Abstract
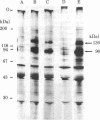
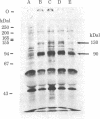
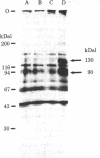
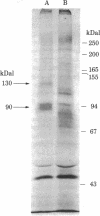
We have identified the subunits of the insulin receptor in cultured human lymphocytes (IM-9 line) by biosynthetic labeling with [35S]methionine and specific precipitation with autoantibodies against the insulin receptor. IM-9 lymphocytes were cultured with [35S]methionine and extracted with Triton X-100. Insulin receptors were concentrated and purified 20-fold by chromatography of the cell extract on wheat germ agglutinin-agarose, and then specifically precipitated by receptor antibodies after addition of a second antibody. Analysis of the immunoprecipitates by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions followed by autoradiography revealed specific precipitation of two major bands with molecular weights of 130,000 and 90,000. Both species were precipitated by receptor antibodies from four different patients with the syndrome of extreme insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. In accord with previous data that insulin bound to receptor reduces the affinity of receptor for anti-receptor antibody, we found that preincubation of the wheat germ-purified cell extract with insulin (1.7 microM) prior to immunoprecipitation caused a decrease in the appearance of both species. The decrease in insulin binding seen after incubation of the lymphocytes with insulin for 12 hr ("down regulation") was associated with a decrease in the labeling of both the 130,000 and 90,000 bands. The apparent molecular weight of both subunits was decreased after pretreatment with mixed glycosidases. In conclusion, we have biosynthetically labeled the insulin receptor with [35S]methionine and showed that the receptor consists of two major glycoprotein subunits with apparent molecular weights of 130,000 and 90,000.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Bar R. S. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.170678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Flier J. S., Roth J., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Immunoprecipitation of the insulin receptor: a sensitive assay for receptor antibodies and a specific technique for receptor purification. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jan;48(1):59–65. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Itin A. Purification of the insulin receptor from human placenta by chromatography on immobilized wheat germ lectin and receptor antibody. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12066–12072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Hazum E., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: covalent labeling and identification of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4918–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Flier J. S., Bar R. S., Archer J. A., Gorden P., Martin M. M., Roth J. The syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Insulin-receptor disorders in man. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):739–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmakos F. C., Roth J. Insulin-induced loss of the insulin receptor in IM-9 lymphocytes. A biological process mediated through the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9860–9869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang U., Kahn C. R., Harrison L. C. Subunit structure of the insulin receptor of the human lymphocyte. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 8;19(1):64–70. doi: 10.1021/bi00542a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked receptor complex in fat cell and liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1722–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C., Lane M. D. Insulin receptor synthesis and turnover in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):285–289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisher M. H., Baron M. D., Jones R. H., Sönksen P. H. Photoreactive insulin analogues used to characterise the insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):492–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor of rat adiopocyte plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1743–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor proteins of liver plasma membrane preparations. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 8;19(1):70–76. doi: 10.1021/bi00542a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]