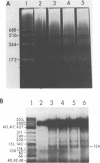
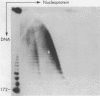
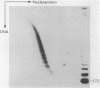
Abstract
By analyzing the accessibility of restriction endonuclease sites in African green monkey alpha-satellite chromatin, we demonstrate the absence of a unique phase relationship between nucleosomes and alpha-satellite DNA. The data indicate a minimum of three different positions for nucleosome cores relative to the alpha-satellite sequence and suggest a random distribution in at least some regions. In addition, while we confirm published reports that staphylococcal nuclease cuts the alpha-satellite sequence in chromatin at a highly preferred site, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of nuclear digests demonstrates that this site is preferentially cut by staphylococcal nuclease even when it is within the nucleosome core. These data indicate that staphylococcal nuclease is not useful for determining nucleosome positions on alpha-satellite DNA, and perhaps on other specific DNA sequences as well.
Full text
PDF




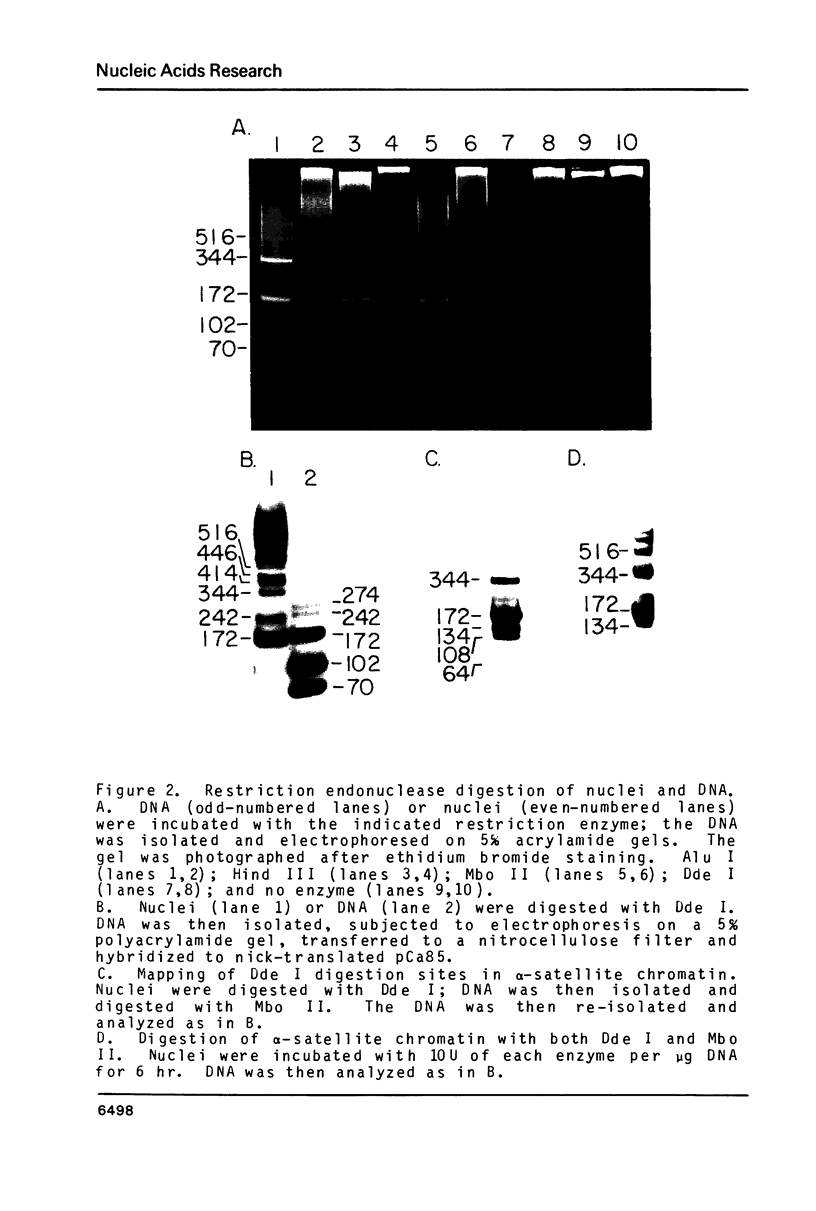








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown F. L., Musich P. R., Maio J. J. The repetitive sequence structure of component alpha DNA and its relationship to the nucleosomes of the African green monkey. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):777–799. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Lomonossoff G. P., Laskey R. A. High sequence specificity of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2659–2673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2643–2658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Fittler F., Zachau H. G. Sequence specific cleavage of African green monkey alpha-satellite DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4275–4285. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Barsoum J., Varshavsky A. Two-dimensional hybridization mapping of nucleosomes. comparison of DNA and protein patterns. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 5;146(3):287–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90389-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis C., Schedl P., Samal B., Worcel A. Chromatin structure of the 5S RNA genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Brown F. L., Maio J. J. Nucleosome phasing and micrococcal nuclease cleavage of African green monkey component alpha DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIAN. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):394–402. doi: 10.1126/science.205944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerdon M. J., Kastan M. B., Lieberman M. W. Distribution of repair-incorporated nucleotides and nucleosome rearrangement in the chromatin of normal and xeroderma pigmentosum human fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3732–3739. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Devine C. S., Cohn S. M., Lieberman M. W. Quantitative electrophoretic transfer of DNA from polyacrylamide or agarose gels to nitrocellulose. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):120–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Singer M. F., McCutchan T. F. Sequence relationships between single repeat units of highly reiterated African Green monkey DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):169–181. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig B., Wittig S. A phase relationship associates tRNA structural gene sequences with nucleosome cores. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1173–1183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. C., Strauss F., Varshavsky A. Nucleosome arrangement in green monkey alpha-satellite chromatin. Superimposition of non-random and apparently random patterns. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):93–117. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Fittler F., Hörz W. Eight different highly specific nucleosome phases on alpha-satellite DNA in the African green monkey. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4287–4306. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]