Abstract
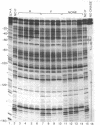
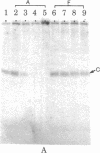
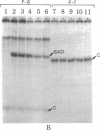
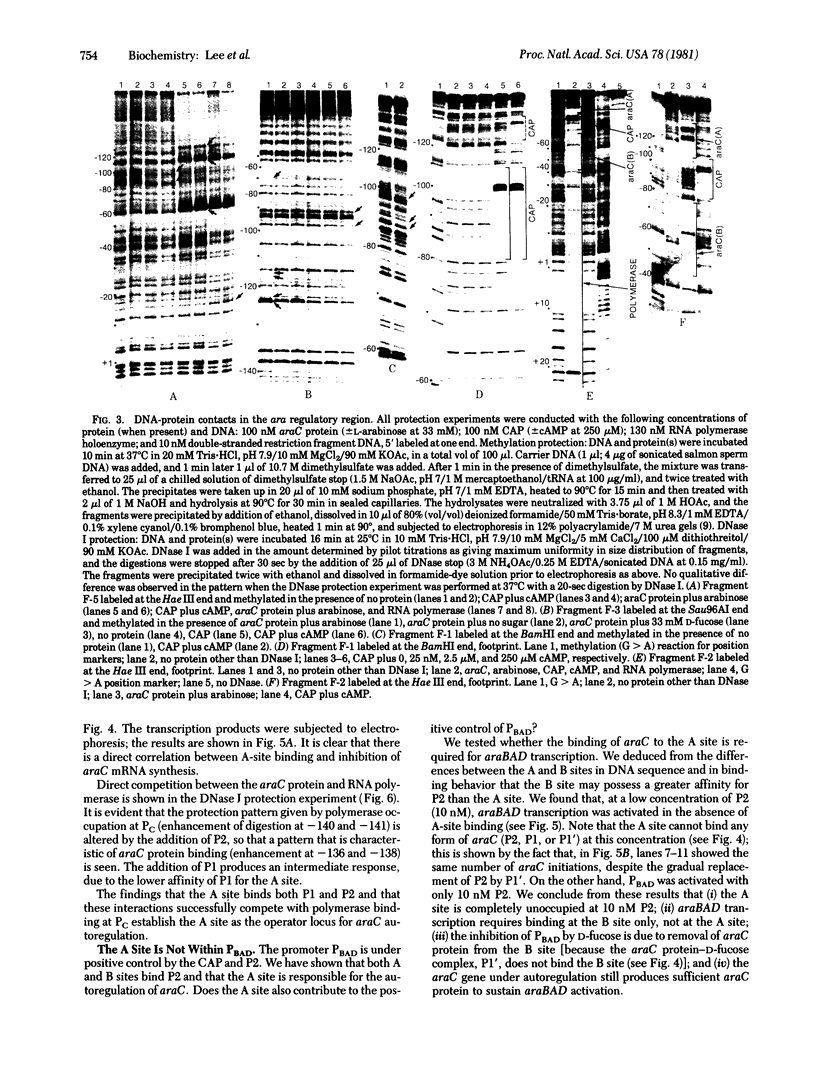
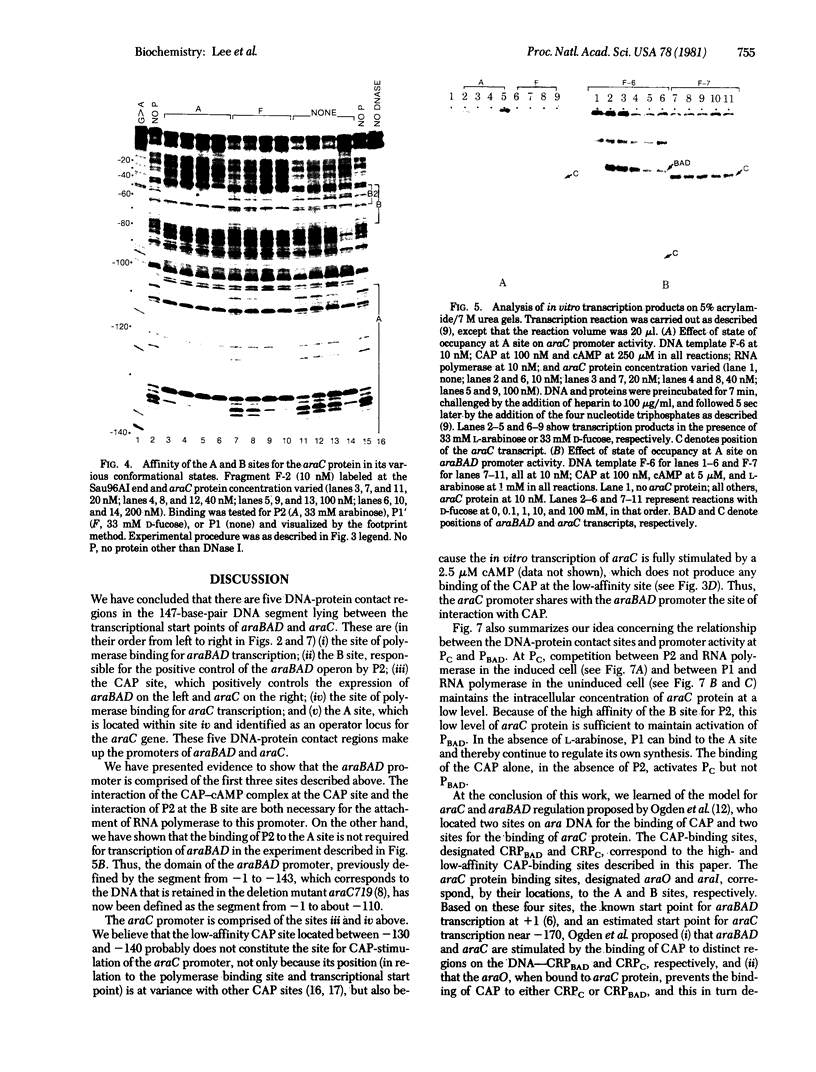
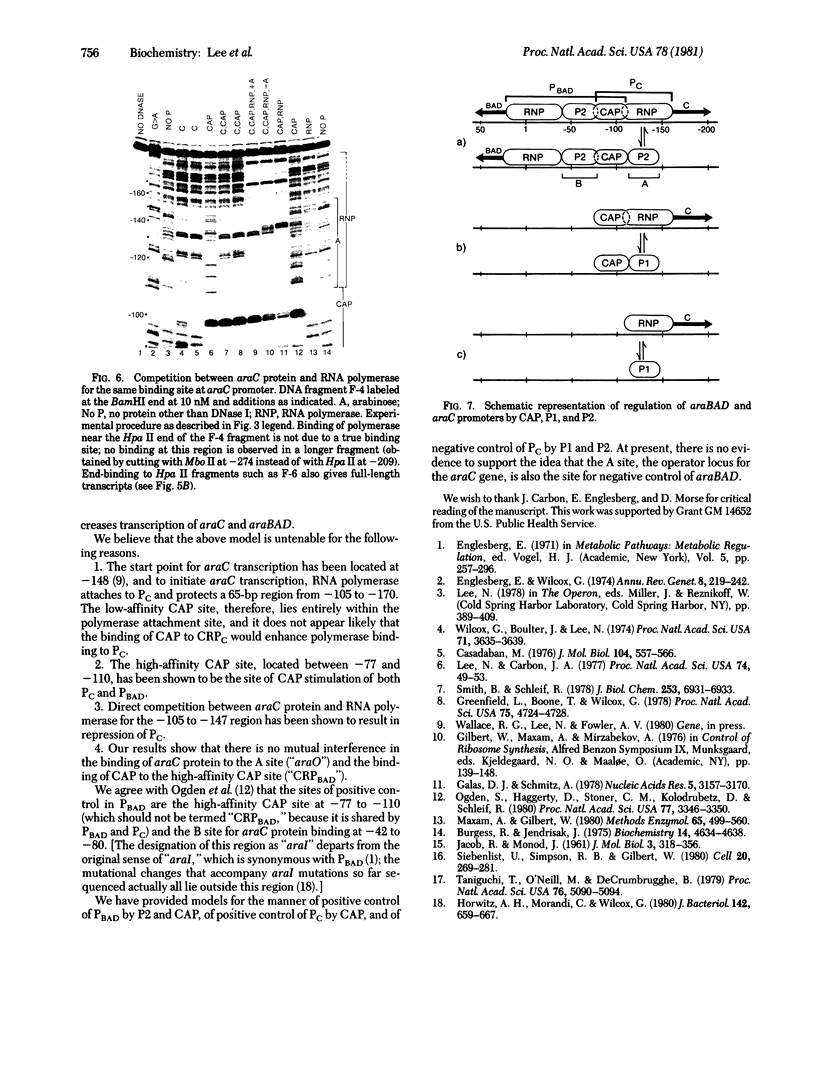
The DNA-protein contact sites in the ara regulatory region, which contains the promoters for araBAD and araC, have been determined for araC protein, the cyclic AMP-binding protein, and RNA polymerase, by using the methylation protection and DNase I protection methods. The functional significance of binding was assessed by correlating the state of occupancy of these sites with promoter activity in transcription initiation. Our results suggest that the basis for araC autoregulation is that araC protein, in either its activator (P2) or repressor (P1) form, acts as a repressor for araC, by binding to the RNA polymerase attachment site at the araC promoter. We also found that the araC and araBAD promoters share a common site of positive control by the cyclic AMP-binding protein, located 90 bases from the araBAD and 60 bases from the araC transcriptional start points. A model for the mechanism of regulation of araBAD and araC expression by the catabolite gene-activator protein, P1, and Pe is proposed. An earlier model proposed by Ogden et al. [Ogden S., Haggerty, D., Stoner, C. M., Kolodrubetz, D. & Schleif, R. (1980) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, USA 77, 3346-3350] is discussed in the light of the data presented in this paper.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Regulation of the regulatory gene for the arabinose pathway, araC. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):557–566. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Wilcox G. Regulation: positive control. Annu Rev Genet. 1974;8:219–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.08.120174.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield L., Boone T., Wilcox G. DNA sequence of the araBAD promoter in Escherichia coli B/r. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4724–4728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A. H., Morandi C., Wilcox G. Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence of araBAD promoter mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):659–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.659-667.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N., Carbon J. Nucleotide sequence of the 5' end of araBAD operon messenger RNA in Escherichia coli B/r. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):49–53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden S., Haggerty D., Stoner C. M., Kolodrubetz D., Schleif R. The Escherichia coli L-arabinose operon: binding sites of the regulatory proteins and a mechanism of positive and negative regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3346–3350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R., Schleif R. Nucleotide sequence of the L-arabinose regulatory region of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6931–6933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., O'Neill M., de Crombrugghe B. Interaction site of Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein on DNA of galactose operon promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5090–5094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox G., Boulter J., Lee N. Direction of transcription of the regulatory gene araC in Escherichia coli B-r. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3635–3639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]