Abstract
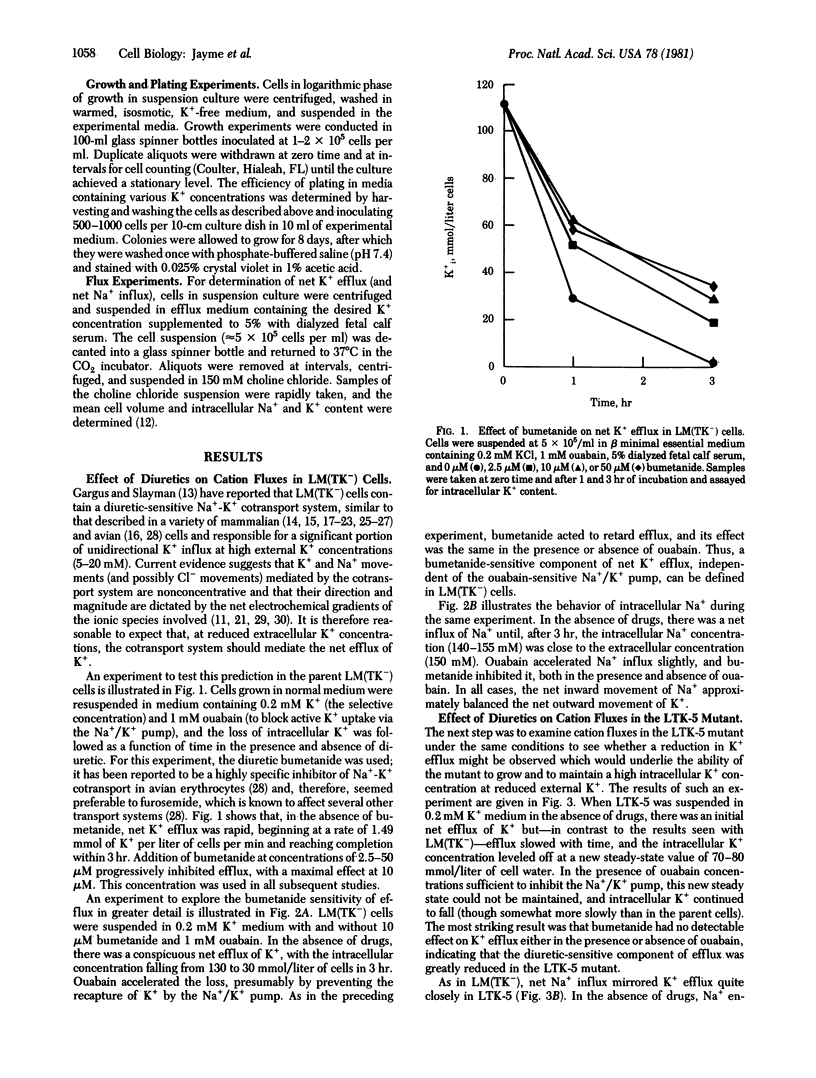
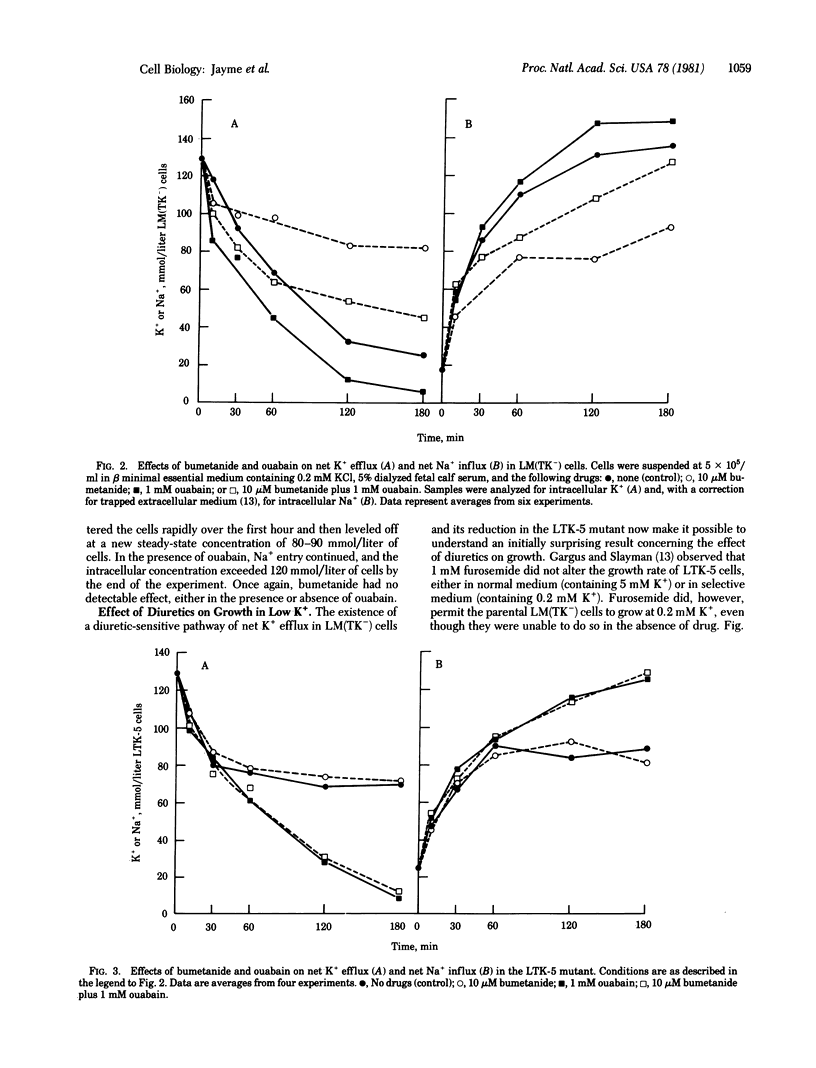
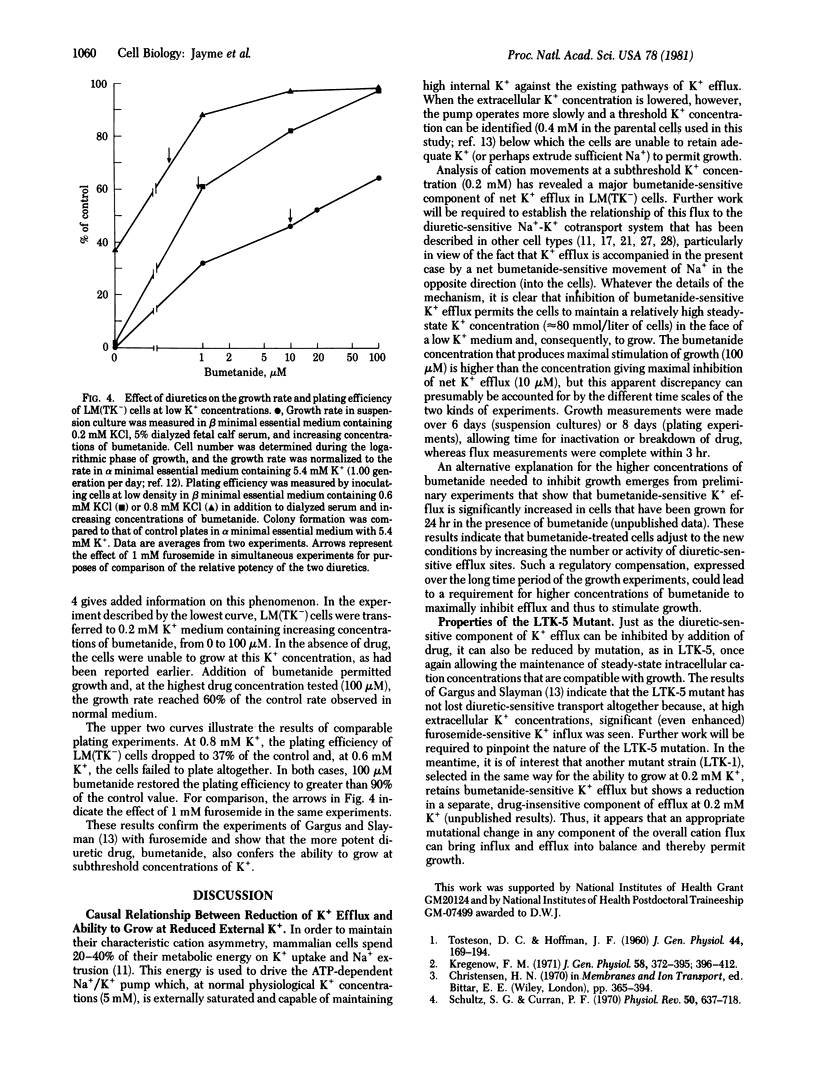
The mouse fibroblastic cell line LM(TK-) is unable to grow at external K+ concentrations below a threshold value of 0.4 mM. At subthreshold K+ concentrations, LM(TK-) cells rapidly lose intracellular K+ and eventually lyse. We have analyzed the pathway primarily responsible for K+ efflux under these experimental conditions and reports its specific inhibition by two diuretics, furosemide and bumetanide. Bumetanide, an analog of furosemide, was a more potent inhibitor (by several orders of magnitude) than was furosemide itself. The effects of ouabain and bumetanide were additive, suggesting independence of diuretic-sensitive K+ efflux from Na+/K+ pump-mediated fluxes. Characterization of K+ efflux in LTK-5, a mutant derived from LM(TK-) and selected for its ability to grow at 0.2 mM K+ indicated that the mutant had lost the diuretic-sensitive K+ efflux pathway. Net cation fluxes, steady-state intracellular cation concentrations, and growth at reduced K+ concentrations were comparable for LM(TK-) cells maximally inhibited by diuretics and for the LTK-5 mutant grown either in the presence or absence of diuretics. Thus, reduction in K+ efflux, either by diuretic addition diuretics. Thus, reduction in K+ efflux, either by diuretic addition or by genetic alteration, can permit the cell to maintain normal cation gradients and to grow at otherwise subthreshold external K+ concentrations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frederiksen O. Functional distinction between two transport mechanisms in rabbit gall-bladder epithelium by use of ouabain, ethacrynic acid and metabolic inhibitors. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:373–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargus J. J., Miller I. L., Slayman C. W., Adelberg E. A. Genetic alterations in potassium transport in L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5589–5593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargus J. J., Slayman C. W. Mechanism and role of furosemide-sensitive K+ transport in L cells: a genetic approach. J Membr Biol. 1980;52(3):245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF01869193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geck P., Heinz E. Coupling in secondary transport. Effect of electrical potentials on the kinetics of ion linked co-transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 4;443(1):49–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90490-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geck P., Pietrzyk C., Burckhardt B. C., Pfeiffer B., Heinz E. Electrically silent cotransport on Na+, K+ and Cl- in Ehrlich cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 4;600(2):432–447. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90446-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn R. B. Co- and counter-transport mechanisms in cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:249–259. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. F., Kregenow F. M. The characterization of new energy dependent cation transport processes in red blood cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):566–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kregenow F. M. The response of duck erythrocytes to nonhemolytic hypotonic media. Evidence for a volume-controlling mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):372–395. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. F., Lindsay R. Transient effects of ethacrynic acid on Na and K movements in cultured cells. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1973 Oct;58(4):345–355. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1973.sp002228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills B., Tupper J. T. Cation permeability and ouabain-insensitive cation flux in the Ehrlich ascites tumor cell. J Membr Biol. 1975;20(1-2):75–97. doi: 10.1007/BF01870629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills B., Tupper J. T. Cell cycle dependent changes in potassium transport. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Sep;89(1):123–132. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Peacock J. H. Transmission on an active electrical response between fibroblasts (L cells) in cell culture. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jul;62(1):25–36. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Doida Y., Roy G., Tsuchiya W., Inouye K., Inouye A. Oscillations of membrane potential in L cells. I. Basic characteristics. J Membr Biol. 1977 Aug 4;35(4):319–335. doi: 10.1007/BF01869957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Roy G., Tsuchiya W., Doida Y., Inouye A. Oscillations of membrane potential in L cells. II. Effect of monovalent ion concentrations and conductance changes associated with oscillations. J Membr Biol. 1977 Aug 4;35(4):337–350. doi: 10.1007/BF01869958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey H. C., Feit P. W., Greengard P. cAMP-stimulated cation cotransport in avian erythrocytes: inhibition by "loop" diuretics. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):C139–C148. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.238.3.C139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Taub M., Saier M. H., Jr Uptake of 22Na+ by cultured dog kidney cells (MDCK). J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11431–11439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. F., 3rd, McManus T. J. Ouabain-insensitive salt and water movements in duck red cells. I. Kinetics of cation transport under hypertonic conditions. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jul;70(1):59–79. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):637–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaggiare S., Wallach M. J., Tupper J. T. Potassium transport in normal and transformed mouse 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Nov;89(3):403–416. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOSTESON D. C., HOFFMAN J. F. Regulation of cell volume by active cation transport in high and low potassium sheep red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Sep;44:169–194. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper J. T. Cation flux in the ehrlich ascites tumor cell. Evidence for Na+-for-Na+ and K+-for-K+ exchange diffusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 18;394(4):586–596. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90144-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper J. T., Zorgniotti F., Mills B. Potassium transport and content during G1 and S phase following serum stimulation of 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):429–440. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S., Cooper R. A. A furosemide-sensitive cotransport of sodium plus potassium in the human red cell. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):745–755. doi: 10.1172/JCI107613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



