Abstract
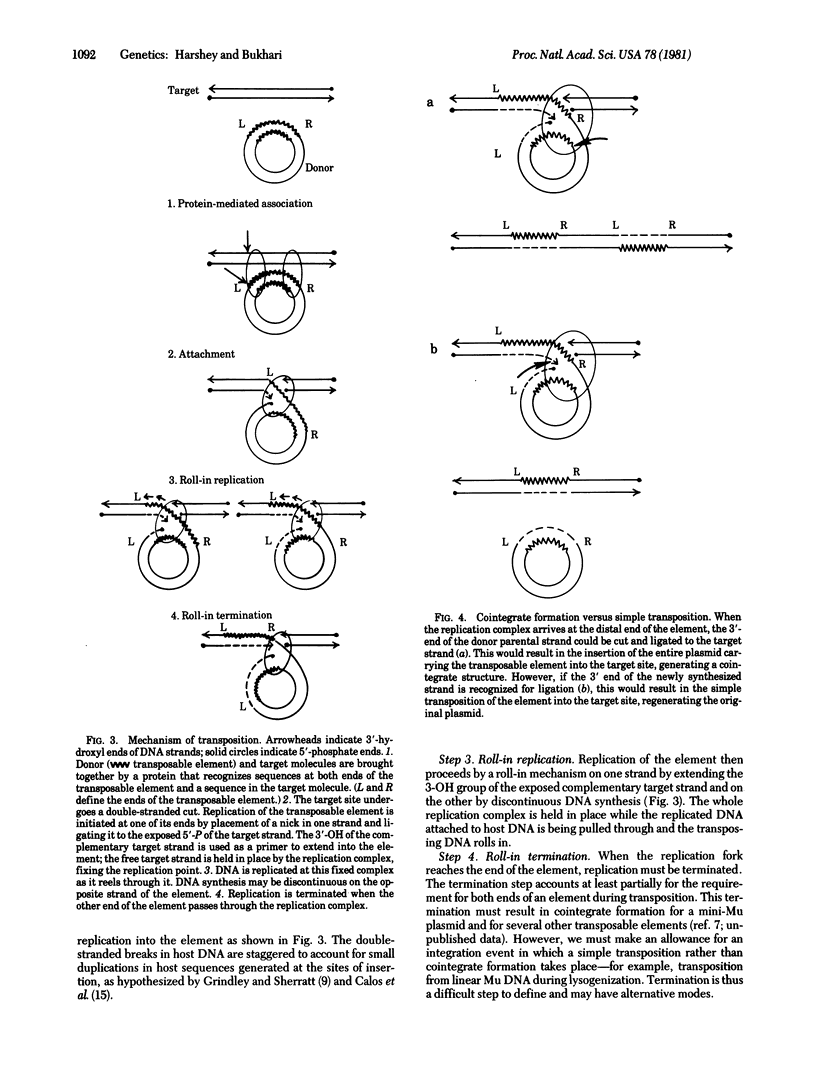
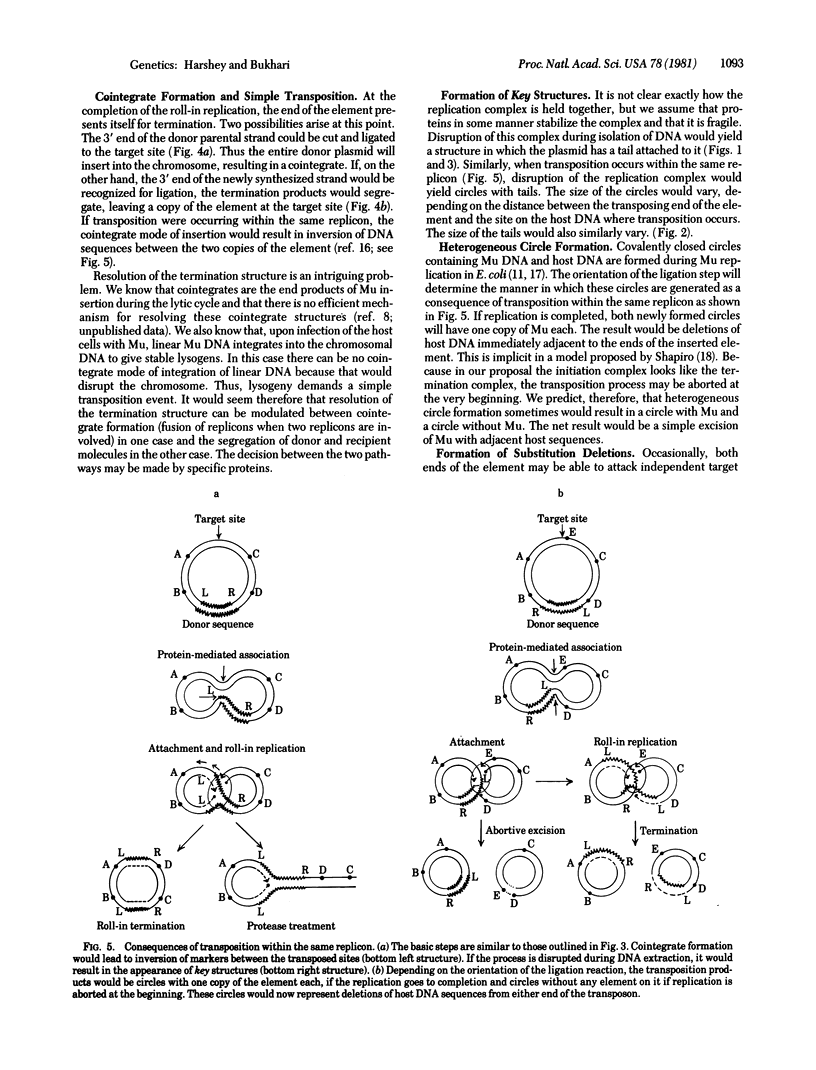
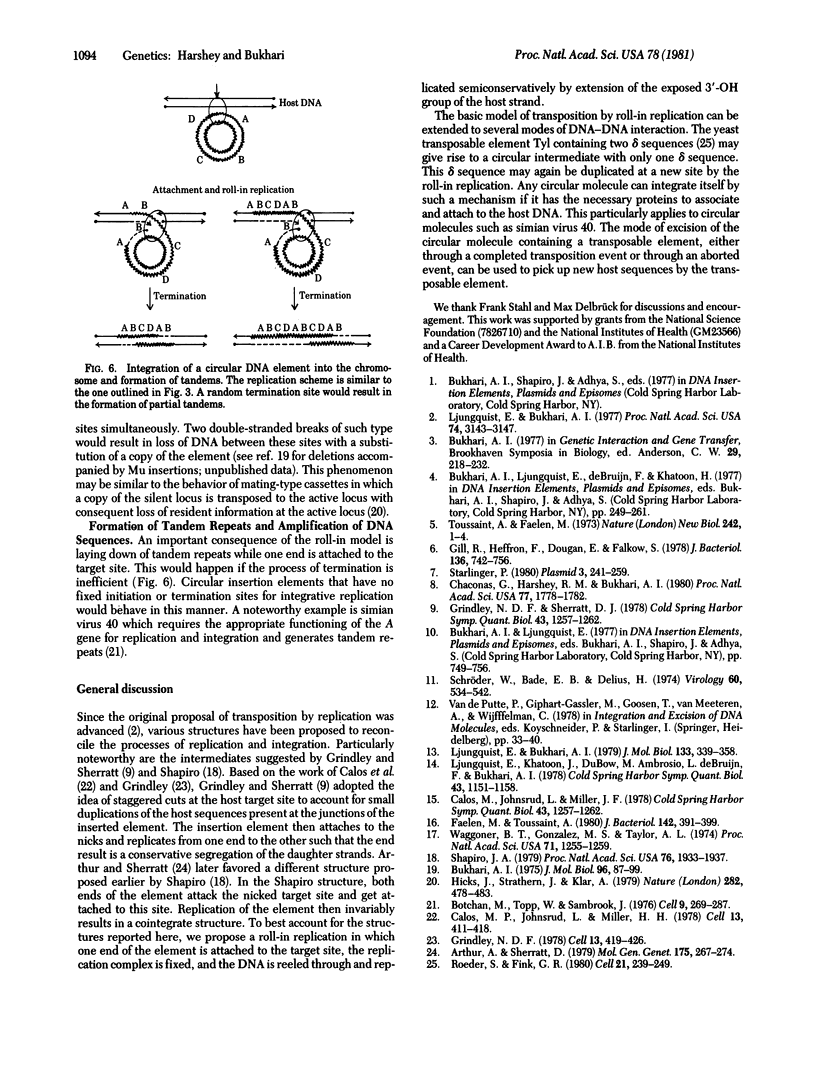
Bacteriophage Mu and many other transposable elements undergo transposition by a process that involves replication of the element. We describe here a mechanism by which such integrative replication may take place. We hve examined electron microscopically the DNA structures generated in host cells after Mu induction and have deduced the following steps in the transposition process, (i) Association. A protein-mediated association is brought about between the transposable element and the target DNA. (ii) Attachment. One end of the element is nicked and attached to a site that undergoes a double-stranded cleavage. (iii) Roll-in replication. While one strand of the target DNA is linked to the nicked strand of the element, the complementary strand of the target DNA is used as a primer for replication into the element such that the replicating DNA is threaded through the replication complex. (iv) Roll-in termination. When the distal end of the element arrives at the replication complex, replication is terminated. The roll-in replication mechanism can also explain laying down of tandem repeats--i.e., amplification of circular DNA sequences.
Full text
PDF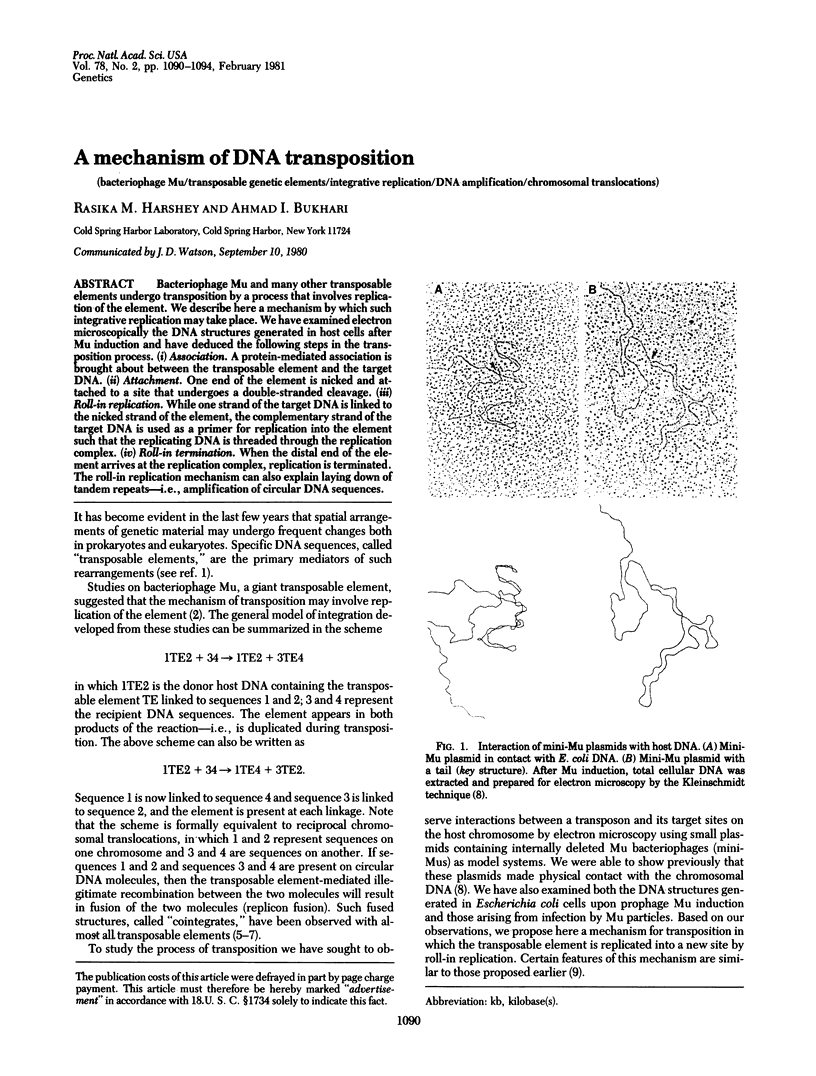

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur A., Sherratt D. Dissection of the transposition process: a transposon-encoded site-specific recombination system. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 1;175(3):267–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00397226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. The arrangement of simian virus 40 sequences in the DNA of transformed cells. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):269–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I. Reversal of mutator phage Mu integration. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Johnsrud L., Miller J. H. DNA sequence at the integration sites of the insertion element IS1. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):411–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., Harshey R. M., Bukhari A. I. Association of Mu-containing plasmids with the Escherichia coli chromosome upon prophage induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1778–1782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faelen M., Toussaint A. Inversion induced by temperature bacteriophage mu-1 in the chromosome of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):391–399. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.391-399.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Heffron F., Dougan G., Falkow S. Analysis of sequences transposed by complementation of two classes of transposition-deficient mutants of Tn3. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):742–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.742-756.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D. IS1 insertion generates duplication of a nine base pair sequence at its target site. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Sherratt D. J. Sequence analysis at IS1 insertion sites: models for transposition. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1257–1261. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks J., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J. Transposable mating type genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):478–473. doi: 10.1038/282478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist E., Bukhari A. I. Behavior of bacteriophage Mu DNA upon infecton of Escherichia coli cells. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 25;133(3):339–357. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90397-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist E., Bukhari A. I. State of prophage Mu DNA upon induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3143–3147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist E., Khatoon H., DuBow M., Ambrosio L., De Bruijn F., Bukhari A. I. Integration of bacteriophage mu DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1151–1158. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Fink G. R. DNA rearrangements associated with a transposable element in yeast. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W., Bade E. G., Delius H. Participation of Escherichia coli DNA in the replication of temperate bacteriophage Mu1. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):534–542. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Molecular model for the transposition and replication of bacteriophage Mu and other transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1933–1937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger P. IS elements and transposons. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):241–259. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint A., Faelen M. Connecting two unrelated DNA sequences with a Mu dimer. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 7;242(114):1–4. doi: 10.1038/newbio242001a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner B. T., González N. S., Taylor A. L. Isolation of heterogeneous circular DNA from induced lysogens of bacteriophage Mu-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1255–1259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





