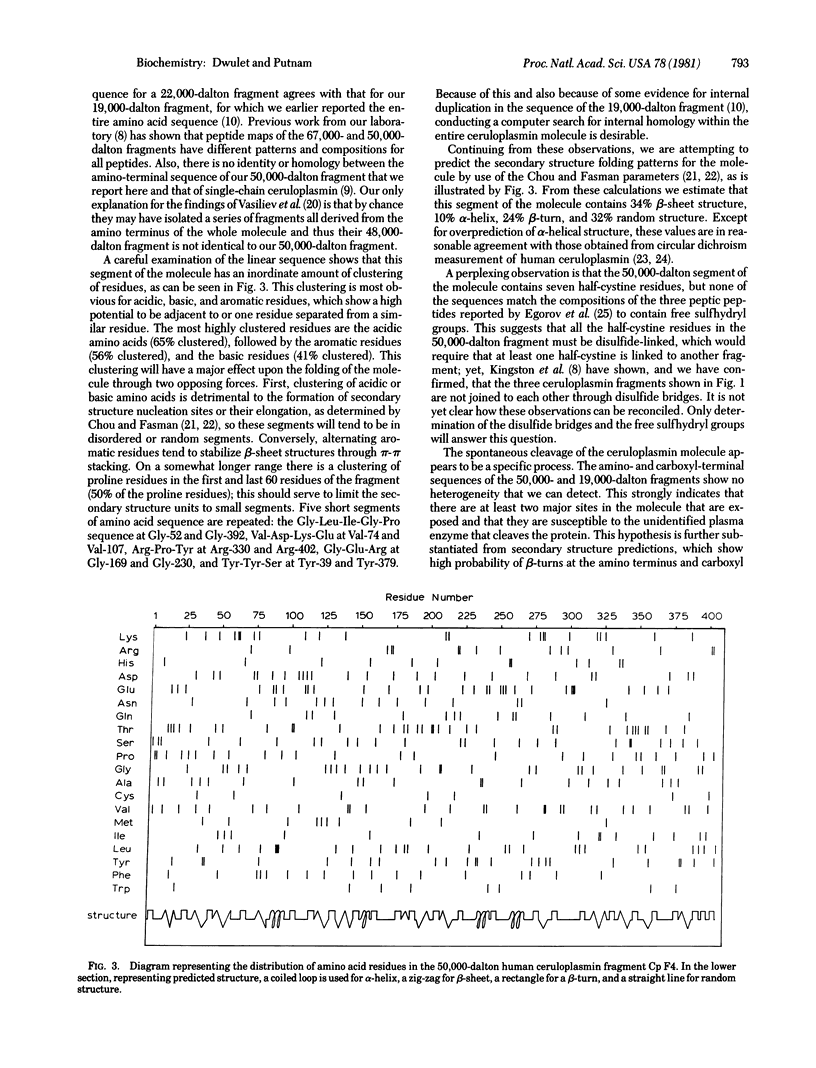
Abstract
The complete amino acid sequence has been determined for a 50,000-dalton fragment that is an internal segment of the single polypeptide chain of human ceruloplasmin [ferroxidase; iron(II):oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.16.3.1]. The fragment (designated Cp F4) contains 405 amino acid residues, has one glucosamine-containing carbohydrate unit, and, together with the 19,000-dalton fragment that follows it, accounts for the carboxyl-terminal half of the molecule. Fragment Cp F4 has a very nonuniform distribution of certain amino acid residues, which show a high potential to be adjacent to or one residue separated from a similar amino acid. This is most pronounced for acid and amide residues (65% clustered), aromatic residues (56% clustered), and basic residues (41% clustered). In addition, there is a long-range clustering of proline residues at the amino- and carboxyl-terminal 60 residues (50% clustered). Also, there are a number of short repeated segments of sequence. Calculations based on parameters predictive of secondary structure folding patterns indicate that the 50,000-dalton fragment has a low content of alpha-helix and is predominantly beta-sheet, beta-turn, and random in structure. Limited enzymatic cleavage of human ceruloplasmin to yield 67,000-, 50,000-, and 19,000-dalton fragments occurs at specific exposed sites of random structure in between domain-like regions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egorov T. A., Svenson A., Rydén L., Carlsson J. A rapid and specific method for isolation of thiol-containing peptides from large proteins by thiol-disulfide exchange on a solid support. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3029–3033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S., Daniel E. A spectral study of human ceruloplasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 24;534(1):132–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90483-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S., Daniel E. Dissociation and reconstitution of human ceruloplasmin. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4806–4810. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY W. R., HARTLEY B. S. THE STRUCTURE OF A CHYMOTRYPTIC PEPTIDE FROM PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:379–380. doi: 10.1042/bj0890379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Kaplan H. B., Edelson H. S., Weissmann G. Ceruloplasmin. A scavenger of superoxide anion radicals. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4040–4045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston I. B., Kingston B. L., Putnam F. W. Chemical evidence that proteolytic cleavage causes the heterogeneity present in human ceruloplasmin preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5377–5381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston I. B., Kingston B. L., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of a histidine-rich proteolytic fragment of human ceruloplasmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1668–1672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston I. B., Kingston B. L., Putnam F. W. Primary structure of a histidine-rich proteolytic fragment of human ceruloplasmin. I. Amino acid sequence of the cyanogen bromide peptides. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2878–2885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston I. B., Kingston B. L., Putnam F. W. Primary structure of a histidine-rich proteolytic fragment of human ceruloplasmin. II. Amino acid sequence of the tryptic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2886–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Capra J. D. Automated amino acid sequence of small peptides utilizing Polybrene. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):126–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombs M. L., Bowman B. H. Biochemical studies on human ceruloplasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 15;434(2):452–461. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyer M., Dwulet F. E., Hao Y. L., Putnam F. W. Purification and characterization of undegraded human ceruloplasmin. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):450–458. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Advances in the gas chromatographic analysis of amino acid phenyl- and methylthiohydantoins. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):43–59. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén L., Eaker D. The amino-acid sequences of three tryptic glycopeptides from human ceruloplasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 2;44(1):171–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén L. Single-chain structure of human ceruloplasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Apr 11;26(3):380–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SGOURIS J. T., CORYELL F. C., GALLICK H., STOREY R. W., McCALL K. B., ANDERSON H. D. A large scale method for the preparation and sterilization of ceruloplasmin and apoceruloplasmin from human plasma. Vox Sang. 1962 Jul-Aug;7:394–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1962.tb03272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Bearn A. G. Isolation and partial characterization of the polypeptide chains in human ceruloplasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar;175(2):260–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman C. L., Appella E., Pisano J. J. Rapid analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1977 Feb;77(2):569–573. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


