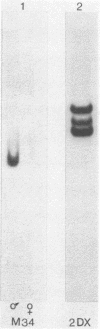
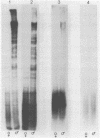
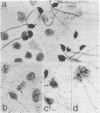
Abstract
The use of heparin as a simple, effective and cheap substitute for conventional methods of controlling background in hybridization procedures is described and illustrated with reference to the use of DNA probes in filter and in situ hybridization. Possible specific mechanisms for this heparin effect are discussed.
Full text
PDF






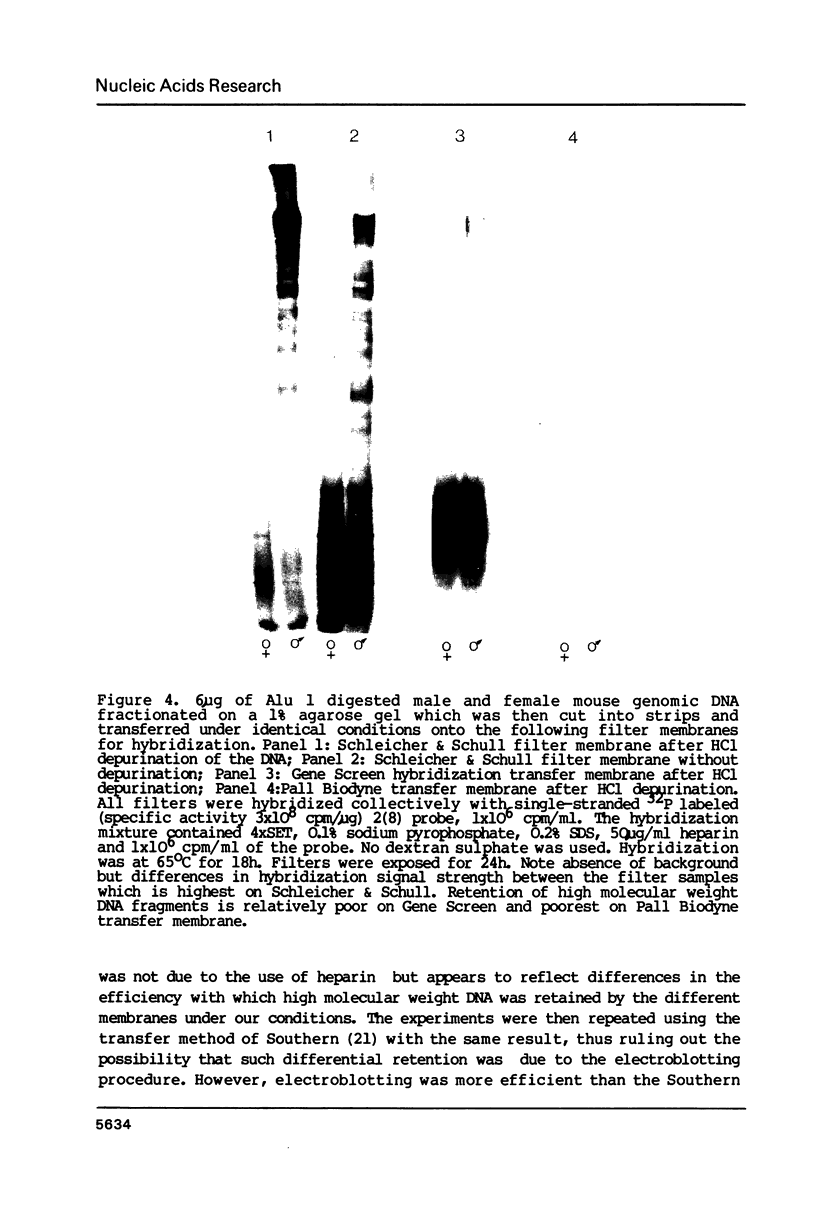




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bickle T. A., Pirrotta V., Imber R. A simple, general procedure for purifying restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2561–2572. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M., Kupferer P., Morris C. F. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins and nucleic acids from slab gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W., Singh L. Conserved repeated DNA sequences in vertebrate sex chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1981;58(1):46–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00284148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitland N. J., Kinross J. H., Busuttil A., Ludgate S. M., Smart G. E., Jones K. W. The detection of DNA tumour virus-specific RNA sequences in abnormal human cervical biopsies by in situ hybridization. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jul;55(Pt 1):123–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Kee S. G., Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C. Amplification and characterization of a beta-globin gene synthesized in vitro. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):163–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYGAARD A. P., HALL B. D. A method for the detection of RNA-DNA complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jul 18;12:98–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Jones K. W. Sex reversal in the mouse (Mus musculus) is caused by a recurrent nonreciprocal crossover involving the x and an aberrant y chromosome. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Phillips C., Jones K. W. The conserved nucleotide sequences of Bkm, which define Sxr in the mouse, are transcribed. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Purdom I. F., Jones K. W. Conserved sex-chromosome-associated nucleotide sequences in eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):805–814. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Purdom I. F., Jones K. W. Effect of different denaturing agents on the detectability of specific DNA sequences of various base compositions by in situ hybridisation. Chromosoma. 1977 Apr 20;60(4):377–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00292860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan R., Bickle T. A., Ebbers W., Brack C. Multiple steps in DNA recognition by restriction endonuclease from E. coli K. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):556–560. doi: 10.1038/256556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan R., Meselson M. A specific complex between a restriction endonuclease and its DNA substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):357–362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]