Abstract
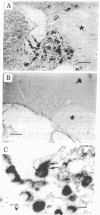
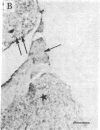
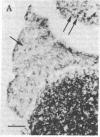
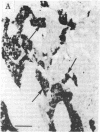
Using antisera specific for the opioid peptide dynorphin, we have carried out immunocytochemical studies of the distribution in rat brain and periphery. In the central nervous system, cells that stain positively for dynorphin are found in the supraoptic nucleus, with less-well-stained cells in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Few positive fibers were detected in brain, suggesting problems with fixation and preservation of antigenicity. In pituitary no staining was seen in the anterior and intermediate lobes but heavy staining was detected in the posterior lobe. In the guinea pig, adrenal chromaffin cells stained with dynorphin antisera. Staining of these cells could be blocked with excess of dynorphin-(1-13) or either enkephalin. Radioimmunoassays revealed a great excess of the enkephalins in the adrenal, suggesting cross competition between dynorphin antiserum and adrenal medullary enkephalin. Finally, the dynorphin antiserum stained a complex of fibers in guinea pig ileum. Staining of these fibers could be blocked by moderate amounts of enkephalin as well as by smaller amounts of dynorphin-(1-13). We conclude that in some places (brain and pituitary) dynorphin exists separately from leucine-enkephalin. In other parts of brain and in the periphery the relationship between dynorphin and the enkephalins is very complex and requires further study and improved antisera.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akil H., Watson S. J., Sullivan S., Barchas J. D. Enkephalin-like material in normal human CSF: measurement and levels. Life Sci. 1978 Jul 10;23(2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F., Battenberg E., Rossier J., Ling N., Guillemin R. Neurons containing beta-endorphin in rat brain exist separately from those containing enkephalin: immunocytochemical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1591–1595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F., Battenberg E., Rossier J., Ling N., Leppaluoto J., Vargo T. M., Guillemin R. Endorphins are located in the intermediate and anterior lobes of the pituitary gland, not in the neurohypophysis. Life Sci. 1977 Jan 1;20(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello A. C., Paxinos G. Evidence for a long Leu-enkephalin striopallidal pathway in rat brain. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):178–180. doi: 10.1038/271178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elde R., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Terenius L. Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-enkephalin: initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1976 Aug;1(4):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazarossian V. E., Chavkin C., Goldstein A. A specific radioimmunoassay for the novel opioid peptide dynorphin. Life Sci. 1980 Jul 7;27(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Ghazarossian V. E. Immunoreactive dynorphin in pituitary and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6207–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Tachibana S., Lowney L. I., Hunkapiller M., Hood L. Dynorphin-(1-13), an extraordinarily potent opioid peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6666–6670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W. Osmotic lysis of bovine chromaffin granules in isotonic solutions of salts of weak organic acids. Release of catecholamines, ATP, dopamine beta-hydroxylase, and enkephalin-like material. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7751–7755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilaver G., Zimmerman E. A., Defendini R., Liotta A. S., Krieger D. T., Brownstein M. J. Adrenocorticotropin and beta-lipotropin in the hypothalamus. Localization in the same arcuate neurons by sequential immunocytochemical procedures. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):50–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier G., Désy L., Lissitszky J. C., Labrie F., Li C. H. Immunohistochemical localization of beta-LPH in the human hypothalamus. Life Sci. 1978 May 22;22(20):1799–1804. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90595-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier G., Leclerc R., Labrie F., Cote J., Chretien M., Lis M. Immunohistochemical localization of beta-lipotropic hormone in the pituitary gland. Endocrinology. 1977 Mar;100(3):770–776. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-3-770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J., Battenberg E., Pittman Q., Bayon A., Koda L., Miller R., Guillemin R., Bloom F. Hypothalamic enkephalin neurones may regulate the neurohypophysis. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):653–655. doi: 10.1038/277653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Brandt J., Elde R. P., Goldstein M. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in gland cells and nerve terminals of the adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1169–1186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Opioid peptide enkephalin: immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofroniew M. V. Immunoreactive beta-endorphin and ACTH in the same neurons of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus in the rat. Am J Anat. 1979 Feb;154(2):283–289. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001540212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Kuhar M. J., Synder S. H. Enkephalin-containing pathway: amygdaloid efferents in the stria terminalis. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 23;149(1):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90602-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Richard C. W., 3rd, Barchas J. D. Evidence for two separate opiate peptide neuronal systems. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):226–228. doi: 10.1038/275226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Sullivan S., Barchas J. D. Immunocytochemical localization of methionine enkephalin: preliminary observations. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):733–738. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Barchas J. D., Li C. H. beta-Lipotropin: localization of cells and axons in rat brain by immunocytochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5155–5158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Richard C. W., 3rd, Barchas J. D. Adrenocorticotropin in rat brain: immunocytochemical localization in cells and axons. Science. 1978 Jun 9;200(4346):1180–1182. doi: 10.1126/science.206967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman E. A., Liotta A., Krieger D. T. beta-Lipotropin in brain: localization in hypothalamic neurons by immunoperoxidase technique. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jan 31;186(3):393–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00224929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]