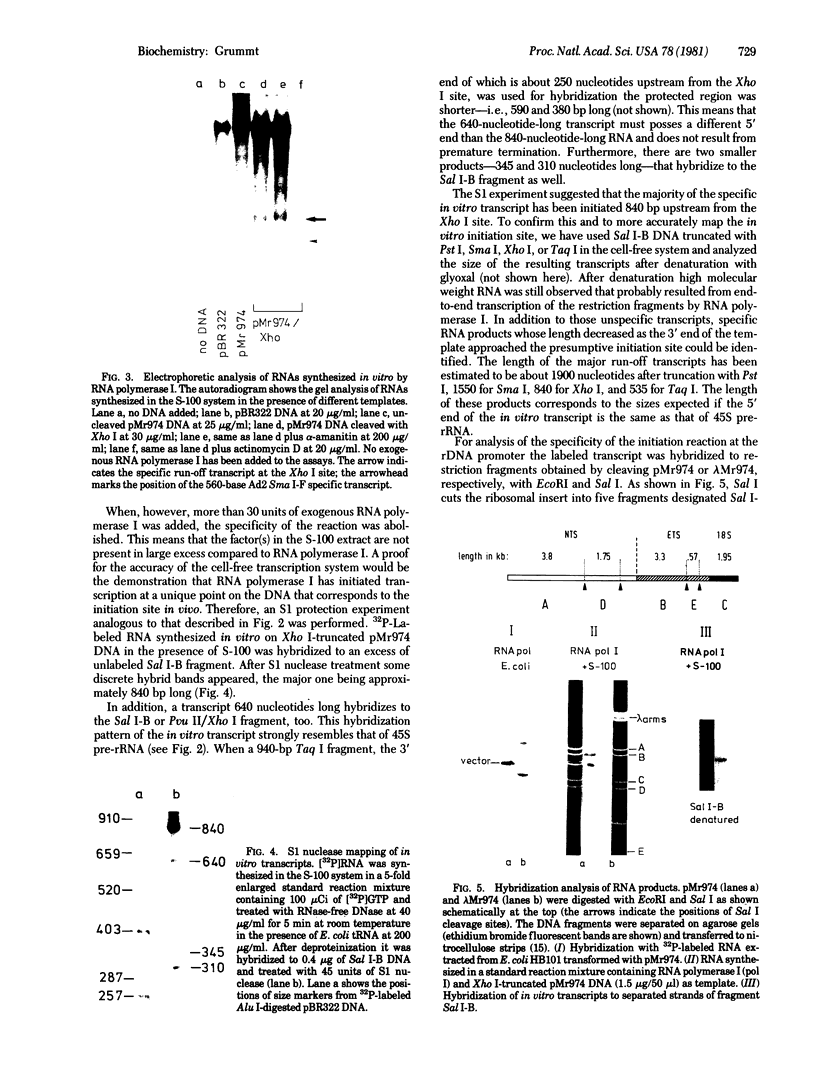
Abstract
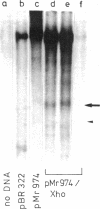
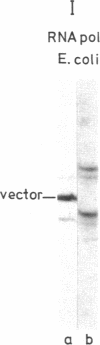
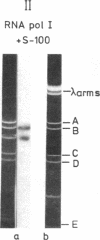
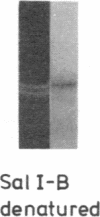
Cloned ribosomal DNA (rDNA) from mouse, which contains the initiation site of 45S pre-rRNA transcription and 5' flanking sequences, has been used as the template in an in vitro transcription system. In the presence of extracts from rapidly growing Ehrlich ascites cells, RNA polymerase I initiates specifically in that region of purified rDNA where the 5' end of 45S rRNA has been mapped. This is shown by electrophoretic analysis of the length of run-off transcripts synthesized from truncated templates, by S1 nuclease mapping, and by hybridization analysis of the in vitro products. The ability of the crude extracts to promote faithful transcription of mouse rDNA correlates with the proliferation rate of the cells. Only extracts prepared from exponentially growing mouse cells contain the factor(s) required for the faithful transcription of mouse ribosomal genes. Extracts from nongrowing or slowly growing mouse cells show very little activity. Thus, the cell-free system somehow reflects the rRNA synthetic activity of the cell and will prove valuable for the identification and purification of the various factors that are involved in the specific read-out of rDNA and may play a central role in the regulation of transcription of the ribosomal genes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayev A. A., Georgiev O. I., Hadjiolov A. A., Kermekchiev M. B., Nikolaev N., Skryabin K. G., Zakharyev V. M. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. 2. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation site for ribosomal RNA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4919–4926. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J., Coupar B. E., Butterworth P. H., Green M. H. Studies on the control of ribosomal RNA synthesis in HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):79–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. C., Busch H. Structural analysis of nucleolar precursors of ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Studies on the 5'-terminal and alkali-resistant dinucleotides of nucleolar high molecular weight ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 25;245(8):1954–1961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert S. F., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. Identification of initiation sites for the in vitro transcription of rRNA operons rrnE and rrnA in E. coli. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K. J., Pogo A. O. Control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in eukaryotes. 3. The effect of cycloheximide and edeine on rna synthesis in yeast. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2082–2086. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Gross H. J. Structural organization of mouse rDNA: comparison of transcribed and non-transcribed regions. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):223–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00267433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Smith V. A., Grummt F. Amino acid starvation affects the initiation frequency of nucleolar RNA polymerase. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Soellner C., Scholz I. Characterization of a cloned ribosomal fragment from mouse which contains the 18S coding region and adjacent spacer sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1351–1369. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Heterogeneity of 5' -termini of nucleolar 45S, 32S and 28S RNA in mouse hepatoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):229–240. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse D. S., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation on a purified mouse beta-globin DNA fragment in a cell-free system. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Birnstiel M. L. The putative promoter of a Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene is reduplicated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3733–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Sollner-Webb B., Wahn H. L. Sites of transcription initiation in vivo on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Crippa M. The primary ribosomal DNA transcript in eukaryotes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1977;31(3):247–269. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(78)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U. Construction and properties of a new cloning vehicle, allowing direct screening for recombinant plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(2):475–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00270503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Galibert F., Boiron M. Evidence for the existence of several molecular species in the "45S fraction" of mammalian ribosomal precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1117–1120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Bell G. I., Venegas A., Sewell E. T., Masiarz F. R., DeGennaro L. J., Weinberg F., Rutter W. J. Ribosomal RNA genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Physical map and nucleotide sequence of the 5 S ribosomal RNA gene and adjacent intergenic regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8126–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Kédinger C., Corden J., Brison O., Chambon P. Specific in vitro initiation of transcription on conalbumin and ovalbumin genes and comparison with adenovirus-2 early and late genes. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):367–373. doi: 10.1038/285367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C., Moss B. 5'-Terminal capping of RNA by guanylyltransferase from HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3758–3761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. J. Adenovirus DNA-directed transcription of 5.5S RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2175–2179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. J., Zubay G. Prolonged transcription in a cell-free system involving nuclei and cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1803–1807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Tandem promoters direct E. coli ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. The rapid turnover of RNA polymerase of rat liver nucleolus, and of its messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B., Evans R. M. Coincidence of the promoter and capped 5' terminus of RNA from the adenovirus 2 major late transcription unit. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1463–1475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]