Abstract
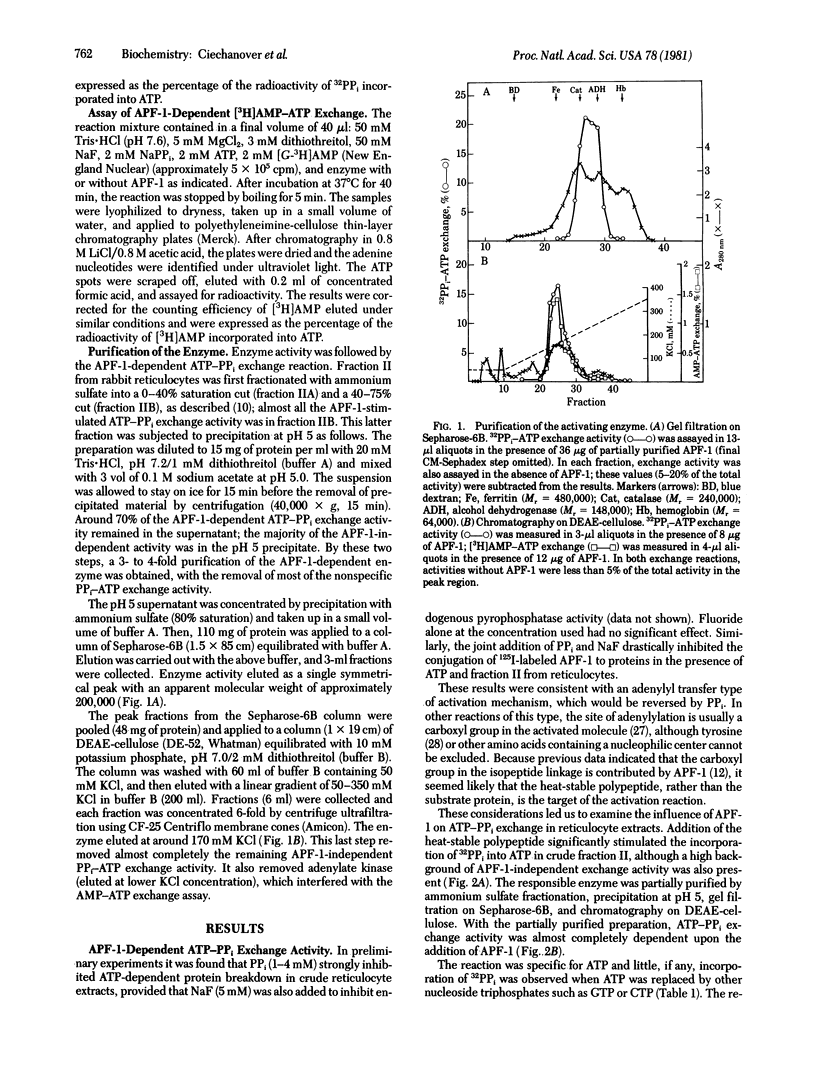
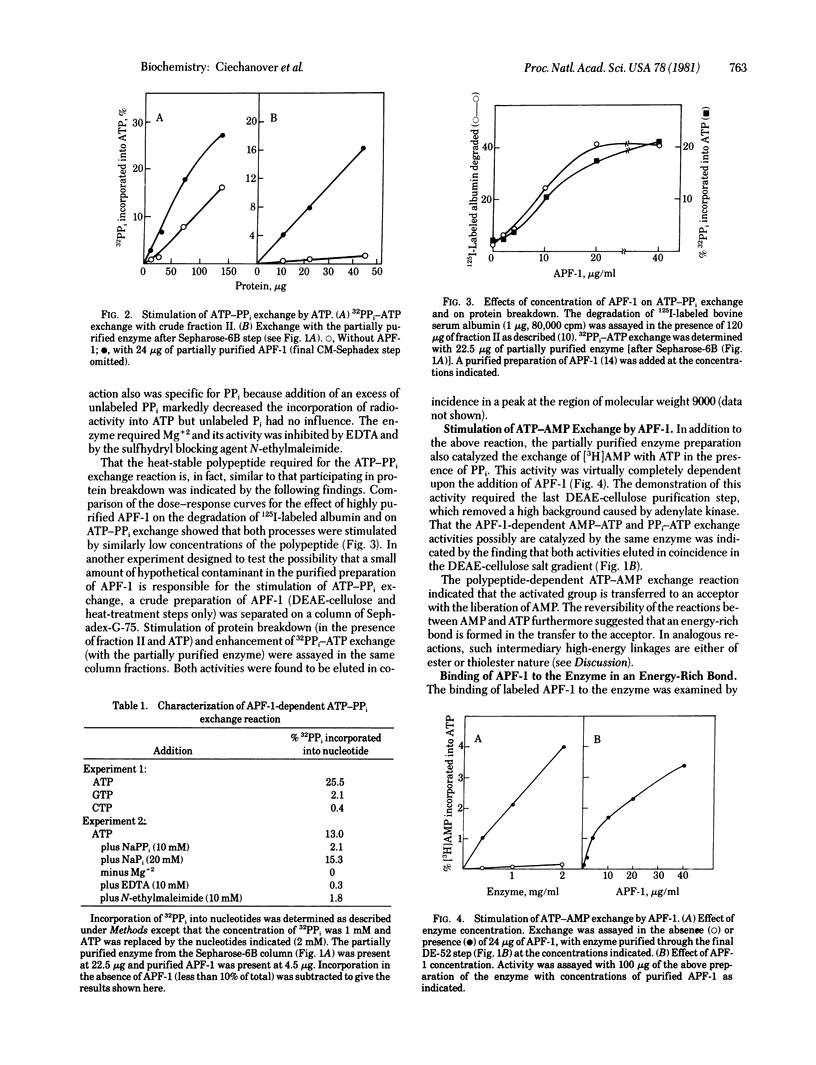
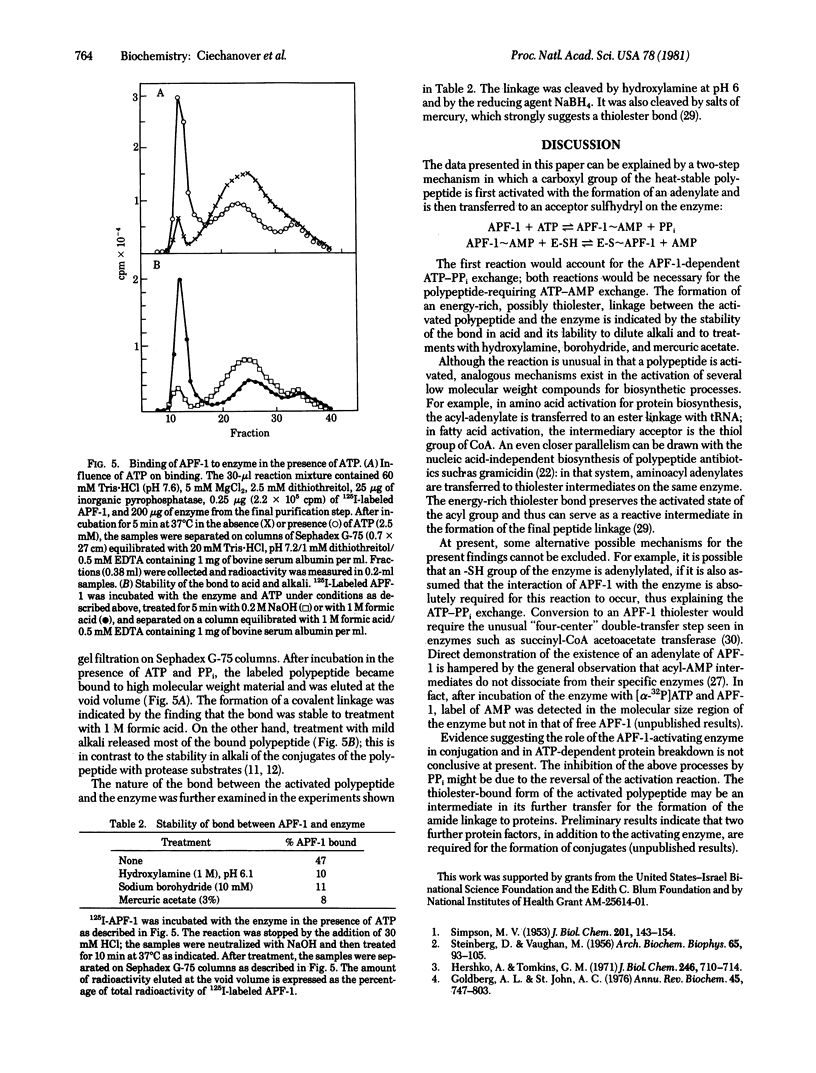
It had been shown previously that the heat-stable polypeptide of the ATP-dependent proteolytic system of reticulocytes, designated APF-1, forms covalent conjugates with protein substrates in an ATP-requiring process. We now describe an enzyme that carries out the activation by ATP of the polypeptide with pyrophosphate displacement. The formation of AMP-polypeptide and transfer of the polypeptide to a secondary acceptor are suggested by an APF-1 requirement for ATP-PPi and ATP-AMP exchange reactions, respectively. With radiolabeled polypeptide, an ATP-dependent labeling of the enzyme was shown to be by a linkage that is acid stable but is labile to treatment with mild alkali, hydroxylamine, borohydride, or mercuric salts. It therefore appears that the AMP-polypeptide undergoes attack by an -SH group of the enzyme to form a thiolester.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ciechanover A., Elias S., Heller H., Ferber S., Hershko A. Characterization of the heat-stable polypeptide of the ATP-dependent proteolytic system from reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7525–7528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Heller H., Elias S., Haas A. L., Hershko A. ATP-dependent conjugation of reticulocyte proteins with the polypeptide required for protein degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1365–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciehanover A., Hod Y., Hershko A. A heat-stable polypeptide component of an ATP-dependent proteolytic system from reticulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1100–1105. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etlinger J. D., Goldberg A. L. A soluble ATP-dependent proteolytic system responsible for the degradation of abnormal proteins in reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):54–58. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gevers W., Kleinkauf H., Lipmann F. Peptidyl transfers in gramicidin S bisoynthesis from enzyme-bound thioester intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldknopf I. L., Busch H. Isopeptide linkage between nonhistone and histone 2A polypeptides of chromosomal conjugate-protein A24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):864–868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A., Heller H., Haas A. L., Rose I. A. Proposed role of ATP in protein breakdown: conjugation of protein with multiple chains of the polypeptide of ATP-dependent proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1783–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A., Rose I. A. Resolution of the ATP-dependent proteolytic system from reticulocytes: a component that interacts with ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3107–3110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Tomkins G. M. Studies on the degradation of tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma cells in culture. Influence of the composition of the medium and adenosine triphosphate dependence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):710–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O. Amino-terminal sequence identity of ubiquitin and the nonhistone component of nuclear protein A24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):650–655. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90352-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNITZ M. An improved method for isolation of crystalline pyrophosphatase from baker's yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Feb;92:270–272. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W. Hybrid troponin reconstituted from vertebrate and arthropod subunits. Nature. 1975 May 29;255(5507):424–426. doi: 10.1038/255424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipmann F. Attempts to map a process evolution of peptide biosynthesis. Science. 1971 Sep 3;173(4000):875–884. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4000.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Goldstein A. L. The chemistry and biology of thymosin. II. Amino acid sequence analysis of thymosin alpha1 and polypeptide beta1. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):987–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midelfort C. F., Rose I. A. A stereochemical method for detection of ATP terminal phosphate transfer in enzymatic reactions. Glutamine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5881–5887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Voellmy R., Goldberg A. L. Protein degradation is stimulated by ATP in extracts of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8194–8200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Goldknopf I. L., Guetzow K. A., James G. T., Hawkins T. C., Mays-Rothberg C. J., Busch H. The NH2- and COOH-terminal amino acid sequence of nuclear protein A24. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5901–5903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W., Mount D. W. Inactivation and proteolytic cleavage of phage lambda repressor in vitro in an ATP-dependent reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON M. V. The release of labeled amino acids from the proteins of rat liver slices. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):143–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG D., VAUGHAN M. Observations on intracellular protein catabolism studied in vitro. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Nov;65(1):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger D. H., Goldstein G., Niall H. D. The complete amino acid sequence of ubiquitin, an adenylate cyclase stimulating polypeptide probably universal in living cells. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2214–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. 5'-adenylyl-O-tyrosine. The novel phosphodiester residue of adenylylated glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3769–3771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson K. D., Urban M. K., Haas A. L. Ubiquitin is the ATP-dependent proteolysis factor I of rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7529–7532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


