Abstract
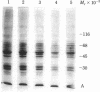
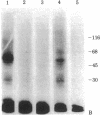
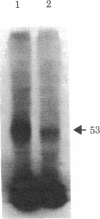
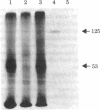
The photoaffinity crosslinker hydroxysuccinimidyl-p-azidobenzoate was used to attach 125I-labeled glucagon covalently to a rat liver membrane protein of Mr ≈ 53,000. Membranes that had been incubated with 125I-labeled glucagon were treated in the dark with hydroxysuccinimidyl-p-azidobenzoate, and a covalent complex was then formed by irradiation with ultraviolet light. Characteristics of 125I-labeled glucagon binding and covalent attachment to the Mr 53,000 peptide were consistent with this peptide being a component of the glucagon receptor involved in the activation of adenylate cyclase [ATP pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing), EC 4.6.1.1]. Binding and covalent attachment of 125I-labeled glucagon to the Mr 53,000 peptide were inhibited by glucagon concentrations that were within the dose-response curve for adenylate cyclase activation, and GTP specifically decreased the photoaffinity crosslinking of 125I-labeled glucagon to the Mr 53,000 peptides. Insulin did not compete for the photoaffinity crosslinking of 125I-labeled glucagon. The same technique of photoaffinity crosslinking that covalently attached 125I-labeled glucagon to the Mr 53,000 peptide with an efficiency of 1-2% can be used to attach 125I-labeled insulin covalently to a Mr 125,000 peptide with an efficiency of approximately 10%. This peptide has been shown to be a subunit of the high-affinity insulin-binding site in rat liver membranes. The technique of photoaffinity crosslinking with agents like hydroxysuccinimidyl-p-azidobenzoate provides a rapid, simple method of covalently attaching ligands to their putative receptors. Photoaffinity crosslinking does not require chemical modification of the labeled ligand and has a less stringent requirement for specific reactive groups than the commonly used bifunctional crosslinking reagents.
Keywords: hydroxysuccinimidyl-p-azidobenzoate, covalent attachment, hormones
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley H., Knowles J. R. Photoaffinity labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:69–114. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregman M. D., Levy D. Labeling of glucagon binding components in hepatocyte plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 23;78(2):584–590. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Miyakawa T., Fox C. F., Pruss R. M., Aharonov A., Herschman H. R. Specific radiolabeling of a cell surface receptor for epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2790–2794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Gammeltoft S. The biological activity and the binding affinity of modified insulins determined on isolated rat fat cells. Diabetologia. 1974 Apr;10(2):105–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01219665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Hazum E., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: covalent labeling and identification of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4918–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Gill D. M., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-promoted coupling of the beta-adrenergic receptor with the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):775–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T. Guanine nucleotide-controlled interactions between components of adenylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):85–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked receptor complex in fat cell and liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1722–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. 3. Binding of glucagon: method of assay and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1861–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. IV. Effects of guanylnucleotides on binding of 125I-glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1872–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., Hock R. A., Hollenberg M. D. Insulin and epidermal growth factor-urogastrone: affinity crosslinking to specific binding sites in rat liver membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1675–1679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welton A. F., Lad P. M., Newby A. C., Yamamura H., Nicosia S., Rodbell M. Solubilization and separation of the glucagon receptor and adenylate cyclase in guanine nucleotide-sensitive states. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5947–5950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor of rat adiopocyte plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1743–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]