Abstract
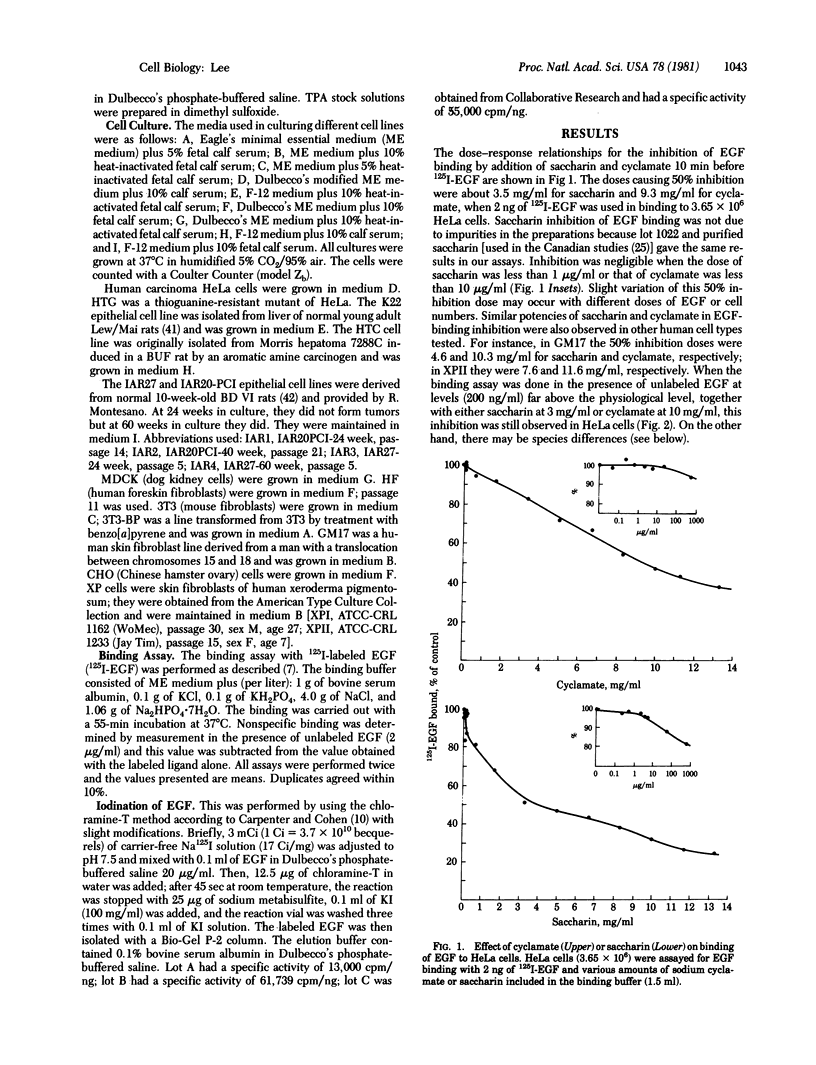
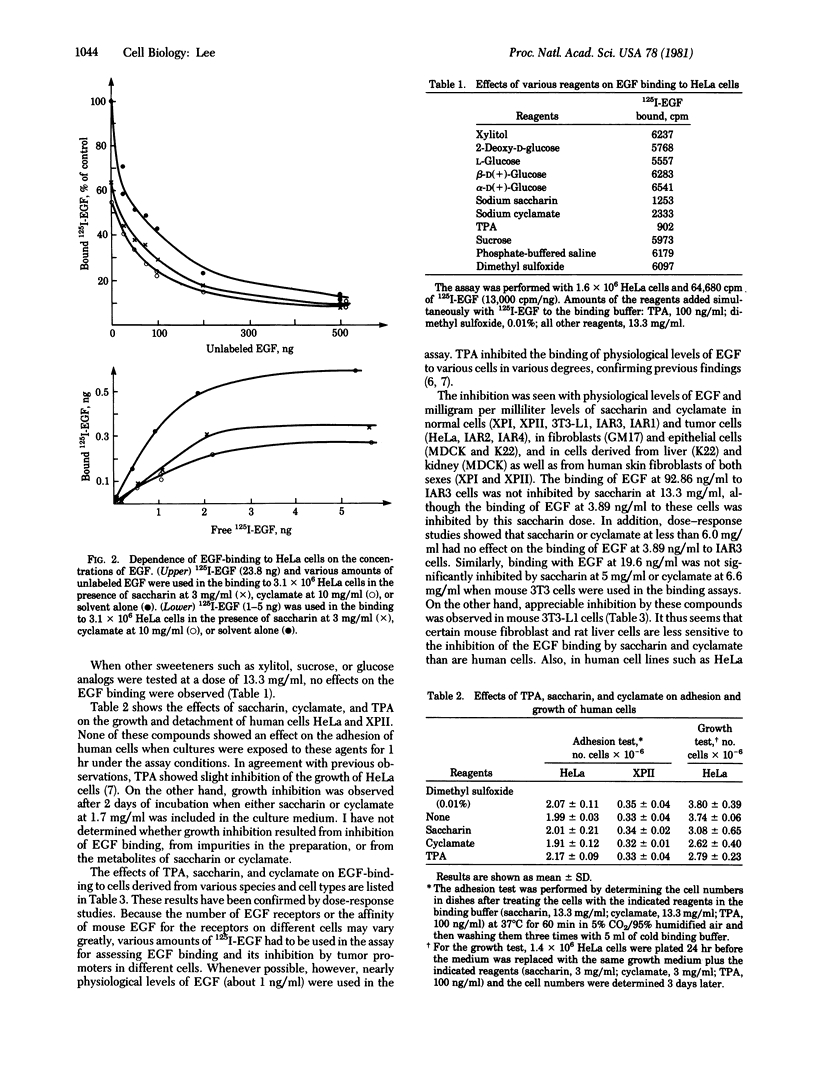
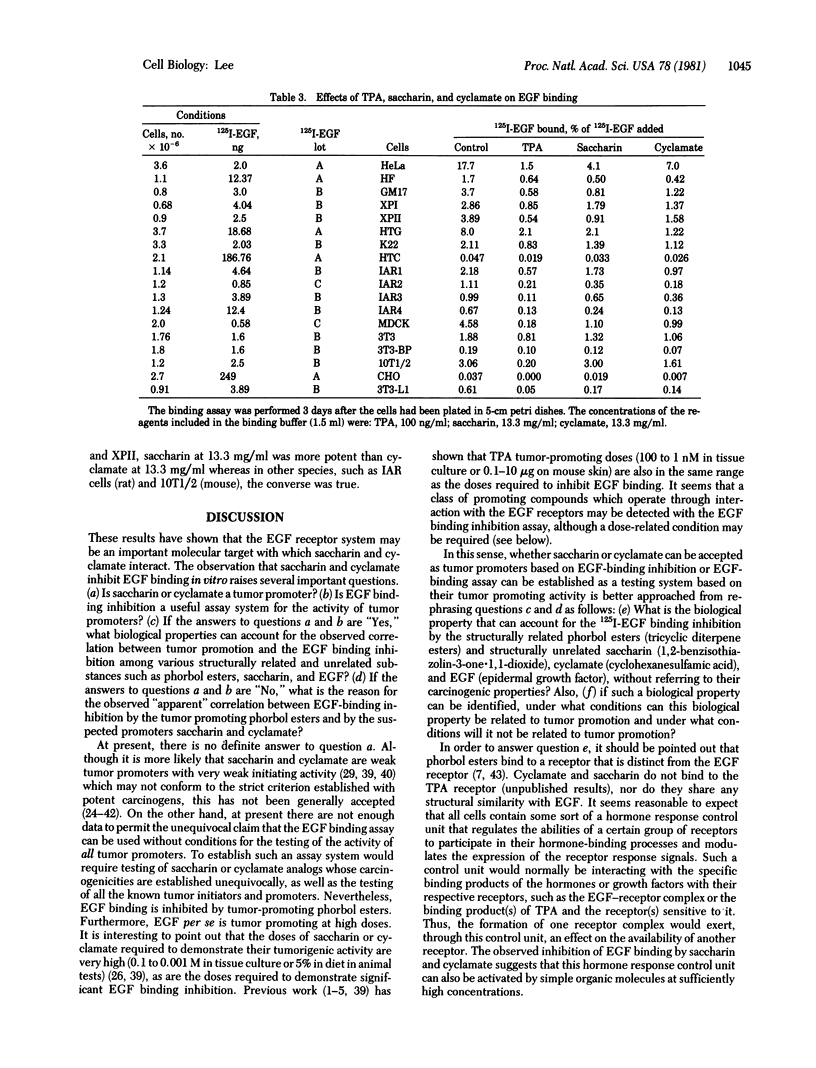
The binding of 125I-labeled mouse epidermal growth factor (EGF) to 18 cell lines, including HeLa (human carcinoma), MDCK (dog kidney cells), HTC (rat hepatoma), K22 (rat liver), HF (human foreskin), GM17 (human skin fibroblasts), XP (human xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts), and 3T3-L1 (mouse fibroblasts), was inhibited by saccharin and cyclamate. The human cells were more sensitive to inhibition by these sweeteners than mouse or rat cells. EGF at doses far above the physiological levels reversed the inhibition in rodent cells but not in HeLa cells. In HeLa cells, the doses of saccharin and cyclamate needed for 50% inhibition were 3.5 and 9.3 mg/ml, respectively. Glucose, 2-deoxyglucose, sucrose, and xylitol did not inhibit EGF binding. Previous studies have shown that phorbol esters, strongly potent tumor promoters, also inhibit EGF binding to tissue culture cells. To explain the EGF binding inhibition by such greatly dissimilar molecules as phorbol esters, saccharin, and cyclamate, it is suggested that they operate through the activation of a hormone response control unit.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold D. L., Moodie C. A., Stavric B., Stoltz D. R., Grice H. C., Munro I. C. Canadian saccharin study. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):320–320. doi: 10.1126/science.197.4301.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D., Colowick S. P. Stimulation of sugar uptake in cultured fibroblasts by epidermal growth factor (EGF) and EGF-binding arginine esterase. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Dec;89(4):633–639. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzinger R. P., Ou S. Y., Bueding E. Saccharin and other sweeteners: mutagenic properties. Science. 1977 Dec 2;198(4320):944–946. doi: 10.1126/science.337489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutwell R. K. The function and mechanism of promoters of carcinogenesis. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1974 Jan;2(4):419–443. doi: 10.3109/10408447309025704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Arai M., Jacobs J. B., Friedell G. H. Promoting effect of saccharin and DL-tryptophan in urinary bladder carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1979 Apr;39(4):1207–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. The stimulation of epidermal proliferation by a specific protein (EGF). Dev Biol. 1965 Dec;12(3):394–407. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(65)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Fox C. F. Molecular mechanism of mitogen action: processing of receptor induced by epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2644–2648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delclos K. B., Nagle D. S., Blumberg P. M. Specific binding of phorbol ester tumor promoters to mouse skin. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Stimulation of DNA synthesis by tumour promoter and pure mitogenic factors. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):723–726. doi: 10.1038/276723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman L., Richardson H. L., Richardson M. E., Lethco E. J., Wallace W. C., Sauro F. M. Toxic response of rats to cyclamates in chow and semisynthetic diets. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):751–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H., Ash J. F., Singer S. J., Cohen S. Visualization by fluorescence of the binding and internalization of epidermal growth factor in human carcinoma cells A-431. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks R. M., Wakefield J., Chowaniec J. Evaluation of a new model to detect bladder carcinogens or co-carcinogens; results obtained with saccharin, cyclamate and cyclophosphamide. Chem Biol Interact. 1975 Sep;11(3):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(75)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. I. The stimulation of protein and ribonucleic acid synthesis in chick embryo epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 18;138(2):347–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe G. R., Burch J. D., Miller A. B., Morrison B., Gordon P., Weldon L., Chambers L. W., Fodor G., Winsor G. M. Artificial sweeteners and human bladder cancer. Lancet. 1977 Sep 17;2(8038):578–581. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91428-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler I. I., Clark J. P. Saccharin, cyclamate, and human bladder cancer. No evidence of an association. JAMA. 1978 Jul 28;240(4):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler I. I. Non-nutritive sweeteners and human bladder cancer: preliminary findings. J Urol. 1976 Feb;115(2):143–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Mechanism of tumor promoter inhibition of cellular binding of epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5168–5172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters inhibit binding of epidermal growth factor to cellular receptors. Science. 1978 Oct 20;202(4365):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.308698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Hassid A. Epidermal growth factor stimulates prostaglandin biosynthesis by canine kidney (MDCK) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 20;76(4):1181–1187. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90980-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Davies P. J., Klempner L., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Epidermal growth factor stimulation of DNA synthesis is potentiated by compounds that inhibit its clustering in coated pits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5731–5735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKanna J. A., Haigler H. T., Cohen S. Hormone receptor topology and dynamics: morphological analysis using ferritin-labeled epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5689–5693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. B., Howe G. R. Artificial sweeteners and bladder cancer. Lancet. 1977 Dec 10;2(8050):1221–1222. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondal S., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Enhancement of oncogenesis in C3H/10T1/2 mouse embryo cell cultures by saccharin. Science. 1978 Sep 22;201(4361):1141–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.684434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Drevon C., Kuroki T., Saint Vincent L., Handleman S., Sanford K. K., DeFeo D., Weinstein I. B. Test for malignant transformation of rat liver cells in culture: cytology, growth in soft agar, and production of plasminogen activator. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Dec;59(6):1651–1658. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.6.1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro I. C., Moodie C. A., Krewski D., Grice H. C. A carcinogenicity study of commercial saccharin in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;32(3):513–526. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(75)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. P., Stahn R., Passovoy D. S., Herschman H. Epidermal growth factor enhancement of skin tumor induction in mice. Experientia. 1976;32(7):913–915. doi: 10.1007/BF02003764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Quantitative determination of the lateral diffusion coefficients of the hormone-receptor complexes of insulin and epidermal growth factor on the plasma membrane of cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5353–5357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Yen S., Cole P. Coffee drinking and cancer of the lower urinary tract. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Mar;54(3):587–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny M., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. IV. The induction of ornithine decarboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):578–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B., Orenstein J. M., Gebert R., Kaighn M. E., Stadler U. C. Growth and structural properties of epithelial cell cultures established from normal rat liver and chemically induced hepatomas. Cancer Res. 1975 Jan;35(1):253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Stellman S. D. Artificial sweetener use and bladder cancer: a case-control study. Science. 1980 Mar 14;207(4436):1214–1216. doi: 10.1126/science.7355283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


