Abstract
Thymocytes are tested for productive rearrangement of the tcrb locus by expression of a preTCR in a process termed β-selection which requires both Notch1 and CXCR4 signalling. It has been shown that activation of the GTPase Ras allows thymocytes to proliferate and differentiate in the absence of a PreTCR: the direct targets of Ras at this checkpoint have not been identified however. Mice with a mutant allele of p110γ unable to bind active Ras revealed that CXCR4-mediated PI3K activation is Ras-dependent. The Ras-p110γ interaction was necessary for efficient β-selection-promoted proliferation but was dispensable for the survival or differentiation of thymocytes. Uncoupling Ras from P110γ provides unambiguous identification of a Ras-interaction required for thymic β-selection.
Introduction
T lymphocytes bearing the αβ T cell receptor (TCR) emerge from the thymus having passed through selective processes (β-selection; positive and negative selection) which collectively serve to select for a functional TCR. The β-selection checkpoint operates on immature thymocytes which lack expression of CD4, CD8 and the TCRα chain and are termed double-negative (DN). β-selection is initiated within thymocytes which have successfully rearranged the tcrb locus and express the TCRβ protein together with the pre-Tα and CD3 signalling complex, forming the preTCR (1). Within the DN compartment it is possible to distinguish cells that have undergone, or are yet to undergo, β-selection on the basis of cell surface phenotype. Thus, DN cells that are surface CD25+CD44loCD27lo are poised to undergo β-selection and have been termed DN3a, while those that have undergone β-selection increase expression of CD27 and have been termed DN3b(2). Amongst the cellular processes promoted by β-selection are allelic exclusion, proliferation, survival, induction of TCRα gene transcription and differentiation to the CD4+ and CD8+ double-positive (DP) stage. Failure to undergo β-selection results in apoptosis (3).
In addition to the pre-TCR, successful β-selection requires signal transduction by Notch1 and CXCR4 on the surface of thymocytes to be triggered by delta-like 4 and stromal cell-derived factor1α (SDF1α;CXCL12) which are expressed by thymic stromal cells (4-9). Activation of these receptors promotes downstream signalling cascades necessary for the processes that define β-selection.
Small GTPases of the Ras family act as digital switches for multiple signal transduction cascades with the potential to integrate signals from different receptors (10). The Ras subfamily includes three highly homologous paralogs H-, K- and N-Ras as well as other related proteins, including Ral, Rap, R-Ras, and TC21. These cycle between an inactive (GDP-bound) and an active (GTP-bound) state under the influence of GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) and guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs)(11).
Transgenic over-expression of a constitutively active form of H-Ras (12) or the Ras activator RasGRP1(13) promotes the development of CD4+CD8+ (DP) thymocytes from recombinase activating gene (RAG)-mutant precursors that are unable to produce a functional preTCR due to lack of VDJ recombination. However the process of allelic exclusion is not impaired in thymocytes expressing active H-Ras (14). Moreover, amongst Ras effectors, transgenic expression of an active mutant of the serine/threonine protein kinase Raf-1 promoted the development of DP thymocytes from rag-deficient precursors(15). This suggests activation of the Ras pathway may contribute to a subset of the changes accompanying β-selection. However, experiments with dominant negative Ras or its effectors have not proven informative on their role in β-selection, possibly due to low expression or specific activity(16).
Amongst Ras effectors are the catalytic subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) enzymes(17). The class IA subfamily of PI3K is comprised of three catalytic subunits termed p110α, β, and δ, while the class IB family consists of p110γ. Genetic studies, using mouse models, have shown that β-selection is mediated, in part, by p110δ in combination with p110γ(18-20). This reflects a requirement for p110δ to transmit signals originating in the pre-TCR and a predominantly p110γ-dependent PI3K signal generated by CXCR4(8). Unopposed activation of the class I PI3K pathway by deletion of the lipid phosphatase PTEN allows the proliferation and development of RAG-deficient thymocytes to the DP stage(21), mimicking some aspects of β-selection.
The class IA and IB PI3Ks are activated by binding to distinct cell surface receptors. Class I PI3Ks are heterodimers comprised of a catalytic subunit and a receptor coupling regulatory subunit. The class IA regulatory subunits (p85α, p55α, p50α, p85β and p55γ) bind to YXXM motifs that have been phosphorylated by protein tyrosine kinases and the class IB regulatory subunits (p101 and p84) bind to the Gβγ subunits liberated upon activation of G-protein coupled receptors(22). It has been demonstrated that during thymocyte development p101 is required to mediate p110γ activation by CXCR4(8) and that p85α is required for pre-TCR-mediated PI3K signalling(23).
The generation of mice with defined mutations that affect protein function but not expression promise to greatly further our understanding of gene function(24). Here we show that thymocytes harbouring a mutation of p110γ that blocked its interaction with Ras were defective when undergoing β-selection in competition with wild-type thymocytes. When combined with deficiency in p110δ the loss of Ras input into p110γ produced the same phenotype as p110γ/δ double knockout mice. Analysis of cell cycle, apoptosis and CD4/8 expression revealed that Ras activation of p110γ is selectively required for optimal proliferation during β-selection but does not affect survival or differentiation. We find CXCR4 activates p110γ independently of the preTCR by a Ras-dependent mechanism. Thus p110γ is a key target of Ras signalling that is required for β-selection.
Material and Methods
Mice
p110δ−/−, p110γ−/− ,p110γD/D and Vav1/2/3−/− mice have all been described previously (25-28). Mice were on the C57BL/6 background and aged 6-13 weeks at analysis. For competitive chimera studies, irradiated Rag2−/−Il2rγ−/− mice were injected intravenously with 3 × 106 bone marrow (BM) cells at 1:1 ratio mix of WT(SJL):WT, WT(SJL):p110γD/D or WT(SJL):p110γ−/− and analysed six weeks later. All animal husbandry and experimentation were in accordance with U.K. Home Office regulations and subject to local ethical review.
Cell Isolation
DN3a and DN3b thymocytes were isolated by FACS. Single cell thymocyte suspensions were first enriched for DN cells by incubation with biotinylated anti–CD8α antibody followed by streptavidin-coated MACS beads and magnetic depletion prior to staining for DN subsets. DN3a and DN3b cells were isolated as [CD4/CD8/CD44/B220/CD11b/NK1.1/Gr1/Ter119/γδTCR]neg and either CD25hiCD98lo (DN3a) or CD25intCD98hi (DN3b).
Cell Culture
OP9-DL1 cells were maintained as previously described (4). 5 × 104 DN3a or 2.5 × 104 DN3b cells were cultured in supplemented α-MEM without additional cytokines in 96-well plates that had been previously seeded with 4000 OP9-DL1 cells. In some experiments DN3a cells were stained before culture with either Cell Trace Violet or Vybrqant CFDA SE cell proliferation dyes (Molecular Probes, Invitrogen) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Cells were cultured for up to 72 hours before harvesting and analysis by FACS. Cell numbers were determined by reference to the inclusion of a fixed number of microbeads (Spherotech).
FACS analysis
Single cell suspensions were stained using various combinations of antibodies conjugated to fluorochromes for analysis by FACS (LSRII Becton Dickinson). For cell cycle analysis, cultured cells were harvested, resuspended in ice-cold 70% EtOH and incubated at −20°C for at least 30mins. Cells were then washed three times in PBS before incubation with 1mg/ml RNase at room temperature for 30mins. Propidium iodide was then added at a final concentration of 400μg/ml. For caspase-3 staining, cultured cells were harvested, fixed and permeabilised using Cytofix/Cytoperm (Becton Dickinson) before staining with PE-labelled antibody to activated caspase-3 (Becton Dickinson). Excess antibody was removed by washing before analysis.
Western Blot
Lysates from 106 thymocytes were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. Blots were probed with rabbit anti-p110γ (Onyx Pharmaceuticals) and antibody binding was revealed using HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit Ab (DakoCytomation) followed by ECL (Amersham). Blots were subsequently probed using mouse anti-β actin.
Phospho-specific flow cytometry
Unfractionated thymocyte suspensions were resuspended at 107cells/ml in DMEM with 0.1% BSA. Cells were incubated at 37°C for 20mins before the addition of 10nM CXCL12. At various time intervals 106 cells were fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde, washed in PBS, and resuspended in 90% ice-cold methanol at −20°C for at least 30mins. Cells were then washed three times in PBS with 2% FCS before incubation with antibodies to surface markers as well as to phosphorylated-Akt (Cell Signaling clone #4058) or phosphorylated-Erk (Cell Signaling clone #4370) for 30mins at room temperature. Phospho-specific antibodies were revealed by subsequent incubation with Cy5-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit antibody and FACS. For data analysis, fold induction was calculated as the median fluorescence of stimulated sample / median fluorescence of unstimulated sample. Unstimulated samples showed no change in phospho-Akt or phospho-Erk throughout the timecourse.
Statistics
Data presented throughout represent the mean and either the SD or SEM (if n ≥ 5). Data were analysed by one-way ANOVA (or repeated measures ANOVA for competitive chimera experiments) and statistical significance represented as: * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 and ***p<0.001.
Results
The interaction of active Ras with p110γ is required for efficient thymic β-selection
To determine whether Ras binding to p110γ is required for T cell development we studied knock-in mice with mutations at five residues of p110γ critical for the binding of activated GTP-Ras (“DASAA”: T232D, K251A, K254S, K255A, and K256A) (27). Using Western blotting we found the expression of p110γDASAA in thymocytes was equivalent to WT p110γ (Supplementary Figure 1).
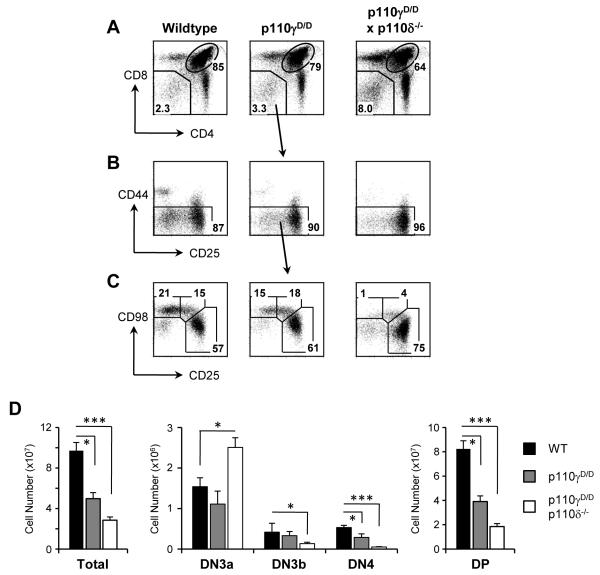
FACS analysis of thymocytes from p110γDASAA/DASAA (hereafter termed p110γD/D) mice revealed thymic cellularity was reduced in p110γD/D mice by approximately 50% and this principally reflected a reduction in the number DP thymocytes (Figure 1A-D). To investigate whether the loss of DP cells was due to a defect at β-selection, we used expression of the heavy chain of the amino acid transporter CD98 to analyse the pre-selection DN3a (CD44-CD25hiCD98lo), the post-selection DN3b (CD44−CD25intCD98hi) and the DN4 (CD44-CD25loCD98hi) populations (Figure 1B-C). Increased CD98 and CD27 expression on DN3 cells has been previously shown to be concomitant with intracellular TCR-β expression (2) and we have found that CD98 and CD27 expression correlate in these populations (Supplementary Figure 2). We found that the number of DN3a and DN3b cells in p110γD/D thymuses was similar to the control but the post β-selection CD44−CD25loCD98hi DN4 population was reduced (Figure 1D), suggestive of a partial block at this selection checkpoint.
Figure 1. Reduced thymic cellularity in mice with a Ras-binding mutant of p110γ.
(A) Flow cytometric analysis of CD4 and CD8 expression on T lymphocytes in the thymus from WT, p110γD/D and p110γD/D × p110δ−/− mice. The percentages of CD4+CD8+ double positive (DP) and CD4−CD8− double negative (DN) cells are shown. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of the DN thymocytes (identified as Thy1+ and [CD4/CD8/CD44/B220/CD11b/NK1.1/Gr1/Ter119/γδTCR]neg) and (C) the DN3/4 subsets. The percentages of CD25hiCD98lo (DN3a), CD25intCD98hi (DN3b) and CD25loCD98hi (DN4) are shown. (D) Thymic cellularity and the numbers of DN3a, DN3b, DN4 and DP thymocytes for each genotype. Graphs represent the mean and SEM (n ≥ 5).
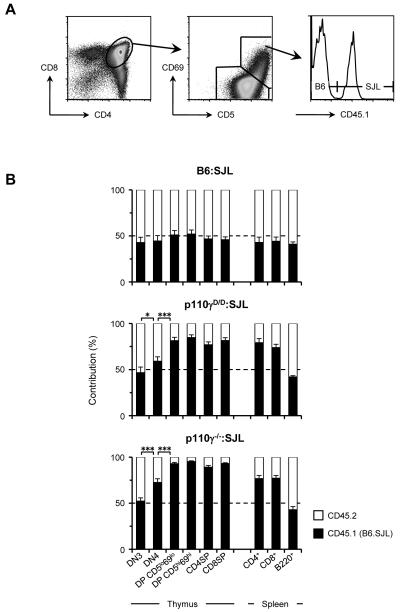
To examine if β-selection was functional in the p110γD/D thymocytes, we used a competitive repopulation assay. Lymphoid-deficient Rag2−/−Il2rγ−/− mice were reconstituted with a 1:1 ratio of WT bone marrow cells expressing the allotypic marker CD45.1 (B6.SJL) and either WT (C57BL/6), p110γD/D, or p110γ−/− bone marrow cells (all expressing CD45.2). The resulting lymphoid compartments were analysed six weeks after reconstitution and the contribution of each genotype to lymphocyte reconstitution determined (Figure 2A). The thymocyte populations were subdivided to enable analysis of progression through β-selection (DN3 to DN4 and small resting DP [CD5loCD69lo]), and positive selection (from DP CD5loCD69lo to DP CD5hiCD69hi) (29). In addition, the SP thymocyte and peripheral T cell populations were analysed. As p110γ is not required for B-lymphocyte development (30), the contribution of each genotype to the reconstitution of peripheral B cells was also determined as a control for haematopoietic reconstitution.
Figure 2. Competitve bone marrow chimeras reveal defective β-selection in p110γD/D thymocytes.
(A) Example of FACS analysis used to distinguish B6.SJL cell origin based upon expression of the CD45.1 allotypic marker. The gating strategy for CD5loCD69lo DP and CD5hiCD69hi DP thymocytes is also shown. (B) The contribution of B6.SJL (CD45.1+) (■) and WT (B6), p110γD/D or p110γ−/− CD45.1neg cells (□) to thymic T cell subsets, splenic T cells and splenic B cells six weeks after bone marrow reconstitution. The graphs show the mean and SEM from analysis of 10 chimaeric mice.
In the B6.SJL:p110γD/D mixed chimeras, the proportion of each genotype in the DN3 thymocyte population was equivalent. However, this ratio shifted to a majority of B6.SJL as the cells progressed through the DN3 to DN4 and DP CD5loCD69lo developmental stages, where approximately 80% were B6.SJL derived (Figure 2B). Thus the p110γD/D thymocytes compete poorly with WT cells at the β-selection checkpoint and in the transition from the DN to DP stage. The ratio of B6SJL:p110γD/D remained at approximately 80% for all subsequent developmental stages, indicating that the p110γD/D cells were not at a disadvantage when subjected to further selection pressure. A similar phenotype was observed in the B6SJL:p110γ−/− mixed chimeras, consistent with the known role for p110γ at this developmental stage.
Previous work has demonstrated that there is functional redundancy between p110γ and p110δ at the β-selection checkpoint (18-20). Therefore, we tested the effect of the p110 γDASAA mutation in the context of p110δ deficiency (Figure 1A-D). Compared to wildtype and p110D/D single mutant mice, the number of CD44−CD25hiCD98lo DN3a cells was increased in the double mutant mice, while the DN3b, DN4 and DP populations were all significantly reduced. This phenotype is further evidence for the importance p110γ at the β-selection checkpoint. Taken together, these data indicate that the function of p110γ at the β-selection checkpoint is critically dependent upon the binding of activated Ras to P110γ.
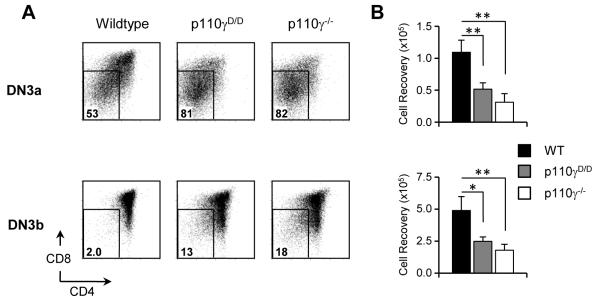
To characterise further the defect in β-selection we evaluated the ability of DN3a and DN3b thymocytes from wildtype, p110γD/D and p110γ−/− mice to proliferate and differentiate in vitro following culture on OP9-DL1 stromal cells. It has been reported that, upon co-culture with Notch-ligand expressing stromal cells, DN3b thymocytes are more efficient at generating CD4+CD8+ cells than DN3a(2, 31). We found that when cultured under these conditions p110γD/D and p110γ−/− DN3a or DN3b cells failed to generate equivalent numbers of more mature cells expressing CD4 and/or CD8 when compared to the control (Figure 3). Thus Ras-mediated regulation of p110γ is necessary to sustain thymocytes during β-selection.
Figure 3. The Ras-p110γ signalling pathway is required in DN3a and DN3b cells.
(A) CD4 and CD8 expression following culture of DN3a (CD25hiCD98lo) and DN3b (CD25intCD98hi) cells on OP9-DL1. The percentages of cells that remain CD4−CD8− are shown. (B) The number of live cells recovered from WT (■), p110γD/D
 and p110γ−/− (□) cultures after three days. The seeding number for each cell type was 5 × 104 DN3a and 2.5 × 104 DN3b. Graphs show the mean and SD from 3 independent groups.
and p110γ−/− (□) cultures after three days. The seeding number for each cell type was 5 × 104 DN3a and 2.5 × 104 DN3b. Graphs show the mean and SD from 3 independent groups.
The Ras-p110γ interaction regulates proliferation but not differentiation or survival
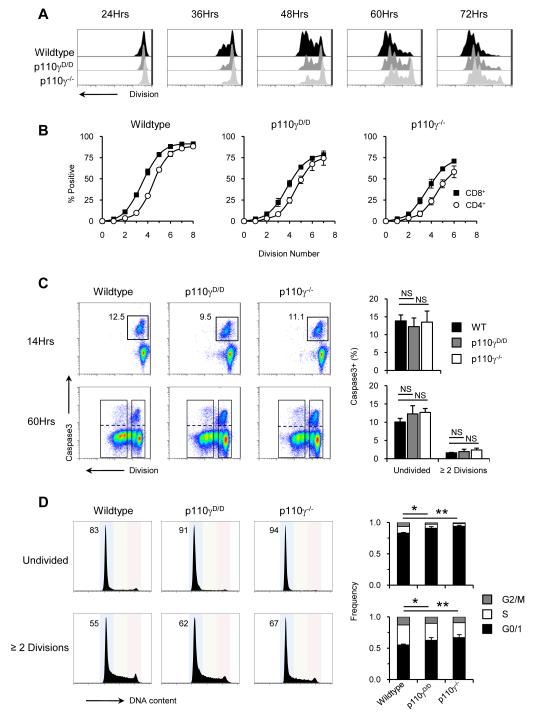
Both the Ras and PI3K signalling pathways have been implicated in the survival, proliferation and differentiation that define β-selection but their exact roles remain unclear. To resolve this, we made use of an in vitro model of β-selection that allows cell division, apoptosis and differentiation to be evaluated independently. Prior to culture on OP9-DL1 stromal cells, sorted CD25hiCD98lo DN3a cells were labelled with a fluorescent dye to reveal the number of cell divisions. At regular intervals cells were harvested and analysed for their division profile and expression of CD4 and CD8 (Supplementary Figure 3A). Of those cells which had undergone four rounds of division, approximately 50% expressed the CD8 co-receptor. Expression of the CD4 co-receptor on an equivalent fraction of the cells required one additional cell division (Figure 4B; Supplementary Figure 3B). When sorted p110γD/D or p110γ−/− DN3a cells were cultured in this manner we found that they underwent fewer rounds of division at all timepoints analysed (Figure 4A) but the division-linked expression of CD8 and CD4 was preserved (Figure 4B). Therefore p110γ is not required for the differentiation program of DN3 cells to become DP.
Figure 4. Analysis of differentiation, proliferation and survival responses at β-selection.
(A) Division profiles of sorted WT, p110γD/D and p110γ−/− DN3a cells (CD25hiCD98lo) after culture on OP9-DL1 for the indicated times. (B) Expression of CD8 (■) and CD4 (○) at each division cycle in WT, p110γD/D and p110γ−/− cultures after 72 hours. (C) Detection of caspase-3+ cells after 14 and 60 hours of culture. FACS plots show the gates used to identify cells which have divided ≥ 2 times and those that remain undivided that are either caspase-3 positive or negative. Graphs show data from three independent experiments where WT = ■, p110γD/D =  and p110γ−/− = □. (D) DNA content profiles from cells cultured for 60hrs. The gating strategy used to identify divided and undivided populations is the same as in Figure 3D. Coloured background on FACS plots show the delineation of cells in G0/1 (blue), S (green) and G2/M (red). Numbers on FACS plots show percentage of cells in G0/1. Graphs show data from three independent experiments where G0/1 = ■, S = □ and G2/M =
and p110γ−/− = □. (D) DNA content profiles from cells cultured for 60hrs. The gating strategy used to identify divided and undivided populations is the same as in Figure 3D. Coloured background on FACS plots show the delineation of cells in G0/1 (blue), S (green) and G2/M (red). Numbers on FACS plots show percentage of cells in G0/1. Graphs show data from three independent experiments where G0/1 = ■, S = □ and G2/M =  . For all statistical analysis a repeated measures ANOVA test was performed. NS = not significant, * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.01.
. For all statistical analysis a repeated measures ANOVA test was performed. NS = not significant, * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.01.
The reduced proportion of divided cells in the p110γD/D and p110γ−/− cultures could be due to increased cell death. To test this, we assessed the proportion of cells undergoing apoptosis in both the undivided and divided populations by staining with an antibody against activated caspase-3 (Figure 4C). Following 14 hours of culture, before cell division had occurred, up to 15% of the cells were caspase-3+, but there was no significant difference in the proportion of cells undergoing apoptosis between the different genotypes. This was also the case for the undivided population at 60 hours. In those cells which had undergone at least two divisions the proportion of caspase-3+ cells was less than 2%, indicating that once cells had entered the cell cycle they were less likely to die than those which remained undivided. These findings show that p110γ is not required for the survival of DN3 cells undergoing β-selection.
To test for changes in proliferation potential, we examined the proportion of cells in G0/1, S and G2/M stages of the cell cycle in the undivided and dividing populations. Amongst the undivided cells, following 60 hours of culture, a significantly increased fraction of p110γD/D and p110γ−/− remained in G0/1 (Figure 4D). Similarly, of those WT cells that had divided at least twice, 55% were in G0/1 whilst 62% of p110γD/D and 67% p110γ−/− were found to be in G0/1. Together, these findings show that the essential role for p110γ is to promote the proliferation of cells upon β-selection and that this signalling pathway is dependent upon Ras.
Ras-mediated p110γ activation is required for CXCR4 signalling
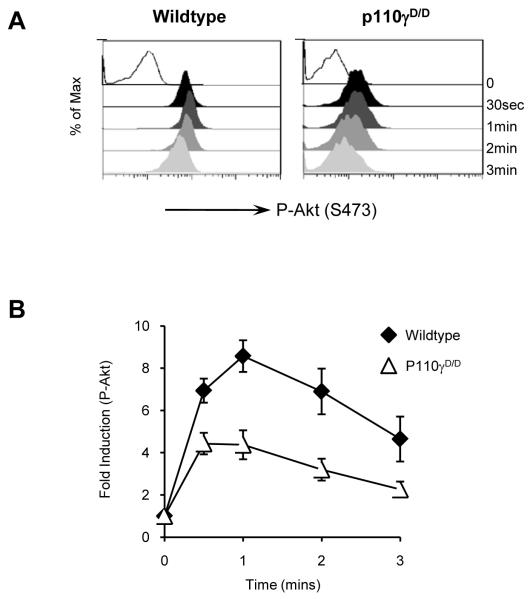
CXCR4, a receptor implicated in β-selection, has previously been shown to activate p110γ in DN3 cells(8). We therefore sought to determine whether active Ras binding to p110γ was necessary for CXCR4 signalling in DN3 cells. Stimulation of WT thymocytes with 10nM CXCL12 (SDF1α) elicited phosphorylation of protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) on serine 473 in DN3 cells (Figure 5A). This phosphorylation peaked at 1 minute and was sustained throughout the short time-course of the experiment. The response of p110γD/D DN3 cells was reduced at all time points compared to WT, although not entirely diminished (Figure 5A-B). This result is similar to that previously observed in DN3 cells lacking p110γ or p101, the regulatory subunit of p110γ in thymocytes(8). We conclude that in DN3 thymocytes p110γ must be activated by active Ras in order to elicit an optimal CXCR4 PI3K signalling response.
Figure 5. Defective induction of PI3K signalling in p110γD/D DN3 cells upon SDF1α stimulation.
(A) FACS histograms showing the detection of phosphorylated-Akt (at S473) in DN3 cells from WT and p110γD/D thymi after stimulation with SDF1α. (B) Graph showing fold induction of p-Akt, (measured as median fluorescence of stimulated / median fluorescence of unstimulated), in WT (■) and p110γD/D ( ) DN3 cells after SDF1α stimulation. Graph shows the mean and SD from analysis of five mice.
) DN3 cells after SDF1α stimulation. Graph shows the mean and SD from analysis of five mice.
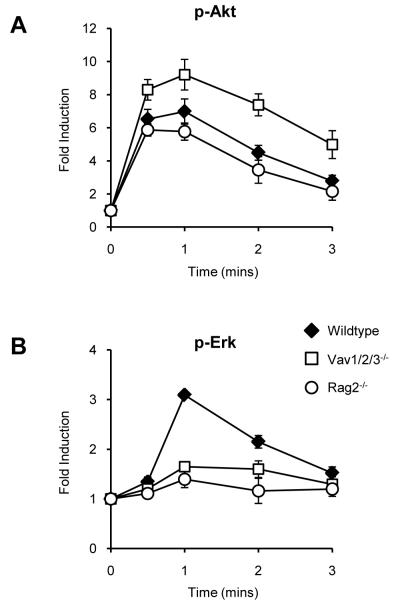
The generation of active Ras in thymocytes is associated with the signalling cascades elicited from the preTCR and TCR. To test whether preTCR signalling is required for the generation of the Ras-GTP that feeds into the CXCR4-PI3K signalling pathway we measured the induction of Akt phosphorylation following SDF1α stimulation of Rag2−/− (which fail to forma PreTCR) or Vav1/2/3−/− DN3 cells in which signalling through the PreTCR is impaired (Figure 6). CXCR4-mediated PI3K signalling was intact in the absence of the preTCR and was elevated in Vav1/2/3−/− DN3 cells. By contrast, activation of the MAPK pathway by SDF1α, which is also Ras dependent(32-33), was almost completely ablated in both mutants. These results suggest that there are distinct CXCR4 signalling responses: a Ras-dependent, preTCR-independent pathway of PI3K activation, and a preTCR-dependent pathway required for the MAPK signalling cascade.
Figure 6. Intact PI3K but defective ERK activation in Rag2−/− and Vav1/2/3−/− DN3 cells following stimulation with SDF1α.
Induction of (A) p-Akt (S473) and (B) p-Erk1/2 (T202/Y204) in WT ( ), Vav1/2/3−/− (□) and Rag2−/− (○) DN3 cells after stimulation with 10nM SDF1α. Graph shows the mean and SD from analysis of four-six mice.
), Vav1/2/3−/− (□) and Rag2−/− (○) DN3 cells after stimulation with 10nM SDF1α. Graph shows the mean and SD from analysis of four-six mice.
CXCR4 signalling is required for an optimal proliferative response at β-selection
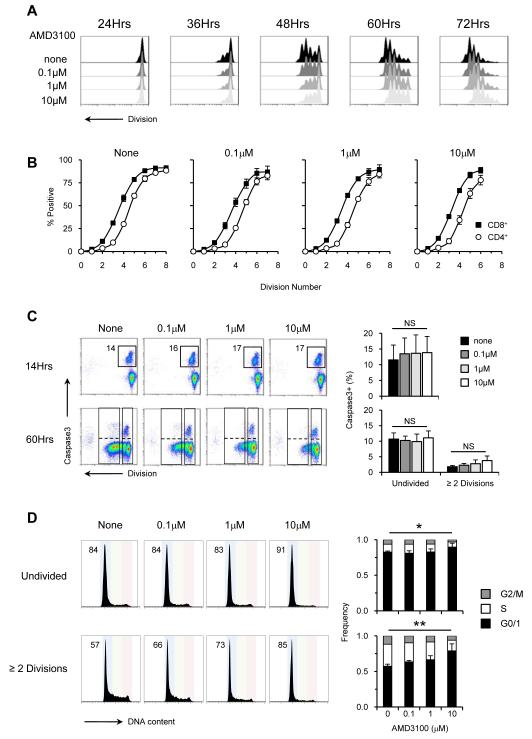
To examine the role of CXCR4 in the proliferation of DN3 cells, we cultured WT DN3a cells in the presence of increasing concentrations of the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100. Inhibition of CXCR4 reduced the number of division peaks in the cultures (Figure 7A). However, AMD3100 did not affect the ability of cells to express CD8 and CD4, provided the requisite number of division cycles was reached (Figure 7B). The defect in cell recovery was not due to an increase in apoptosis, as demonstrated by equivalent proportions of caspase-3+ cells in both the undivided and cycling populations under all culture conditions (Figure 7C). However, the presence of AMD3100 did increase the proportion of cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell-cycle in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 7D), most notably at the highest concentration of 10μM when statistical significance was reached. Thus CXCR4 signalling is necessary to overcome a G0/1 cell cycle block but it is not required for cell survival or differentiation.
Figure 7. CXCR4 inhibition affects the proliferative response of DN3 cells.
(A) Division profiles of sorted WT DN3 cells (CD25hiCD98lo) cultured on OP9-DL1 in the presence of 0, 0.1, 1 and 10μM of the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100. (B) Expression of CD8 (■) and CD4 (○) at each division cycle at 72 hours in untreated and cultured supplemented with 0.1μM, 1μM and 10μM of AMD3100. (C) FACS plots show the gates used to identify cells which have divided ≥ 2 times and those that remain undivided that are either caspase-3 positive or negative. Graphs show aggregate data from three independent experiments; no AMD3100 (■), 0.1μM  , 1μM
, 1μM  and 10μM (□). (D) DNA content profiles from cells cultured for 60hrs. The gating strategy used to identify divided and undivided populations is the same as in Figure 3D. Graphs show data from three independent experiments where G0/1 = ■, S = □ and G2/M =
and 10μM (□). (D) DNA content profiles from cells cultured for 60hrs. The gating strategy used to identify divided and undivided populations is the same as in Figure 3D. Graphs show data from three independent experiments where G0/1 = ■, S = □ and G2/M =  . For all statistical analysis a repeated measures ANOVA test was performed. NS = not significant, * = p<0.05.
. For all statistical analysis a repeated measures ANOVA test was performed. NS = not significant, * = p<0.05.
Discussion
The results presented in this manuscript show that Ras activation of p110γ is required for optimal proliferation triggered following the successful generation of a preTCR. This is the first study to identify a target of Ras signalling required for β-selection and to place it within the context of a signalling pathway important for thymocyte development. Thus the p110γ catalytic isoform of PI3K is activated by the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in a Ras-dependent manner. Taken together with our previous results(8), we conclude that in DN3 thymocytes p110γ must be activated by both Gβγ (via P101) and active Ras in order to elicit an optimal CXCR4 PI3K signalling response. This signalling pathway specifically promotes proliferation and, when it is disrupted, a G0/1 cell cycle block is observed. CXCR4 and Ras-mediated activation of P110γ appear not to be essential for survival or differentiation. This constitutes a new Ras-mediated signalling pathway in thymocyte development that is activated independently of the preTCR and contributes to preTCR-triggered proliferation.
By using in vitro culture to measure cell division, apoptosis and differentiation in the undivided and dividing cell populations, we have shown that disruption of the CXCR4-Ras-PI3K signalling pathway does not lead to increased apoptosis amongst DN3 cells. The proportion of apoptotic cells amongst undivided mutant, AMD3100 treated and control cultures was similar. However, there are more numerically more apoptotic cells in the cultures treated with PI3K or CXCR4 antagonist because fewer cells have divided. This is consistent with studies in mouse embryonic fibroblasts deficient for H-, N-, and K-Ras which were unable to proliferate but survived in culture for several weeks (34).
A novel finding in these studies is that the differentiation from the DN3 to DP stage is division-linked. That is, the expression of the cd4 and cd8 genes is dependent upon the cells undergoing a defined number of divisions, which is independent of time. This phenomenon has been reported previously for the differentiation of peripheral lymphocytes, including immunoglobulin class switching in B cells (35), cytokine secretion in CD4 T cells (36) and perforin and granzyme gene expression in CD8 T cells(37). The rationale for division-linked differentiation is not yet understood but it is interesting to speculate that it provides a simple means for transcription factors and other critical regulatory proteins either to accumulate, as a result of continued expression over time, or be diluted as a consequence of cell division in the absence of de novo production. Studies by Rothenberg and colleagues have shown that many transcription factors which are expressed from the DN1 stage of thymocyte development are rapidly down-regulated after β-selection. They propose that this down-regulation is commensurate with permanent commitment to the T-cell lineage, as transcription factors that promote alternative lineage fates are diluted away during the accompanying burst of proliferation(38).
Our study reveals that the activation of the ERK pathway after CXCR4 stimulation requires the preTCR and the Vav family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors. However, the Ras-dependent activation of p110γ following CXCR4 stimulation is independent of the preTCR and Vav. Thus, the active Ras required for CXCR4 mediated p110γ activation is generated by CXCR4 independently of the preTCR. This raises the question of how the preTCR regulates ERK activation downstream of CXCR4 as this is also thought to be dependent upon Ras-mediated activation of Raf. ERK activation by GPCR agonists such as lysophosphatidic acid, bombesin and carbachol has been shown to occur by the transactivation of the Epidermal Growth Factor receptor(39-40). The preTCR may be required to promote ERK activation by an analogous process in which the preTCR and its associated tyrosine kinases fulfil the role of the EGR-R. In this model, trans-activation would require a fully assembled preTCR and would not operate in the absence of TCRβ chain. Furthermore, it is worth considering if functionally and physically distinct nanoclusters of active Ras could explain the independent activation of ERK and P110γ downstream of CXCR4. One pool of active Ras may be preTCR dependent and activate the ERK pathway and a distinct pool of active Ras, which is preTCR independent, may activate P110γ. This possibility is supported by the known ability of Ras-proteins to signal from distinct internal membrane compartments such as the plasma membrane, Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum(11, 41).
The second class I PI3K isoform required for efficient β-selection is p110δ which signals downstream of the preTCR(8). Based upon sequence alignments, the predicted target residues required for the interaction with Ras are conserved across the human and mouse p110α, p110δ and p110γ isoforms(42). Intriguingly, H-, N-, or K-Ras appear not to activate p110δ. Instead, this ability has been attributed to TC21(43). Although a role for TC21 in the thymus has not been described, peripheral TC21−/− T cells show phenotypes similar to those found in p110δ−/− T cells(44), prompting the hypothesis that the TC21-p110δ interaction has a biological role in β-selection. In order to demonstrate this definitively, in addition to examining TC21 mutant mice, a Ras-binding p110δ mutant mouse will need to be generated.
Studies examining Ras-PI3K interactions have focussed predominantly upon oncogenesis. Ras activation of p110α has been found to be critical for the formation of lung adenocarcinomas and skin tumours(45). Our findings may also be relevant to understanding malignancy. T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL) typically presents as the expansion and dissemination of cells which are arrested between the β-selection and DP stages. Mutations that result in enhanced activity of the Notch1 pathway are found in over 60% of T-ALL (46). Although Notch1 is considered a weak tumour initiator, when combined with constitutively active Ras in mouse models T-ALL occurs at an increased frequency indicative of synergy between the pathways(47-48). The mechanism by which this occurs is not yet understood but might involve Ras-mediated activation of PI3K. The constitutive activation of PI3K is a common feature of T-ALL (49) and in T-ALL lines Notch1 signalling results in the suppression of PTEN, a phosphatase which opposes PI3K enzymatic function(50). Our findings show that Ras is required for the activation of the PI3K p110γ to enhance proliferation. Thus the combination of activated Notch1 and Ras might establish an amplified feed-forward PI3K signalling response that drives the oncogenic transformation required for T-ALL.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank our many colleagues for comments on the manuscript; P.D. Hodgkin and E. Vigorito for critical discussion of the data; S. Suire, L.R. Stephens and P.T. Hawkins for the provision of the p110γD/D mice and the anti-p110γ antibody; J.C. Zúñiga-Pflücker for provision of the OP9-DL1 stromal cell line; K. Bates and SABU staff for technical support; and G. Morgan for FACS expertise.
This work was supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council and by a Senior Non Clinical Fellowship from the Medical Research Council, U.K. (M.T).
Abbreviations used
- DP
double-positive
- DN
double-negative
- GPCR
G protein-coupled receptor
- PI3K
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- T-ALL
T cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Footnotes
Conflict of Interests Statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
References
- 1.Yamasaki S, Saito T. Molecular basis for pre-TCR-mediated autonomous signaling. Trends in Immunology. 2007;28:39–43. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2006.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Taghon T, Yui MA, Pant R, Diamond RA, Rothenberg EV. Developmental and molecular characterization of emerging beta- and gammadelta-selected pre-T cells in the adult mouse thymus. Immunity. 2006;24:53–64. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Falk I, Biro J, Kohler H, Eichmann K. Proliferation kinetics associated with T cell receptor-beta chain selection of fetal murine thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1996;184:2327–2339. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.6.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ciofani M, Zuniga-Pflucker JC. Notch promotes survival of pre-T cells at the beta-selection checkpoint by regulating cellular metabolism. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:881–888. doi: 10.1038/ni1234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Maillard I, Tu L, Sambandam A, Yashiro-Ohtani Y, Millholland J, Keeshan K, Shestova O, Xu L, Bhandoola A, Pear WS. The requirement for Notch signaling at the beta-selection checkpoint in vivo is absolute and independent of the pre-T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2239–2245. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hozumi K, Mailhos C, Negishi N, Hirano K.-i., Yahata T, Ando K, Zuklys S, Holländer GA, Shima DT, Habu S. Delta-like 4 is indispensable in thymic environment specific for T cell development. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2008;205:2507–2513. doi: 10.1084/jem.20080134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Koch U, Fiorini E, Benedito R, Besseyrias V, Schuster-Gossler K, Pierres M, Manley NR, Duarte A, MacDonald HR, Radtke F. Delta-like 4 is the essential, nonredundant ligand for Notch1 during thymic T cell lineage commitment. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2008;205:2515–2523. doi: 10.1084/jem.20080829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Janas ML, Varano G, Gudmundsson K, Noda M, Nagasawa T, Turner M. Thymic development beyond beta-selection requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation by CXCR4. J Exp Med. 2010;207:247–261. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Trampont PC, Tosello-Trampont AC, Shen Y, Duley AK, Sutherland AE, Bender TP, Littman DR, Ravichandran KS. CXCR4 acts as a costimulator during thymic beta-selection. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:162–170. doi: 10.1038/ni.1830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Genot E, Cantrell DA. Ras regulation and function in lymphocytes. Current Opinion in Immunology. 2000;12:289–294. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(00)00089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mor A, Philips MR. Compartmentalized Ras/MAPK signaling. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:771–800. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.24.021605.090723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Swat W, Shinkai Y, Cheng HL, Davidson L, Alt FW. Activated Ras signals differentiation and expansion of CD4+8+ thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:4683–4687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Norment AM, Bogatzki LY, Klinger M, Ojala EW, Bevan MJ, Kay RJ. Transgenic expression of RasGRP1 induces the maturation of double-negative thymocytes and enhances the production of CD8 single-positive thymocytes. J Immunol. 2003;170:1141–1149. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.3.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gartner F, Alt FW, Monroe R, Chu M, Sleckman BP, Davidson L, Swat W. Immature thymocytes employ distinct signaling pathways for allelic exclusion versus differentiation and expansion. Immunity. 1999;10:537–546. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Iritani BM, Alberola-Ila J, Forbush KA, Perimutter RM. Distinct signals mediate maturation and allelic exclusion in lymphocyte progenitors. Immunity. 1999;10:713–722. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80070-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cantrell DA. Transgenic analysis of thymocyte signal transduction. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:20–27. doi: 10.1038/nri703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rodriguez-Viciana P, Warne PH, Dhand R, Vanhaesebroeck B, Gout I, Fry MJ, Waterfield MD, Downward J. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase as a direct target of Ras. Nature. 1994;370:527–532. doi: 10.1038/370527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Webb LM, Vigorito E, Wymann MP, Hirsch E, Turner M. Cutting edge: T cell development requires the combined activities of the p110gamma and p110delta catalytic isoforms of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Immunol. 2005;175:2783–2787. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.5.2783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ji H, Rintelen F, Waltzinger C, Bertschy Meier D, Bilancio A, Pearce W, Hirsch E, Wymann MP, Ruckle T, Camps M, Vanhaesebroeck B, Okkenhaug K, Rommel C. Inactivation of PI3Kgamma and PI3Kdelta distorts T-cell development and causes multiple organ inflammation. Blood. 2007;110:2940–2947. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-04-086751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Swat W, Montgrain V, Doggett TA, Douangpanya J, Puri K, Vermi W, Diacovo TG. Essential role of PI3Kdelta and PI3Kgamma in thymocyte survival. Blood. 2006;107:2415–2422. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hagenbeek TJ, Naspetti M, Malergue F, Garcon F, Nunes JA, Cleutjens KB, Trapman J, Krimpenfort P, Spits H. The loss of PTEN allows TCR alphabeta lineage thymocytes to bypass IL-7 and Pre-TCR-mediated signaling. J Exp Med. 2004;200:883–894. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hawkins PT, Anderson KE, Davidson K, Stephens LR. Signalling through Class I PI3Ks in mammalian cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:647–662. doi: 10.1042/BST0340647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shiroki F, Matsuda S, Doi T, Fujiwara M, Mochizuki Y, Kadowaki T, Suzuki H, Koyasu S. The p85α Regulatory Subunit of Class IA Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Regulates β-Selection in Thymocyte Development. The Journal of Immunology. 2007;178:1349–1356. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.3.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Saveliev A, Tybulewicz VL. Lymphocyte signaling: beyond knockouts. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:361–364. doi: 10.1038/ni.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hirsch E, Katanaev VL, Garlanda C, Azzolino O, Pirola L, Silengo L, Sozzani S, Mantovani A, Altruda F, Wymann MP. Central role for G protein-coupled phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma in inflammation. Science. 2000;287:1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5455.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Clayton E, Bardi G, Bell SE, Chantry D, Downes CP, Gray A, Humphries LA, Rawlings D, Reynolds H, Vigorito E, Turner M. A Crucial Role for the p110δ Subunit of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase in B Cell Development and Activation. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2002;196:753–763. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Suire S, Condliffe AM, Ferguson GJ, Ellson CD, Guillou H, Davidson K, Welch H, Coadwell J, Turner M, Chilvers ER, Hawkins PT, Stephens L. Gbetagammas and the Ras binding domain of p110gamma are both important regulators of PI(3)Kgamma signalling in neutrophils. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:1303–1309. doi: 10.1038/ncb1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vigorito E, Gambardella L, Colucci F, McAdam S, Turner M. Vav proteins regulate peripheral B-cell survival. Blood. 2005;106:2391–2398. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-12-4894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hare KJ, Jenkinson EJ, Anderson G. CD69 expression discriminates MHC-dependent and -independent stages of thymocyte positive selection. J Immunol. 1999;162:3978–3983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sasaki T, Irie-Sasaki J, Jones RG, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Stanford WL, Bolon B, Wakeham A, Itie A, Bouchard D, Kozieradzki I, Joza N, Mak TW, Ohashi PS, Suzuki A, Penninger JM. Function of PI3Kgamma in thymocyte development, T cell activation, and neutrophil migration. Science. 2000;287:1040–1046. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5455.1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xiong J, Armato MA, Yankee TM. Immature single-positive CD8+ thymocytes represent the transition from Notch-dependent to Notch-independent T-cell development. Int Immunol. 2011;23:55–64. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxq457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Okabe S, Fukuda S, Kim Y-J, Niki M, Pelus LM, Ohyashiki K, Pandolfi PP, Broxmeyer HE. Stromal cell–derived factor-1α/CXCL12–induced chemotaxis of T cells involves activation of the RasGAP-associated docking protein p62Dok-1. Blood. 2005;105:474–480. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-03-0843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Patrussi L, Ulivieri C, Lucherini OM, Paccani SR, Gamberucci A, Lanfrancone L, Pelicci PG, Baldari CT. p52Shc is required for CXCR4-dependent signaling and chemotaxis in T cells. Blood. 2007;110:1730–1738. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-068411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Drosten M, Dhawahir A, Sum EY, Urosevic J, Lechuga CG, Esteban LM, Castellano E, Guerra C, Santos E, Barbacid M. Genetic analysis of Ras signalling pathways in cell proliferation, migration and survival. EMBO J. 2010;29:1091–1104. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hodgkin PD, Lee JH, Lyons AB. B cell differentiation and isotype switching is related to division cycle number. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 1996;184:277–281. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gett AV, Hodgkin PD. Cell division regulates the T cell cytokine repertoire, revealing a mechanism underlying immune class regulation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1998;95:9488–9493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Janas ML, Groves P, Kienzle N, Kelso A. IL-2 regulates perforin and granzyme gene expression in CD8+ T cells independently of its effects on survival and proliferation. J Immunol. 2005;175:8003–8010. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.12.8003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.David-Fung E-S, Butler R, Buzi G, Yui MA, Diamond RA, Anderson MK, Rowen L, Rothenberg EV. Transcription factor expression dynamics of early T-lymphocyte specification and commitment. Developmental Biology. 2009;325:444–467. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Blesen T. v., Hawes BE, Luttrell DK, Krueger KM, Touhara K, Porfflri E, Sakaue M, Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ. Receptor-tyrosine-kinase- and G[beta][gamma]-mediated MAP kinase activation by a common signalling pathway. Nature. 1995;376:781–784. doi: 10.1038/376781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Daub H, Ulrich Weiss F, Wallasch C, Ullrich A. Role of transactivation of the EGF receptor in signalling by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature. 1996;379:557–560. doi: 10.1038/379557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Daniels MA, Teixeiro E, Gill J, Hausmann B, Roubaty D, Holmberg K, Werlen G, Hollander GA, Gascoigne NR, Palmer E. Thymic selection threshold defined by compartmentalization of Ras/MAPK signalling. Nature. 2006;444:724–729. doi: 10.1038/nature05269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Berndt A, Miller S, Williams O, Le DD, Houseman BT, Pacold JI, Gorrec F, Hon WC, Liu Y, Rommel C, Gaillard P, Ruckle T, Schwarz MK, Shokat KM, Shaw JP, Williams RL. The p110delta structure: mechanisms for selectivity and potency of new PI(3)K inhibitors. Nat Chem Biol. 2010;6:244. doi: 10.1038/nchembio0310-244b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rodriguez-Viciana P, Sabatier C, McCormick F. Signaling specificity by Ras family GTPases is determined by the full spectrum of effectors they regulate. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:4943–4954. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.11.4943-4954.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Delgado P, Cubelos B, Calleja E, Martinez-Martin N, Cipres A, Merida I, Bellas C, Bustelo XR, Alarcon B. Essential function for the GTPase TC21 in homeostatic antigen receptor signaling. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:880–888. doi: 10.1038/ni.1749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gupta S, Ramjaun AR, Haiko P, Wang Y, Warne PH, Nicke B, Nye E, Stamp G, Alitalo K, Downward J. Binding of ras to phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110alpha is required for ras-driven tumorigenesis in mice. Cell. 2007;129:957–968. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zuurbier L, Homminga I, Calvert V, te Winkel ML, Buijs-Gladdines JG, Kooi C, Smits WK, Sonneveld E, Veerman AJ, Kamps WA, Horstmann M, Petricoin EF, 3rd, Pieters R, Meijerink JP. NOTCH1 and/or FBXW7 mutations predict for initial good prednisone response but not for improved outcome in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients treated on DCOG or COALL protocols. Leukemia. 2010;24:2014–2022. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kindler T, Cornejo MG, Scholl C, Liu J, Leeman DS, Haydu JE, Frohling S, Lee BH, Gilliland DG. K-RasG12D-induced T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemias harbor Notch1 mutations and are sensitive to gamma-secretase inhibitors. Blood. 2008;112:3373–3382. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-147587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dupuy AJ, Akagi K, Largaespada DA, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA. Mammalian mutagenesis using a highly mobile somatic Sleeping Beauty transposon system. Nature. 2005;436:221–226. doi: 10.1038/nature03691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gutierrez A, Sanda T, Grebliunaite R, Carracedo A, Salmena L, Ahn Y, Dahlberg S, Neuberg D, Moreau LA, Winter SS, Larson R, Zhang J, Protopopov A, Chin L, Pandolfi PP, Silverman LB, Hunger SP, Sallan SE, Look AT. High frequency of PTEN, PI3K, and AKT abnormalities in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009;114:647–650. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-206722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Palomero T, Dominguez M, Ferrando AA. The role of the PTEN/AKT Pathway in NOTCH1-induced leukemia. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:965–970. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.8.5753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.