Abstract
In the crystal structure of the title compound, C14H13NO2, the molecules are approximately planar, the r.m.s. deviation for all non-H atoms being 0.0435 Å; the dihedral angle between the two rings is 3.45 (12)°. The planarity is accounted for in terms of the presence of intramolecular N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding, each of which completes an S(6) ring motif. The molecules are stabilized in the form of supramolecular chains extending along the crystallographic c axis due to intermolecular O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding; each type leads to an R 2 1(6) ring motif.
Related literature
For related benzamide structures, see: Raza et al. (2010a
▶,b
▶,c
▶). For graph-set notation, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).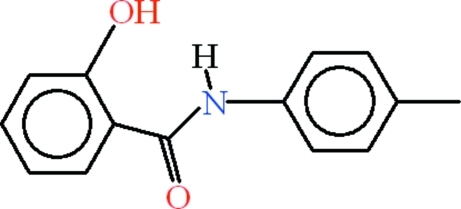
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H13NO2
M r = 227.25
Monoclinic,
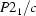
a = 19.4067 (17) Å
b = 4.9122 (5) Å
c = 12.7261 (11) Å
β = 104.793 (4)°
V = 1172.96 (19) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.34 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.979, T max = 0.988
10416 measured reflections
2771 independent reflections
1243 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.060
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.059
wR(F 2) = 0.159
S = 0.96
2771 reflections
156 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030716/tk2771sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030716/tk2771Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030716/tk2771Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯O2i | 0.82 | 1.78 | 2.596 (2) | 179 |
| N1—H1A⋯O1 | 0.86 | 1.92 | 2.647 (2) | 141 |
| C3—H3⋯O2i | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.179 (3) | 129 |
| C9—H9⋯O2 | 0.93 | 2.25 | 2.840 (3) | 121 |
Symmetry code: (i) 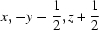 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the provision of funds for the purchase of the diffractometer and encouragement by Dr Muhammad Akram Chaudhary, Ex-Vice Chancellor, University of Sargodha, Pakistan. ARR also acknowledges the Higher Education Commission, Government of Pakistan, for generous support of a research project (20-819).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
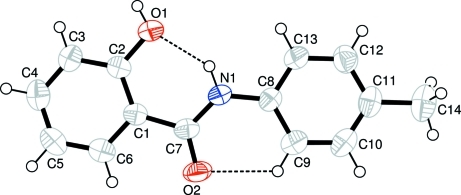
We have reported the crystal structures of (II) i.e. 2-hydroxy-N-(3-nitrophenyl)benzamide (Raza et al., 2010a), (III) i.e. N-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxybenzamide (Raza et al., 2010b) and (IV) i.e. N-(3-chlorophenyl)-2 -hydroxybenzamide (Raza et al., 2010c). In this connection, the title compound (I, Fig. 1) has been prepared as a precursor for the synthesis of symmetric as well as asymmetric benzoxazepines.
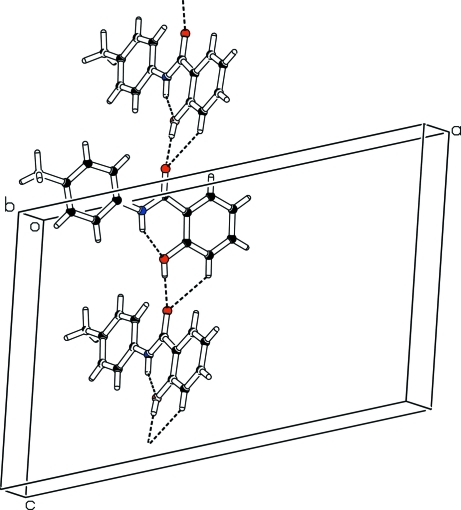
In (I), the 2-hydroxyphenyl group A (C1–C6/O1) and 4-methylanilinic group B (C8—C14/N1) are planar with r.m.s. deviations of 0.0048 and 0.0086 Å, respectively. The dihedral angle between A/B is 3.45 (12) °. There is intramolecular H-bonding of the type N—H···O and C—H···O types (Table 1, Fig. 1), each of which completes a S(6) ring motif (Bernstein et al., 1995). There is also intermolecular H-bonding of the type C—H···O and O—H···O (Table 1). These lead to the formation of two R21(6) ring motifs and to supramolecular chains extending along the crystallographic c-axis (Fig. 2).
Experimental
To a well stirred solution of 2-hydroxy benzoic acid (2.76 g, 0.02 mol, 1 equiv.) and SOCl2 (1.74 mL, 2.84 g, 0.024 mol, 1.2 equiv.) in dry CHCl3, 4-metylaniline (2.14 g, 0.02 mol, 1 equiv.) and Et3N (4.16 mL, 3 g, 0.03 mol, 1.5 equiv.) were added slowly at room temperature followed by 3 h reflux. After completion of reaction, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, neutralized with aqueous NaHCO3 (10 %) and extracted with CHCl3 (3×25 mL). The organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to afford a brown solid. The column chromatographic purification with 1%, 2% and 3% CHCl3 in petrol (300 mL each) over a silica gel packed column (of 25.5 cm length) afforded white needles of (I) in the 96th-280th fractions (50 mL each).
Refinement
Although H atoms appeared in difference Fourier maps they were positioned geometrically with (O–H = 0.82, N–H = 0.86 and C–H = 0.93-0.96 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C), where x = 1.5 for hydroxy- & methyl-H atoms and x = 1.2 for other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H-atoms are shown by small circles of arbitrary radii. The dotted line indicate the intramolecular H-bonding.
Fig. 2.
The partial packing diagram which shows that molecules form supramolecular chains extending along the c-axis. The dotted line indicate the intramolecular H-bonding.
Crystal data
| C14H13NO2 | F(000) = 480 |
| Mr = 227.25 | Dx = 1.287 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1243 reflections |
| a = 19.4067 (17) Å | θ = 1.1–27.9° |
| b = 4.9122 (5) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 12.7261 (11) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 104.793 (4)° | Needle, colorless |
| V = 1172.96 (19) Å3 | 0.34 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2771 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1243 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.060 |
| Detector resolution: 7.6 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.9°, θmin = 1.1° |
| ω scans | h = −25→25 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | k = −4→6 |
| Tmin = 0.979, Tmax = 0.988 | l = −16→16 |
| 10416 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.059 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.159 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.96 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0648P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2771 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 156 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.29367 (9) | −0.2157 (4) | 0.22720 (13) | 0.0599 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.29429 (9) | −0.0348 (3) | −0.09273 (12) | 0.0598 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.24804 (9) | 0.0722 (4) | 0.04697 (14) | 0.0438 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.33925 (11) | −0.2782 (5) | 0.07185 (18) | 0.0407 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.33876 (12) | −0.3489 (5) | 0.17802 (18) | 0.0438 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.38382 (13) | −0.5515 (5) | 0.2327 (2) | 0.0516 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.42941 (13) | −0.6849 (5) | 0.1833 (2) | 0.0596 (11) | |
| C5 | 0.43143 (13) | −0.6168 (6) | 0.0796 (2) | 0.0615 (11) | |
| C6 | 0.38654 (13) | −0.4161 (5) | 0.0249 (2) | 0.0539 (10) | |
| C7 | 0.29213 (12) | −0.0712 (5) | 0.00262 (18) | 0.0416 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.19724 (12) | 0.2725 (5) | −0.00178 (18) | 0.0428 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.18909 (14) | 0.3743 (5) | −0.1055 (2) | 0.0564 (10) | |
| C10 | 0.13704 (14) | 0.5697 (6) | −0.1449 (2) | 0.0605 (11) | |
| C11 | 0.09251 (13) | 0.6670 (5) | −0.0859 (2) | 0.0544 (10) | |
| C12 | 0.10233 (14) | 0.5654 (5) | 0.0186 (2) | 0.0592 (10) | |
| C13 | 0.15368 (13) | 0.3727 (5) | 0.06023 (19) | 0.0524 (9) | |
| C14 | 0.03636 (15) | 0.8783 (5) | −0.1313 (2) | 0.0751 (11) | |
| H1 | 0.29314 | −0.29364 | 0.28396 | 0.0899* | |
| H1A | 0.25091 | 0.03812 | 0.11424 | 0.0525* | |
| H3 | 0.38315 | −0.59736 | 0.30329 | 0.0619* | |
| H4 | 0.45896 | −0.82174 | 0.22036 | 0.0714* | |
| H5 | 0.46273 | −0.70494 | 0.04648 | 0.0739* | |
| H6 | 0.38794 | −0.37165 | −0.04556 | 0.0647* | |
| H9 | 0.21810 | 0.31275 | −0.14848 | 0.0677* | |
| H10 | 0.13229 | 0.63728 | −0.21461 | 0.0726* | |
| H12 | 0.07355 | 0.62883 | 0.06158 | 0.0711* | |
| H13 | 0.15915 | 0.30919 | 0.13074 | 0.0628* | |
| H14A | 0.03008 | 0.89281 | −0.20839 | 0.1127* | |
| H14B | 0.05114 | 1.05104 | −0.09782 | 0.1127* | |
| H14C | −0.00787 | 0.82537 | −0.11655 | 0.1127* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0753 (12) | 0.0677 (13) | 0.0429 (11) | 0.0164 (10) | 0.0262 (9) | 0.0130 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0889 (13) | 0.0586 (13) | 0.0371 (10) | 0.0035 (10) | 0.0256 (9) | 0.0009 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0496 (12) | 0.0504 (14) | 0.0318 (10) | 0.0029 (10) | 0.0111 (9) | 0.0039 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0437 (13) | 0.0379 (15) | 0.0409 (14) | −0.0064 (11) | 0.0117 (11) | −0.0060 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0449 (14) | 0.0444 (16) | 0.0438 (14) | −0.0034 (12) | 0.0147 (12) | −0.0036 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0500 (14) | 0.0479 (18) | 0.0534 (16) | −0.0010 (13) | 0.0070 (12) | 0.0053 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0506 (16) | 0.0481 (19) | 0.077 (2) | 0.0041 (13) | 0.0109 (15) | 0.0031 (14) |
| C5 | 0.0525 (16) | 0.061 (2) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0033 (15) | 0.0257 (15) | −0.0090 (16) |
| C6 | 0.0557 (16) | 0.0571 (19) | 0.0522 (16) | −0.0014 (14) | 0.0197 (13) | −0.0048 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0494 (14) | 0.0400 (16) | 0.0365 (14) | −0.0101 (12) | 0.0132 (11) | −0.0050 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0474 (14) | 0.0383 (15) | 0.0400 (14) | −0.0038 (12) | 0.0062 (11) | 0.0006 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0608 (16) | 0.0616 (19) | 0.0465 (16) | −0.0014 (15) | 0.0130 (13) | 0.0051 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0673 (18) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0515 (17) | −0.0024 (15) | 0.0028 (14) | 0.0110 (14) |
| C11 | 0.0544 (16) | 0.0360 (16) | 0.0628 (19) | −0.0060 (13) | −0.0031 (14) | −0.0021 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0613 (17) | 0.0524 (19) | 0.0615 (18) | 0.0060 (14) | 0.0112 (14) | −0.0038 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0599 (16) | 0.0563 (18) | 0.0397 (14) | 0.0043 (14) | 0.0105 (12) | 0.0046 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0718 (19) | 0.0511 (19) | 0.086 (2) | 0.0023 (16) | −0.0097 (16) | 0.0010 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C2 | 1.366 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.368 (4) |
| O2—C7 | 1.238 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.387 (3) |
| O1—H1 | 0.8200 | C11—C14 | 1.509 (4) |
| N1—C7 | 1.339 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.379 (4) |
| N1—C8 | 1.419 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C7 | 1.495 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.392 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.397 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.389 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.375 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.372 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.381 (4) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C13 | 1.386 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.382 (3) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.391 (4) | ||
| C2—O1—H1 | 109.00 | C11—C12—C13 | 121.6 (2) |
| C7—N1—C8 | 128.90 (19) | C8—C13—C12 | 120.8 (2) |
| C8—N1—H1A | 116.00 | C2—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| C7—N1—H1A | 116.00 | C4—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.5 (2) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 125.8 (2) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 116.7 (2) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 120.6 (2) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 119.2 (2) | C1—C6—H6 | 119.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.3 (2) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.6 (2) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.2 (2) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.3 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 118.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 122.1 (2) | C11—C10—H10 | 118.00 |
| N1—C7—C1 | 118.03 (19) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.00 |
| O2—C7—C1 | 120.5 (2) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.00 |
| O2—C7—N1 | 121.5 (2) | C8—C13—H13 | 120.00 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 124.5 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.00 |
| N1—C8—C13 | 117.0 (2) | C11—C14—H14A | 109.00 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 118.5 (2) | C11—C14—H14B | 109.00 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 119.3 (2) | C11—C14—H14C | 109.00 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 123.1 (2) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.00 |
| C10—C11—C14 | 121.7 (2) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.00 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 116.7 (2) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.00 |
| C12—C11—C14 | 121.6 (2) | ||
| C8—N1—C7—O2 | 2.0 (4) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.0 (4) |
| C8—N1—C7—C1 | −178.1 (2) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.8 (4) |
| C7—N1—C8—C9 | −6.3 (4) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.0 (4) |
| C7—N1—C8—C13 | 174.3 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.4 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—O1 | 179.2 (2) | N1—C8—C9—C10 | 179.6 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.5 (4) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −1.0 (4) |
| C7—C1—C2—O1 | −2.3 (4) | N1—C8—C13—C12 | −179.2 (2) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | 177.9 (2) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 1.4 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.3 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.4 (4) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | −178.3 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.4 (4) |
| C2—C1—C7—O2 | −176.0 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C14 | −179.7 (2) |
| C2—C1—C7—N1 | 4.1 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.0 (4) |
| C6—C1—C7—O2 | 2.5 (3) | C14—C11—C12—C13 | −179.9 (2) |
| C6—C1—C7—N1 | −177.5 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.4 (4) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.8 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O2i | 0.82 | 1.78 | 2.596 (2) | 179 |
| N1—H1A···O1 | 0.86 | 1.92 | 2.647 (2) | 141 |
| C3—H3···O2i | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.179 (3) | 129 |
| C9—H9···O2 | 0.93 | 2.25 | 2.840 (3) | 121 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y−1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK2771).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Raza, A. R., Nisar, B. & Tahir, M. N. (2010a). Acta Cryst. E66, o2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Raza, A. R., Nisar, B., Tahir, M. N. & Shamshad, S. (2010b). Acta Cryst. E66, o2922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Raza, A. R., Nisar, B., Tahir, M. N. & Shamshad, S. (2010c). Acta Cryst. E66, o3100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030716/tk2771sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030716/tk2771Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030716/tk2771Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report