Abstract
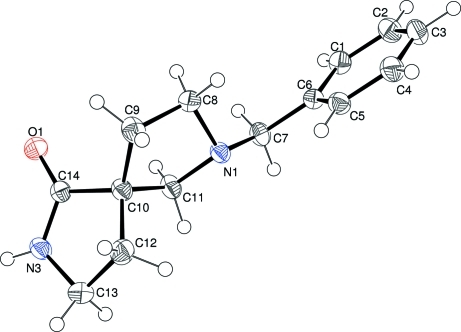
In the title compound, C14H18N2O, both the spiro-linked five-membered rings adopt envelope conformations, with a C atom as the flap in one ring and an N atom in the other. The dihedral angle between the two four-atom planes is 80.46 (8)°. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to generate C(4) chains propagating in [010].
Related literature
For background to pyrrolidine derivatives, see: Kuroki et al. (1999 ▶); Hale et al. (2001 ▶); Shen et al. (2004 ▶).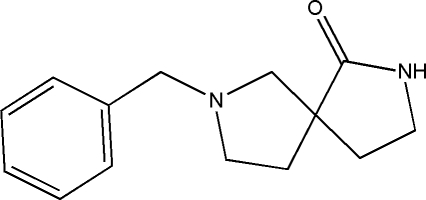
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H18N2O
M r = 230.30
Orthorhombic,
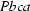
a = 9.630 (2) Å
b = 8.4322 (18) Å
c = 29.848 (7) Å
V = 2423.8 (9) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.21 × 0.18 × 0.17 mm
Data collection
MM007-HF CCD (Saturn 724+) diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.983, T max = 0.986
9156 measured reflections
2761 independent reflections
2495 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.046
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.059
wR(F 2) = 0.120
S = 1.16
2761 reflections
154 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811034301/hb6338sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811034301/hb6338Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811034301/hb6338Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3⋯O1i | 0.88 | 2.14 | 2.9839 (19) | 160 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (grant No. Y2008B29) and Yuandu Scholar of Weifang City for support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
While a great number of pyrrolidines and their derivatives with specific substitution pattern are of particular interest, new methods for their preparation are needed; e.g. Kuroki et al., (1999); Hale et al., (2001); Shen et al., (2004). As part of our research work in this area, the title compound, (I), was synthesized, and herein we report the structure of it.
In the molecule (Fig. 1), all bond lengths and angles are within normal ranges. Atoms C8, C9, C10, and C11 lie in a plane (p1),with a maximum deviation of 0.01102 (11)Å for C10; atoms C10, C13, C14, and N3 lie in a plane (p2) too, the maximum deviation is 0.0045 (10)Å for N3. The dihedral angle between the two plans is 80.46 (8)°. The dihedral angles made by the phenyl ring with p1anes p1 and p2 are 53.56 (9)° and 50.21 (6)°, respectively. The structure exhibits intermolecular N3—H···O1 hydrogen bonding interactions (Table 1), which link the molecules into chains.
Experimental
The title molecule, C14H18N2O1, was synthesized from methyl 1-benzyl-3-(cyanomethyl) pyrrolidine-3-carboxylate and Raney Ni (w/w = 4: 1) in methanol under H2 (50 Psi) atmosphere at room temperature. Colourless blocks of (I) were obtained by recrystallization from ethanol at room temperature.
Refinement
All H atoms were fixed geometrically and allowed to ride on their attached atoms, the C—H distances is in the range 0.95–0.98 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C); the N—H distances is 0.88 Å, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C14H18N2O | F(000) = 992 |
| Mr = 230.30 | Dx = 1.262 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 6994 reflections |
| a = 9.630 (2) Å | θ = 1.4–27.5° |
| b = 8.4322 (18) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 29.848 (7) Å | T = 173 K |
| V = 2423.8 (9) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 8 | 0.21 × 0.18 × 0.17 mm |
Data collection
| MM007-HF CCD (Saturn 724+) diffractometer | 2761 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | 2495 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Confocal | Rint = 0.046 |
| ω scans at fixed χ = 45° | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2007) | h = −7→12 |
| Tmin = 0.983, Tmax = 0.986 | k = −7→10 |
| 9156 measured reflections | l = −38→38 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.059 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.120 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.16 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.030P)2 + 1.3429P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2761 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 154 parameters | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.27133 (12) | 0.12904 (14) | 0.47500 (4) | 0.0295 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.48470 (14) | 0.35120 (16) | 0.37041 (4) | 0.0226 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.39956 (15) | −0.08606 (16) | 0.45320 (5) | 0.0265 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.3485 | −0.1589 | 0.4664 | 0.032* | |
| C1 | 0.39718 (18) | 0.6967 (2) | 0.29710 (6) | 0.0279 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.3010 | 0.6777 | 0.2924 | 0.033* | |
| C2 | 0.4556 (2) | 0.8372 (2) | 0.28234 (6) | 0.0324 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.3996 | 0.9135 | 0.2675 | 0.039* | |
| C3 | 0.5953 (2) | 0.8667 (2) | 0.28919 (6) | 0.0319 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.6352 | 0.9636 | 0.2793 | 0.038* | |
| C4 | 0.67658 (19) | 0.7545 (2) | 0.31053 (6) | 0.0305 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.7726 | 0.7741 | 0.3153 | 0.037* | |
| C5 | 0.61789 (17) | 0.61353 (19) | 0.32491 (6) | 0.0255 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.6746 | 0.5365 | 0.3392 | 0.031* | |
| C6 | 0.47727 (17) | 0.58284 (19) | 0.31871 (5) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.41177 (18) | 0.4289 (2) | 0.33361 (6) | 0.0259 (4) | |
| H7B | 0.3149 | 0.4501 | 0.3430 | 0.031* | |
| H7A | 0.4085 | 0.3554 | 0.3078 | 0.031* | |
| C8 | 0.48226 (19) | 0.4420 (2) | 0.41228 (5) | 0.0266 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.3889 | 0.4870 | 0.4178 | 0.032* | |
| H8B | 0.5508 | 0.5294 | 0.4115 | 0.032* | |
| C9 | 0.5201 (2) | 0.3210 (2) | 0.44804 (6) | 0.0315 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.4680 | 0.3417 | 0.4760 | 0.038* | |
| H9B | 0.6207 | 0.3248 | 0.4547 | 0.038* | |
| C10 | 0.47966 (17) | 0.15873 (19) | 0.42824 (5) | 0.0237 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.41627 (19) | 0.2024 (2) | 0.38238 (5) | 0.0264 (4) | |
| H11B | 0.4358 | 0.1191 | 0.3599 | 0.032* | |
| H11A | 0.3145 | 0.2169 | 0.3848 | 0.032* | |
| C12 | 0.59701 (18) | 0.0370 (2) | 0.42444 (6) | 0.0310 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.6471 | 0.0487 | 0.3957 | 0.037* | |
| H12B | 0.6640 | 0.0489 | 0.4494 | 0.037* | |
| C13 | 0.52313 (19) | −0.1232 (2) | 0.42691 (6) | 0.0317 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.4981 | −0.1622 | 0.3967 | 0.038* | |
| H13B | 0.5814 | −0.2036 | 0.4421 | 0.038* | |
| C14 | 0.37117 (16) | 0.06900 (19) | 0.45541 (5) | 0.0220 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0269 (6) | 0.0299 (7) | 0.0317 (6) | 0.0042 (5) | 0.0045 (5) | 0.0012 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0255 (7) | 0.0193 (7) | 0.0231 (7) | −0.0027 (6) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0010 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0277 (7) | 0.0197 (7) | 0.0321 (8) | −0.0019 (6) | 0.0035 (6) | 0.0033 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0259 (8) | 0.0299 (9) | 0.0279 (8) | 0.0013 (8) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0021 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0361 (10) | 0.0283 (9) | 0.0329 (9) | 0.0047 (8) | −0.0023 (8) | 0.0071 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0383 (10) | 0.0255 (9) | 0.0320 (9) | −0.0055 (8) | 0.0031 (8) | 0.0054 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0273 (9) | 0.0283 (9) | 0.0358 (9) | −0.0047 (7) | 0.0024 (7) | −0.0001 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0246 (8) | 0.0232 (8) | 0.0289 (9) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0015 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0245 (8) | 0.0214 (8) | 0.0226 (8) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0007 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0244 (8) | 0.0258 (9) | 0.0276 (8) | −0.0035 (7) | −0.0021 (6) | 0.0036 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0308 (9) | 0.0227 (8) | 0.0263 (8) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0028 (7) | −0.0020 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0399 (10) | 0.0272 (9) | 0.0273 (9) | −0.0090 (8) | −0.0052 (7) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0265 (8) | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0237 (8) | −0.0025 (7) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0012 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0307 (9) | 0.0240 (8) | 0.0245 (8) | −0.0058 (7) | −0.0035 (7) | 0.0032 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0264 (9) | 0.0344 (10) | 0.0324 (9) | 0.0023 (8) | 0.0053 (7) | 0.0032 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0352 (10) | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0341 (9) | 0.0066 (8) | 0.0034 (8) | −0.0010 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0218 (8) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0214 (7) | −0.0004 (7) | −0.0019 (6) | 0.0010 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C14 | 1.2341 (19) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C7 | 1.459 (2) | C7—H7A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C11 | 1.462 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.521 (2) |
| N1—C8 | 1.466 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| N3—C14 | 1.337 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| N3—C13 | 1.460 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.540 (2) |
| N3—H3 | 0.8800 | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.383 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C6 | 1.390 (2) | C10—C14 | 1.524 (2) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C10—C12 | 1.531 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.384 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.544 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.384 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9500 | C12—C13 | 1.529 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.391 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C6—C7 | 1.510 (2) | ||
| C7—N1—C11 | 110.62 (13) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.9 |
| C7—N1—C8 | 113.55 (13) | C8—C9—C10 | 105.45 (14) |
| C11—N1—C8 | 103.47 (13) | C8—C9—H9A | 110.7 |
| C14—N3—C13 | 113.77 (14) | C10—C9—H9A | 110.7 |
| C14—N3—H3 | 123.1 | C8—C9—H9B | 110.7 |
| C13—N3—H3 | 123.1 | C10—C9—H9B | 110.7 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.90 (16) | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.8 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.5 | C14—C10—C12 | 102.28 (13) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.5 | C14—C10—C9 | 114.22 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.16 (17) | C12—C10—C9 | 115.95 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C14—C10—C11 | 108.61 (13) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C12—C10—C11 | 112.71 (14) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.67 (17) | C9—C10—C11 | 103.19 (13) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.2 | N1—C11—C10 | 104.07 (13) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.2 | N1—C11—H11B | 110.9 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.94 (17) | C10—C11—H11B | 110.9 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 | N1—C11—H11A | 110.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C10—C11—H11A | 110.9 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.06 (16) | H11B—C11—H11A | 109.0 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C13—C12—C10 | 104.21 (14) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C13—C12—H12A | 110.9 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.26 (15) | C10—C12—H12A | 110.9 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 119.90 (15) | C13—C12—H12B | 110.9 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.82 (15) | C10—C12—H12B | 110.9 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 113.99 (13) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| N1—C7—H7B | 108.8 | N3—C13—C12 | 102.45 (13) |
| C6—C7—H7B | 108.8 | N3—C13—H13A | 111.3 |
| N1—C7—H7A | 108.8 | C12—C13—H13A | 111.3 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 108.8 | N3—C13—H13B | 111.3 |
| H7B—C7—H7A | 107.7 | C12—C13—H13B | 111.3 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 104.13 (14) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.2 |
| N1—C8—H8A | 110.9 | O1—C14—N3 | 125.71 (15) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 110.9 | O1—C14—C10 | 125.64 (15) |
| N1—C8—H8B | 110.9 | N3—C14—C10 | 108.61 (14) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 110.9 | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.4 (3) | C7—N1—C11—C10 | −165.66 (13) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.6 (3) | C8—N1—C11—C10 | −43.71 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 (3) | C14—C10—C11—N1 | 149.00 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.7 (3) | C12—C10—C11—N1 | −98.41 (16) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.3 (2) | C9—C10—C11—N1 | 27.42 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −178.67 (16) | C14—C10—C12—C13 | 28.06 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.9 (2) | C9—C10—C12—C13 | 153.01 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.16 (16) | C11—C10—C12—C13 | −88.38 (16) |
| C11—N1—C7—C6 | −179.16 (13) | C14—N3—C13—C12 | 17.26 (19) |
| C8—N1—C7—C6 | 65.02 (18) | C10—C12—C13—N3 | −27.63 (17) |
| C1—C6—C7—N1 | −156.04 (15) | C13—N3—C14—O1 | 178.80 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | 25.7 (2) | C13—N3—C14—C10 | 0.86 (19) |
| C7—N1—C8—C9 | 162.37 (14) | C12—C10—C14—O1 | 163.51 (16) |
| C11—N1—C8—C9 | 42.41 (16) | C9—C10—C14—O1 | 37.4 (2) |
| N1—C8—C9—C10 | −24.29 (18) | C11—C10—C14—O1 | −77.1 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C14 | −119.53 (15) | C12—C10—C14—N3 | −18.55 (17) |
| C8—C9—C10—C12 | 121.90 (16) | C9—C10—C14—N3 | −144.63 (14) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.82 (18) | C11—C10—C14—N3 | 100.81 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3···O1i | 0.88 | 2.14 | 2.9839 (19) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, y−1/2, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB6338).
References
- Hale, J. J., Budhu, R. J., Mills, S. G., MacCoss, M., Malkowitz, L., Siciliano, S., Gould, S. L., DeMartino, J. A. & Springer, M. S. (2001). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 1437–1440. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kuroki, Y. & Iseki, K. (1999). Tetrahedron Lett. 40, 8231–8234.
- Rigaku (2007). CrystalClear Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shen, D. M., et al. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 953–957.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811034301/hb6338sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811034301/hb6338Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811034301/hb6338Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report