Abstract
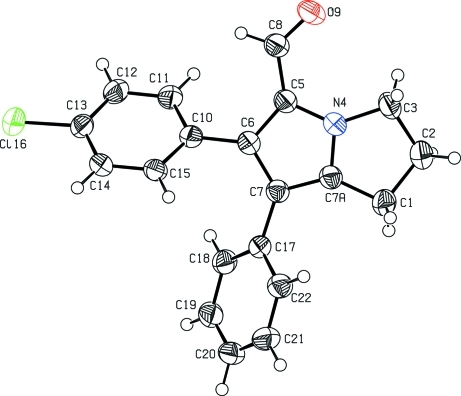
The 4-chlorophenyl residue in the title compound, C20H16ClNO, is oriented at a dihedral angle of 53.6 (3)° towards the phenyl ring and 42.0 (9)° towards the pyrrole ring of the pyrrolizine template. The phenyl ring is oriented at a dihedral angle of 45.4 (4)° towards the pyrrole ring.
Related literature
For the biological activity of arylpyrrolizines as mPGES-1 inhibitors, see: Liedtke et al. (2009 ▶). For dual COX/LOX inhibitors, see: Laufer (2001a
▶,b
▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H16ClNO
M r = 321.79
Monoclinic,
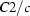
a = 21.1526 (13) Å
b = 11.5723 (9) Å
c = 17.1484 (12) Å
β = 130.843 (4)°
V = 3175.5 (4) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 193 K
0.34 × 0.31 × 0.05 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDS 2T diffractometer
9492 measured reflections
3804 independent reflections
2633 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.036
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.117
S = 1.02
3804 reflections
208 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: X-AREA; data reduction: X-RED (Stoe & Cie, 2010 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811031369/bt5600sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811031369/bt5600Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811031369/bt5600Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
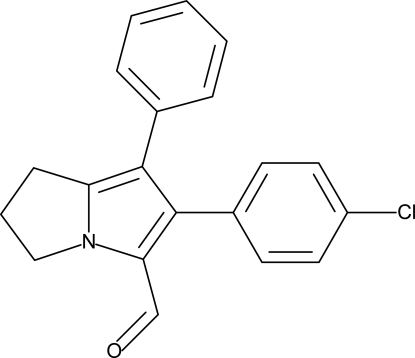
Based on ML3000 (Laufer et al., 2001a,b) as dual COX/LOX inhibitor, we synthesized and evaluated inhibitors for the microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 (mPGES-1) (Liedtke et al., 2009). The title compound was synthesized to obtain a template with a reactive group in position 5 of the pyrrolizine moiety which lead to series of differend derivates of the arylpyrrolizine scaffold.
Towards the unsaturated and planar part of the pyrrolizine residue the 4-chlorophenyl residue is oriented at a dihedral angle of 42.0 (9)° and the plain phenyl ring is oriented at a dihedral angle of 45.4 (4)°. The two phenyl rings are oriented at a dihedral angle of 53.6 (3)° and both centromers show a distance of 5.07 (6) Å. The distance between the para C atoms of the rings (C13, C20) is 6.85 (0) Å.
Experimental
The compound was prepared by Vilsmeyer reaction. Phosphoryl chloride (0.484 ml, 5.31 mmol) is added dropwise to ice-cooled solution of 1.18 ml dimethylformamide and 6-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine (1.5 g, 5.11 mmol); the temperature is kept under 293 K during the addition. Then the mixture is stirred for 1 h at room temperature. Finally the mixture is heated to 333 K for 1 h. The mixture was cooled to 273 K, quenched by water and adjusted to pH 6 with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution 10%.
The product was collected as precipitated solid by filtration, was dissolved in dichloromethane and washed with water three times and finally dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The product was concentrated under vacuum and precipitated out of diisopropylic ether to yield 1.13 g (69%). Crystals of the title compound were obtained by slow evaporation of ethanol at room temperature.
Refinement
Hydrogen atoms attached to carbons were placed at calculated positions with C—H = 0.95 Å (aromatic) or 0.99–1.00 Å (sp3 C-atom). All H atoms were refined with isotropic displacement parameters (set at 1.2–1.5 times of the Ueq of the parent atom).
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of compound I. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C20H16ClNO | F(000) = 1344 |
| Mr = 321.79 | Dx = 1.346 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 6848 reflections |
| a = 21.1526 (13) Å | θ = 2.5–29.7° |
| b = 11.5723 (9) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| c = 17.1484 (12) Å | T = 193 K |
| β = 130.843 (4)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 3175.5 (4) Å3 | 0.34 × 0.31 × 0.05 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS 2T diffractometer | 2633 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: sealed X-ray tube, 12 x 0.4 mm long-fine focus | Rint = 0.036 |
| graphite | θmax = 28.0°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Detector resolution: 6.67 pixels mm-1 | h = −27→27 |
| rotation method scans | k = −15→13 |
| 9492 measured reflections | l = −22→16 |
| 3804 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.117 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0654P)2 + 0.4776P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3804 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 208 parameters | Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.62354 (11) | 0.11928 (15) | 0.31943 (15) | 0.0441 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.5719 | 0.0923 | 0.3037 | 0.053* | |
| H1B | 0.6721 | 0.0780 | 0.3810 | 0.053* | |
| C2 | 0.61862 (13) | 0.10249 (16) | 0.22614 (16) | 0.0510 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.6461 | 0.0294 | 0.2326 | 0.061* | |
| H2B | 0.5597 | 0.1007 | 0.1610 | 0.061* | |
| C3 | 0.66451 (11) | 0.20673 (16) | 0.22833 (15) | 0.0451 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.7241 | 0.1889 | 0.2663 | 0.054* | |
| H3B | 0.6379 | 0.2328 | 0.1578 | 0.054* | |
| N4 | 0.65521 (8) | 0.29317 (12) | 0.28297 (10) | 0.0375 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.66339 (10) | 0.41119 (14) | 0.29645 (12) | 0.0369 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.64365 (9) | 0.43919 (13) | 0.35826 (12) | 0.0351 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.62553 (9) | 0.33471 (14) | 0.38334 (12) | 0.0349 (3) | |
| C7A | 0.63337 (9) | 0.24695 (14) | 0.33439 (12) | 0.0367 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.69420 (10) | 0.48273 (16) | 0.25951 (13) | 0.0423 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.7003 | 0.5629 | 0.2748 | 0.051* | |
| O9 | 0.71332 (9) | 0.44865 (13) | 0.20975 (11) | 0.0543 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.64265 (9) | 0.55686 (14) | 0.39052 (12) | 0.0349 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.60820 (10) | 0.64988 (15) | 0.32190 (13) | 0.0411 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.5853 | 0.6372 | 0.2530 | 0.049* | |
| C12 | 0.60672 (11) | 0.75998 (15) | 0.35203 (14) | 0.0435 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.5839 | 0.8225 | 0.3047 | 0.052* | |
| C13 | 0.63874 (10) | 0.77793 (14) | 0.45162 (14) | 0.0401 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.67412 (10) | 0.68840 (14) | 0.52186 (13) | 0.0387 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.6972 | 0.7020 | 0.5907 | 0.046* | |
| C15 | 0.67564 (9) | 0.57881 (14) | 0.49104 (12) | 0.0361 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.6996 | 0.5171 | 0.5393 | 0.043* | |
| Cl16 | 0.63185 (3) | 0.91463 (4) | 0.48838 (4) | 0.05391 (15) | |
| C17 | 0.59919 (9) | 0.31301 (13) | 0.44330 (12) | 0.0343 (3) | |
| C18 | 0.53753 (10) | 0.37916 (15) | 0.42983 (14) | 0.0408 (4) | |
| H18 | 0.5134 | 0.4426 | 0.3834 | 0.049* | |
| C19 | 0.51117 (11) | 0.35325 (16) | 0.48348 (15) | 0.0460 (4) | |
| H19 | 0.4690 | 0.3988 | 0.4734 | 0.055* | |
| C20 | 0.54598 (11) | 0.26142 (17) | 0.55167 (14) | 0.0483 (4) | |
| H20 | 0.5276 | 0.2435 | 0.5882 | 0.058* | |
| C21 | 0.60775 (12) | 0.19570 (17) | 0.56642 (14) | 0.0486 (4) | |
| H21 | 0.6321 | 0.1328 | 0.6135 | 0.058* | |
| C22 | 0.63404 (11) | 0.22143 (15) | 0.51282 (13) | 0.0416 (4) | |
| H22 | 0.6765 | 0.1759 | 0.5236 | 0.050* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0489 (9) | 0.0362 (9) | 0.0538 (10) | 0.0032 (7) | 0.0364 (8) | −0.0003 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0619 (11) | 0.0429 (10) | 0.0578 (11) | −0.0025 (8) | 0.0434 (10) | −0.0094 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0520 (9) | 0.0457 (9) | 0.0490 (9) | −0.0016 (7) | 0.0379 (8) | −0.0100 (8) |
| N4 | 0.0421 (7) | 0.0388 (7) | 0.0386 (7) | 0.0002 (5) | 0.0294 (6) | −0.0017 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0390 (7) | 0.0386 (8) | 0.0354 (8) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0254 (7) | −0.0023 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0361 (7) | 0.0365 (8) | 0.0337 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0232 (6) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0355 (7) | 0.0354 (8) | 0.0354 (7) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0239 (6) | 0.0016 (6) |
| C7A | 0.0386 (7) | 0.0361 (8) | 0.0396 (8) | 0.0031 (6) | 0.0274 (7) | 0.0012 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0471 (8) | 0.0455 (9) | 0.0397 (8) | −0.0059 (7) | 0.0308 (8) | −0.0039 (7) |
| O9 | 0.0679 (8) | 0.0623 (9) | 0.0545 (8) | −0.0101 (7) | 0.0496 (7) | −0.0086 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0359 (7) | 0.0352 (8) | 0.0369 (8) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0253 (7) | 0.0003 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0477 (8) | 0.0389 (9) | 0.0371 (8) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0279 (7) | 0.0021 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0500 (9) | 0.0348 (8) | 0.0458 (9) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0313 (8) | 0.0062 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0452 (8) | 0.0330 (8) | 0.0518 (9) | −0.0034 (6) | 0.0360 (8) | −0.0027 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0449 (8) | 0.0397 (8) | 0.0414 (8) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0325 (7) | −0.0022 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0403 (8) | 0.0372 (8) | 0.0372 (8) | 0.0031 (6) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0032 (6) |
| Cl16 | 0.0722 (3) | 0.0334 (2) | 0.0704 (3) | −0.00204 (19) | 0.0529 (3) | −0.0052 (2) |
| C17 | 0.0361 (7) | 0.0326 (8) | 0.0366 (8) | −0.0022 (6) | 0.0248 (7) | −0.0015 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0424 (8) | 0.0369 (8) | 0.0482 (9) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0319 (8) | 0.0024 (7) |
| C19 | 0.0486 (9) | 0.0449 (9) | 0.0595 (10) | −0.0057 (7) | 0.0420 (9) | −0.0083 (8) |
| C20 | 0.0591 (10) | 0.0515 (10) | 0.0512 (10) | −0.0127 (8) | 0.0434 (9) | −0.0072 (8) |
| C21 | 0.0592 (10) | 0.0454 (10) | 0.0467 (9) | −0.0022 (8) | 0.0370 (9) | 0.0062 (8) |
| C22 | 0.0452 (8) | 0.0403 (9) | 0.0427 (8) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0302 (7) | 0.0035 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C7A | 1.491 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.397 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.546 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.383 (2) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C12—C13 | 1.380 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.533 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C13—C14 | 1.380 (2) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C13—Cl16 | 1.7440 (17) |
| C3—N4 | 1.469 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.382 (2) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9900 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9900 | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| N4—C7A | 1.345 (2) | C17—C22 | 1.392 (2) |
| N4—C5 | 1.377 (2) | C17—C18 | 1.395 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.408 (2) | C18—C19 | 1.385 (2) |
| C5—C8 | 1.432 (2) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C7 | 1.417 (2) | C19—C20 | 1.383 (3) |
| C6—C10 | 1.475 (2) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C7A | 1.395 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.385 (3) |
| C7—C17 | 1.476 (2) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| C8—O9 | 1.224 (2) | C21—C22 | 1.383 (3) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C21—H21 | 0.9500 |
| C10—C15 | 1.396 (2) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| C7A—C1—C2 | 102.13 (15) | C15—C10—C11 | 117.63 (15) |
| C7A—C1—H1A | 111.3 | C15—C10—C6 | 120.84 (14) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 111.3 | C11—C10—C6 | 121.52 (15) |
| C7A—C1—H1B | 111.3 | C12—C11—C10 | 121.46 (16) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 111.3 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.3 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.2 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.3 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 105.23 (14) | C13—C12—C11 | 119.22 (16) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 110.7 | C13—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 110.7 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 110.7 | C12—C13—C14 | 120.94 (16) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 110.7 | C12—C13—Cl16 | 119.62 (14) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.8 | C14—C13—Cl16 | 119.42 (13) |
| N4—C3—C2 | 101.81 (13) | C13—C14—C15 | 119.33 (15) |
| N4—C3—H3A | 111.4 | C13—C14—H14 | 120.3 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 111.4 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.3 |
| N4—C3—H3B | 111.4 | C14—C15—C10 | 121.41 (15) |
| C2—C3—H3B | 111.4 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 109.3 | C10—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| C7A—N4—C5 | 110.10 (14) | C22—C17—C18 | 118.26 (15) |
| C7A—N4—C3 | 113.20 (14) | C22—C17—C7 | 119.75 (14) |
| C5—N4—C3 | 136.70 (15) | C18—C17—C7 | 121.94 (15) |
| N4—C5—C6 | 106.74 (14) | C19—C18—C17 | 120.67 (16) |
| N4—C5—C8 | 122.86 (15) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.7 |
| C6—C5—C8 | 130.15 (16) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.7 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 107.71 (14) | C20—C19—C18 | 120.32 (16) |
| C5—C6—C10 | 125.36 (15) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.8 |
| C7—C6—C10 | 126.92 (14) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.8 |
| C7A—C7—C6 | 106.05 (14) | C19—C20—C21 | 119.58 (16) |
| C7A—C7—C17 | 122.87 (14) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.2 |
| C6—C7—C17 | 131.02 (14) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.2 |
| N4—C7A—C7 | 109.39 (14) | C22—C21—C20 | 120.13 (17) |
| N4—C7A—C1 | 110.50 (14) | C22—C21—H21 | 119.9 |
| C7—C7A—C1 | 140.10 (16) | C20—C21—H21 | 119.9 |
| O9—C8—C5 | 125.12 (17) | C21—C22—C17 | 121.02 (16) |
| O9—C8—H8 | 117.4 | C21—C22—H22 | 119.5 |
| C5—C8—H8 | 117.4 | C17—C22—H22 | 119.5 |
| C7A—C1—C2—C3 | 25.15 (18) | C6—C5—C8—O9 | 176.32 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—N4 | −25.45 (18) | C5—C6—C10—C15 | −137.95 (16) |
| C2—C3—N4—C7A | 16.96 (19) | C7—C6—C10—C15 | 41.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—N4—C5 | −163.46 (18) | C5—C6—C10—C11 | 42.7 (2) |
| C7A—N4—C5—C6 | −1.26 (18) | C7—C6—C10—C11 | −137.55 (17) |
| C3—N4—C5—C6 | 179.14 (17) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.1 (2) |
| C7A—N4—C5—C8 | 173.57 (15) | C6—C10—C11—C12 | 179.48 (15) |
| C3—N4—C5—C8 | −6.0 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.1 (3) |
| N4—C5—C6—C7 | 1.41 (17) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.8 (3) |
| C8—C5—C6—C7 | −172.90 (16) | C11—C12—C13—Cl16 | −176.36 (13) |
| N4—C5—C6—C10 | −178.77 (14) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −1.5 (2) |
| C8—C5—C6—C10 | 6.9 (3) | Cl16—C13—C14—C15 | 176.68 (12) |
| C5—C6—C7—C7A | −1.06 (17) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | 0.4 (2) |
| C10—C6—C7—C7A | 179.13 (14) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.2 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C17 | −178.20 (15) | C6—C10—C15—C14 | −179.16 (14) |
| C10—C6—C7—C17 | 2.0 (3) | C7A—C7—C17—C22 | 45.3 (2) |
| C5—N4—C7A—C7 | 0.60 (18) | C6—C7—C17—C22 | −137.98 (18) |
| C3—N4—C7A—C7 | −179.70 (13) | C7A—C7—C17—C18 | −132.22 (17) |
| C5—N4—C7A—C1 | 179.45 (13) | C6—C7—C17—C18 | 44.5 (2) |
| C3—N4—C7A—C1 | −0.85 (19) | C22—C17—C18—C19 | −0.7 (2) |
| C6—C7—C7A—N4 | 0.30 (17) | C7—C17—C18—C19 | 176.81 (15) |
| C17—C7—C7A—N4 | 177.73 (14) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 0.3 (3) |
| C6—C7—C7A—C1 | −178.0 (2) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 0.3 (3) |
| C17—C7—C7A—C1 | −0.6 (3) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −0.4 (3) |
| C2—C1—C7A—N4 | −15.54 (18) | C20—C21—C22—C17 | −0.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C7A—C7 | 162.8 (2) | C18—C17—C22—C21 | 0.7 (3) |
| N4—C5—C8—O9 | 2.8 (3) | C7—C17—C22—C21 | −176.92 (16) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5600).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 115–119.
- Laufer, S. (2001a). Inflammopharmacology, 9, 101–112.
- Laufer, S. (2001b). Inflammopharmacology, 9, 113–124.
- Liedtke, A. J., Keck, P. R. W. E. F., Lehmann, F., Koeberle, A., Werz, O. & Laufer, S. (2009). J. Med. Chem. 52, 4968–4972. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2010). X-AREA and X-RED Stoe & Cie GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811031369/bt5600sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811031369/bt5600Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811031369/bt5600Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report