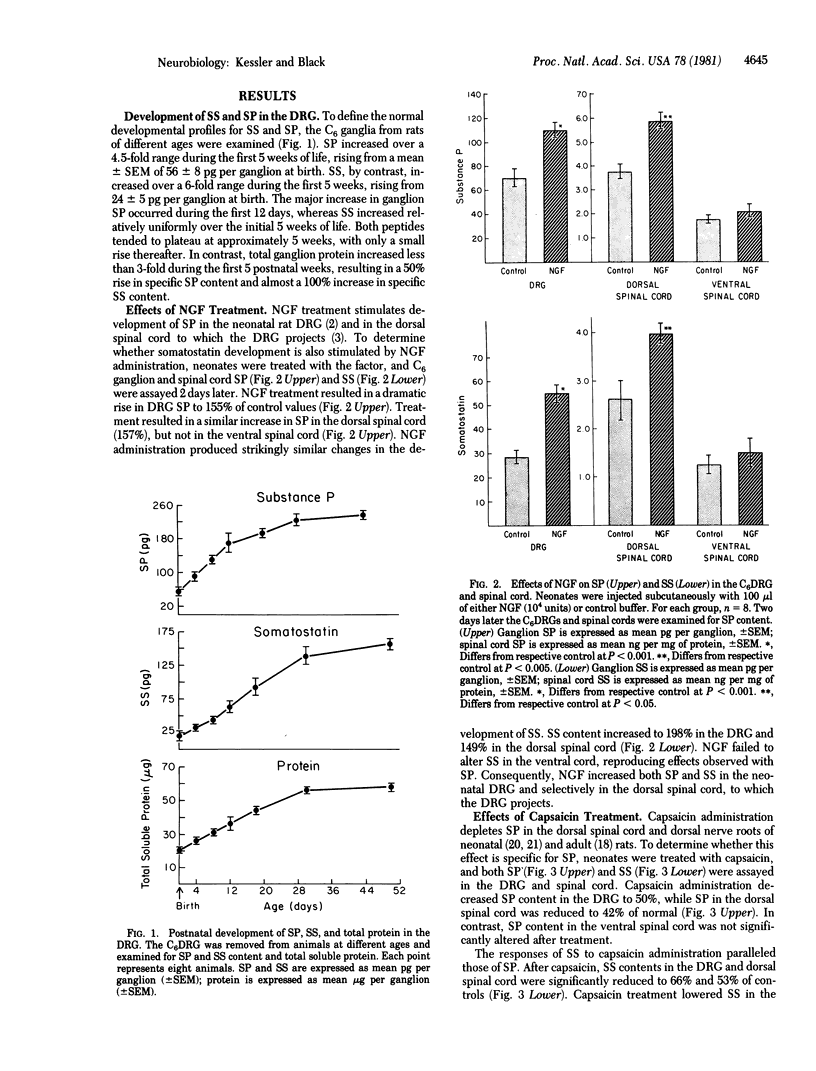
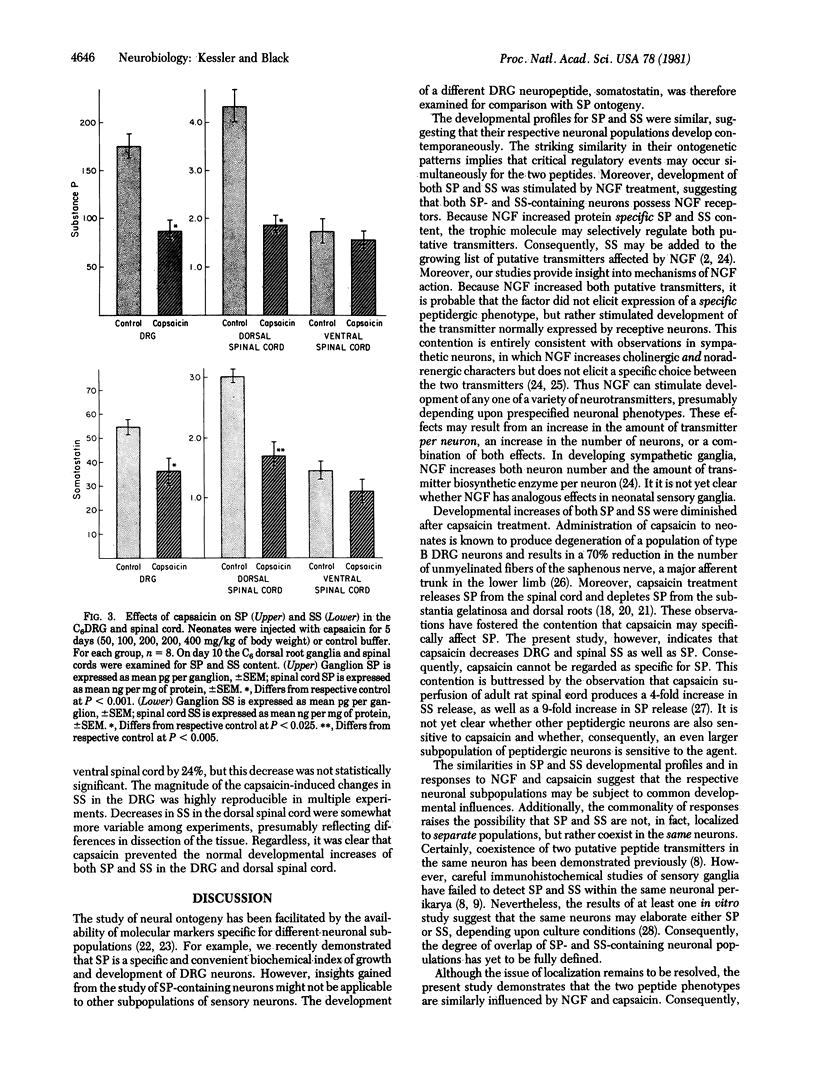
Development of the two putative peptide neurotransmitters, substance P (SP) and somatostatin (SS), were compared in rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and spinal cord in vivo. The content of SS in the sixth cervical DRG increased 5-fold during the first 5 weeks of life, rising from 24 pg per ganglion at birth. SP content increased 4.5-fold during the first 5 weeks, from 56 pg per ganglion at birth. The developmental profiles for these two peptides were virtually parallel, suggesting that their respective neuronal populations developed in synchrony. Treatment with nerve growth factor (NGF) significantly increased the content of both SP and SS in the DRG and dorsal spinal cord. Conversely, treatment with capsaicin significantly decreased both SP and SS in the DRG and dorsal spinal cord. Consequently, experiments involving NGF or capsaicin treatment of sensory neurons must be interpreted with extreme care, because specificity is not limited to a single peptide phenotype. Although the mechanisms of action of NGF and capsaicin on SP and SS have not been defined, the similarity of the responses of the two peptides suggests that their development may be regulated by similar processes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold M. A., Fernstrom J. D. Administration of antisomatostatin serum to rats reverses the inhibition of pulsatile growth hormone secretion produced by injection of metergoline but not yohimbine. Neuroendocrinology. 1980 Sep;31(3):194–199. doi: 10.1159/000123073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B., Hendry I. A., Iversen L. L. Trans-synaptic regulation of growth and development of adrenergic neurones in a mouse sympathetic ganglion. Brain Res. 1971 Nov;34(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B. Regulation of autonomic development. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:183–214. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun L. L., Patterson P. H. Role of nerve growth factor in the development of rat sympathetic neurons in vitro. III. Effect on acetylcholine production. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):712–718. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibner M. D., Black I. B. The effect of taget organ removal on the development of sympathetic neurons. Brain Res. 1976 Feb 13;103(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamse R., Holzer P., Lembeck F. Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurones and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;68(2):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMBURGER V. Regression versus peripheral control of differentiation in motor hypoplasia. Am J Anat. 1958 May;102(3):365–409. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. L. Effects of substance P on functionally identified units in cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):439–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. E., Hendry I. A. Development of neurons synthesizing noradrenaline and acetylcholine in the superior cervical ganglion of the rat in vivo and in vitro. Neuroscience. 1977;2(5):741–749. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Elde R., Johansson O., Luft R., Nilsson G., Arimura A. Immunohistochemical evidence for separate populations of somatostatin-containing and substance P-containing primary afferent neurons in the rat. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Ljungdahl A., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M. Peptidergic neurones. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):515–521. doi: 10.1038/284515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancsó G., Kiraly E., Jancsó-Gábor A. Pharmacologically induced selective degeneration of chemosensitive primary sensory neurones. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):741–743. doi: 10.1038/270741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancsó N., Jancsó-Gábor A., Szolcsányi J. Direct evidence for neurogenic inflammation and its prevention by denervation and by pretreatment with capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):138–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L., Cuello A. C. Capsaicin-induced depletion of substance P from primary sensory neurones. Brain Res. 1978 Aug 18;152(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Opiate analgesics inhibit substance P release from rat trigeminal nucleus. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):549–551. doi: 10.1038/268549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A., Black I. B. Nerve growth factor stimulates development of substance P in the embryonic spinal cord. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 9;208(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90626-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A., Black I. B. Nerve growth factor stimulates the development of substance P in sensory ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):649–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A., Black I. B. The effects of nerve growth factor (NGF) and antiserum to NGF on the development of embryonic sympathetic neurons in vivo. Brain Res. 1980 May 5;189(1):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmesser L., Pilar G. Synapse formation during embryogenesis on ganglion cells lacking a periphery. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(3):715–736. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Schenker A., Shooter E. M. Characterization and isolation of proteolytically modified nerve growth factor. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 14;15(25):5543–5552. doi: 10.1021/bi00670a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J. I., Vincent S. R., Staines W. A., Fibiger H. C., Reisine T. D., Yamamura H. I. Neurotoxic action of capsaicin on spinal substance P neurons. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 31;186(2):435–444. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90987-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Konishi S. Substance P and excitatory transmitter of primary sensory neurons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:135–143. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestige M. C. The control of cell number in the lumbar ventral horns during the development of Xenopus laevis tadpoles. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1967 Dec;18(3):359–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randić M., Miletić V. Depressant actions of methionine-enkephalin and somatostatin in cat dorsal horn neurones activated by noxious stimuli. Brain Res. 1978 Aug 18;152(1):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seybold V., Elde R. Immunohistochemical studies of peptidergic neurons in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Apr;28(4):367–370. doi: 10.1177/28.4.6154731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



