Abstract
Actinomycotic infections are known to have an association with difficulties in diagnosis and treatment. These infections usually involve the head, neck, thorax, and abdomen. Actinomycosis of the upper lip is a rare condition and an important one as well, because it can imitate other diseases. As the initial impression, it can easily be mistaken for a mucocele, venous lake, or benign neoplasm. An 82-year-old man presented with an asymptomatic normal skin colored nodule on the upper lip. Histopathologic findings showed an abscess and sulfur granules in the dermis. Gram staining results showed a mesh of branching rods. In this report, we present an unusual case of actinomycosis of the upper lip and discuss its characteristics and therapeutic modalities.
Keywords: Actinomycosis, Sulfur granules
INTRODUCTION
Actinomycosis is a chronic, suppurative infection, caused mainly by Actinomyces israelii, Gram-positive anaerobic bacilli of which cultivation is difficult1. In humans, it lives as a commensal organism in the oral cavity and respiratory and digestive tracts2. The organism is unable to penetrate intact tissue; therefore, infection is often secondary to local injury or spreading from visceral sites. This infection is characterized by localized swelling with suppuration, abscess formation, tissue fibrosis, and sinus drainage3. Oral actinomycosis is rare, compared with occurrence at common sites, which include the cervicofacial, respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal tract. Clinical features of our patient were similar with a mucocele or venous lake; however, the biopsy specimen revealed an abscess and sulfur granules in the dermis. Therefore, we made a diagnosis and report an unusual case of actinomycosis of the upper lip.
CASE REPORT
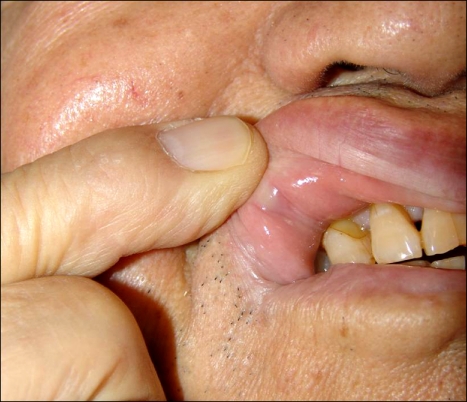
An 82-year-old man presented to our dermatology department with a subcutaneous nodule on the mucosal aspect of his right upper lip. He noticed the lesion 15 days before the visit and had not taken any treatment for it. Intraoral examination revealed an almost non-tender normal skin colored nodule on the lip, which measured 8-mm, and was covered with normal mucosa (Fig. 1). The nodule was smooth on palpation, and no discharge of pus or exudates was observed upon gentle pressure. No cervical lymphadenopathy was noted. Under the impression of a mucocele or venous lake, the lesion was totally excised.
Fig. 1.
A normal skin colored subcutaneous nodule measuring 8 mm on the mucosal aspect of the right upper lip.
The patient's past medical history included hypertension and benign prostate hyperplasia since the age of 72. Antianginal medication had been started 3 months earlier, and there was no recent history of dental manipulation.
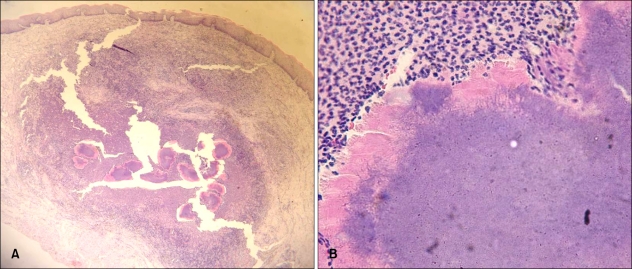
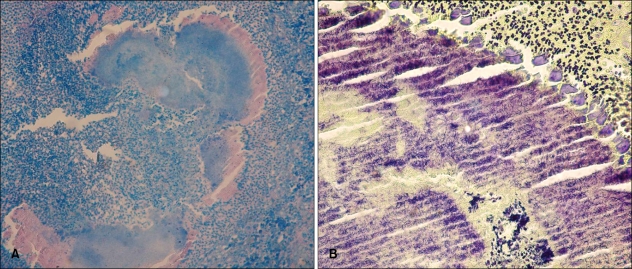
Histopathological examination showed characteristic basophilic clumps of organism, and sulfur granules with associated suppurative inflammation in the dermis (Fig. 2). Gram staining showed numerous radially oriented, bluish purple, filamentous bacteria with peripheral clubs at its edge (Fig. 3A). AFB staining showed no acid-fast bacilli (Fig. 3B). Actinomycosis was diagnosed after other diseases that show sulfur granules, like nocardiosis and botryomycosis, had been ruled out. Sulfur granules observed in nocardiosis contain gram-positive, weakly acid-fast bacilli, and those observed in botryomycosis consist of nonfilamentous cocci or bacilli, which may be gram-positive or negative. No pus or other symptoms suggestive of infectious origin were observed; therefore, we did not consider performing bacterial culture or other laboratory methods for identification of a causativeorganism.
Fig. 2.
(A) Sulfur granules associated with suppurative inflammation in the dermis (H&E, ×40). (B) The magnified view shows a group of filamentous bacteria forming a sulfur granule with peripheral Hoeppli-Splendore phenomenon (H&E, ×400).
Fig. 3.
(A) No acid-fast-bacilli are seen (AFB, ×200). (B) A gram stain demonstrates numerous, radially oriented, gram-positive filamentous bacteria and peripheral clubs at its edge (Gram stain, ×400).
Routine hematological and biochemical tests were conducted on the next visit; however, there were no abnormal findings. ELISA for HIV also showed negative results.
The lesion had already been completely removed, and, on the basis of the above findings, the patient was treated complementarily with a daily oral dose of 300 mg cefditoren pivoxil. After 1 month of treatment, we were unable to contact the patient and follow up assessment was not continued.
DISCUSSION
Actinomycosis is a rare, chronic, slowly progressive bacterial infection that induces both suppurative and granulomatous inflammation3. It is caused by anaerobic, gram-positive bacilli, most of which belong to the genus Actinomyces. Actinomyces israelii is the agent isolated in most cases4 and is responsible for cervico-facial (55%), pulmonary (15%), abdomino-pelvic (20%), and mixed organ (10%) infections4. Actinomyces spp. are non-virulent commensal organisms found in the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and female genitalia5.
Disruption of the mucosal barrier and alteration of resident microbial flora are important factors for initiation of infection6. Clinical infections are often opportunistic and may result from dental procedures or oral trauma in the cervicofacial region7. Our patient had a recent history of a lip bite, and his medical history was generally unremarkable.
The male to female ratio of the disease is 3:1, and it usually presents in the fourth to fifth decade of life8. Infection commonly presents as a chronic or subacute painless or painful soft tissue swelling or mass involving the submandibular or paramandibular region3. Chronic lesions may have yellowish purulent discharge containing sulfur granules9. Insidious onset of constitutional symptoms, including fever, anorexia, malaise, weight loss, and night sweat may also be observed10.
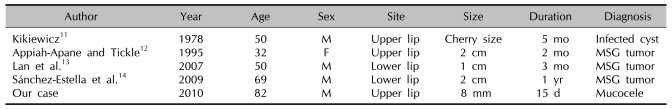
Actinomycosis of the upper lip is rare, and a review of the English literature found only 4 reported cases of lip involvement over the last 30 years (Table 1)11-14. The rarity of this condition may be explained by the richly vascular parenchyma and great mobility of the upper lip, which is mechanically cleansed by saliva; therefore, bacteria cannot easily adhere to it and multiply, as in the case of the uncommon lingual actinomycosis9. Immune-compromised hosts, such as those with HIV infection or diabetes, and those undergoing chemotherapy or taking steroids, are not at greater risk of actinomycosis than immunocompetent hosts15.
Table 1.
Clinical features of actinomycosis of the lip
MSG: minor salivary gland.
Characteristic histopathological findings include an outer zone of granulation around central purulent loculations containing multiple granules16. These pathognomic granules are matted colonies of the causative organism and show basophilic, oval masses with distinct eosinophilic clubs radiating from the entire border. Granules contain gram-positive, non-acid-fast bacteria, which are typically branching filaments of diameter <1µm1. On the basis of these characteristics, actinomycosis can be differentiated from nocardiosis, in which granules are gram-positive and partially acid-fast17. Granules in botryomycosis consist of nonfilamentous cocci or bacilli, which may be gram-positive or negative17.
Definitive diagnosis is established by culture on brain-heart agar or blood agar in anaerobic media18. However, culture results are negative in more than 50% of cases19; therefore, incisional biopsy is often undertaken for diagnosis. Actinomycosis can be treated with long-term penicillin therapy5. Effective short-term antibiotic therapy has recently been reported in cases with less involvement20. Alternative first-line antibiotics include amoxicillin, cephalosporine, tetracycline, erythromycin, and clindamycin. As actinomycosis can recur a few months or years after an apparent cure, antibiotic therapy should be prolonged in order to prevent the chance of recurrence9.
Cervicofacial actinomycosis is known to be the most common type; however, though rare, localized intraoral lesions can sometimes occur. As the initial impression, it can be easily mistaken for a mucocele, venous lake, or benign neoplasm; as a result, the treatment administered may be inappropriate or inadequate9.
Our patient presented with a subcutaneous nodulemeasuring almost 8 mm on the mucosal aspect of the upper lip without immunosuppression and specific past history. Previously reported cases of actinomycosis of the lip have also shown tender or non-tender nodular lesions without immunosuppression and there were no past histories of interest11-14. We performed total excision of the lesion and culture was not performed because we did not consider an infectious origin, as in previously reported cases. Infection of minor self-injury might be favored by poor oral hygiene.
In this study, we report on an unusual case of actinomycosis located on the upper lip. On the basis of our findings, we think that actinomycosis should be included in differential diagnosis of neoplasm and chronic suppurative granulomatous lesions of the oral region.
References
- 1.Al-Niaimi F, Patel A, Blessing K, Fox R, Burden AD. Cutaneous actinomycosis presenting as chronic mastitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:149–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Belmont MJ, Behar PM, Wax MK. Atypical presentations of actinomycosis. Head Neck. 1999;21:264–268. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0347(199905)21:3<264::aid-hed12>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brook I. Actinomycosis: diagnosis and management. South Med J. 2008;101:1019–1023. doi: 10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3181864c1f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mirza M, Sarwar M. Recurrent cutaneous actinomycosis. Pak J Medical Sci. 2003;19:230–232. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Patil D, Siddaramappa B, Manjunathswamy BS, Pandit AM, Dastikop S, Fernandes C, et al. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:1271–1273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.03854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pulverer G, Schütt-Gerowitt H, Schaal KP. Human cervicofacial actinomycoses: microbiological data for 1997 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37:490–497. doi: 10.1086/376621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hermida MD, Della Giovanna P, Lapadula M, García S, Cabrera HN. Actinomyces meyeri cutaneous actinomycosis. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:154–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Santos JW, Zambenedetti RM, Mann KC, Cibin LF. Thoracic actinomycosis: report of a patient with advanced-stage disease. Braz J Infect Dis. 2007;11:157–159. doi: 10.1590/s1413-86702007000100032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Habibi A, Salehinejad J, Saghafi S, Mellati E, Habibi M. Actinomycosis of the tongue. Arch Iran Med. 2008;11:566–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ngow HA, Wan Khairina WM. Cutaneous actinomycosis: the great mimicker. J Clin Pathol. 2009;62:766. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2008.063842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kikiewicz D. A case of actinomycosis of the upper lip. Czas Stomatol. 1978;31:187–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Appiah-Anane S, Tickle M. Actinomycosis-an unusual presentation. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995;33:248–249. doi: 10.1016/0266-4356(95)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lan MC, Huang TY, Lin TY, Lan MY. Pathology quiz case 1. Actinomycosis of the lip mimicking minor salivary gland tumor. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;133:411–414. doi: 10.1001/archotol.133.4.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sánchez-Estella J, Bordel-Gómez MT, Cardeñoso-Alvarez E, Garabito-Solovera E. Actinomycosis of the lip: an exceptional site. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009;100:824–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kanna B, Soni A. Disseminated actinomycosis with unusual cardiac involvement: case report and review. Infect Dis Clin Pract. 2002;11:408–413. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Belmont MJ, Behar PM, Wax MK. Atypical presentations of actinomycosis. Head Neck. 1999;21:264–268. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0347(199905)21:3<264::aid-hed12>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gayraud A, Grosieux-Dauger C, Durlach A, Salmon-Ehr V, Elia A, Grosshans E, et al. Cutaneous actinomycosis in the perianal area and buttocks. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2000;127:393–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bennhoff DF. Actinomycosis: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations and a review of 32 cases. Laryngoscope. 1984;94:1198–1217. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198409000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tomb RR, Stephan F, Haddad A, Choucair J. Cutaneous granular bacteriosis, a rarely diagnosed infection of the head and the neck. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:887–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.03036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Trutnovsky G, Tamussino K, Reich O. Short-term antibiotic treatment of pelvic actinomycosis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2008;101:203–204. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2007.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]