Abstract
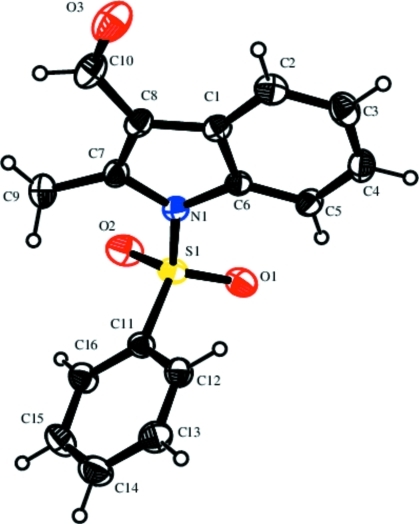
In the title compound, C16H13NO3S, the sulfonyl-bound phenyl ring forms a dihedral angle of 84.17 (6)° with the indole ring system. An intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond generates an S(6) ring motif. The crystal structure exhibits weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and π–π interactions between the five- and six-membered rings of the indole group [centroid–centroid distance = 3.6871 (9) Å].
Related literature
For the biological activities of indole compounds, see: Chai et al. (2006 ▶); Singh et al. (2000 ▶); Andreani et al. (2001 ▶). For related structures, see: Chakkaravarthi et al. (2007 ▶, 2008 ▶); Ramathilagam et al. (2011 ▶). For graph-set notation, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). 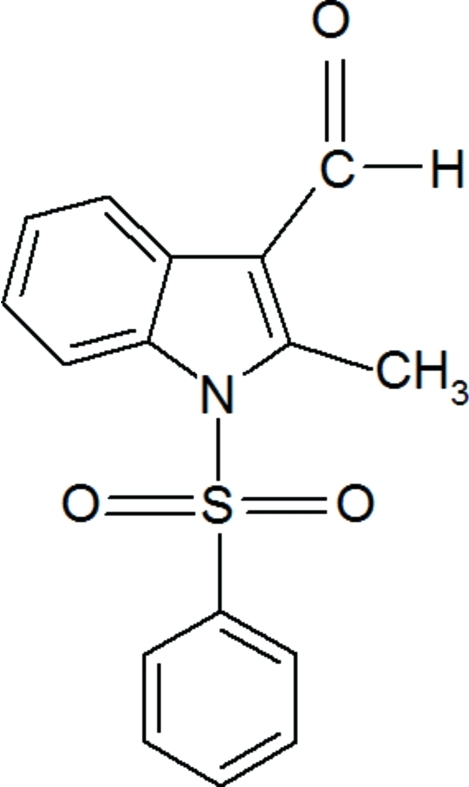
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H13NO3S
M r = 299.33
Monoclinic,
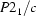
a = 11.6305 (5) Å
b = 8.4039 (4) Å
c = 14.3128 (8) Å
β = 93.126 (1)°
V = 1396.87 (12) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.22 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.949, T max = 0.958
18442 measured reflections
4242 independent reflections
3212 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.024
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.116
S = 1.06
4242 reflections
191 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035665/ci5199sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035665/ci5199Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035665/ci5199Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5—H5⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.28 | 2.8723 (19) | 121 |
| C12—H12⋯O3i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.1664 (19) | 131 |
| C16—H16⋯O2ii | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.388 (2) | 167 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 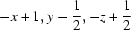 ; (ii)
; (ii) 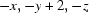 .
.
Acknowledgments
CR wishes to acknowledge AMET University management, India, for their kind support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Indole derivatives are found in many natural products and these derivatives exhibit antibacterial, antifungal (Singh et al., 2000) and antitumour activities (Andreani et al., 2001). In addition, certain indole derivatives exhibit anti-hepatitis B virus (Chai et al., 2006) activity.
The geometric parameters of the title molecule (Fig. 1) agree well with those observed in related structures (Chakkaravarthi et al., 2007, 2008; Ramathilagam et al., 2011). The dihedral angle between the benzene (C1–C6) and phenyl rings (C11–C16) is 83.81 (7)°. The sum of bond angles around N1 [359.9°] indicates sp2 hybridization.
The molecular structure is stabilized by a weak intramolecular C—H···O hydrogen bond and the crystal packing is stabilized by weak intermolecular C—H···O hydrogen bonds. The intramolecular C5—H5···O1 hydrogen bond generates an S(6) ring (Bernstein et al., 1995).
Experimental
2-Methylindole-3-carboxaldehyde (5 g, 31.4 mmol) was dissolved in distilled benzene (100 ml). To this benzenesulfonylchloride (6.6 g, 4.8 ml, 37.7 mmol) and 60% aqueous NAOH (32g in 53ml) were added along with tetrabutyl ammonium hydrogensulfate (1.0 g). This two phase system was stirred at room temperature for 2h. It was then diluted with water (200 ml) and the organic layer was separated. The aqueous layer was extracted with benzene (2× 30 ml) and the combined organic extracts were dried (Na2SO4). The solvent was removed completely and the crude product was recrystallized from methanol (m.p 431–433 K).
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using riding model, with d(C–H) = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic C–H and d(C–H) = 0.96 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl C–H.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labels and 30% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Crystal data
| C16H13NO3S | F(000) = 624 |
| Mr = 299.33 | Dx = 1.423 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2Ybc | Cell parameters from 4242 reflections |
| a = 11.6305 (5) Å | θ = 2.8–30.5° |
| b = 8.4039 (4) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| c = 14.3128 (8) Å | T = 295 K |
| β = 93.126 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1396.87 (12) Å3 | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4242 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3212 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.024 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 30.5°, θmin = 2.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −8→16 |
| Tmin = 0.949, Tmax = 0.958 | k = −11→11 |
| 18442 measured reflections | l = −20→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.116 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.051P)2 + 0.3293P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4242 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 191 parameters | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.51033 (11) | 1.03657 (16) | 0.11957 (9) | 0.0372 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.62740 (13) | 1.0134 (2) | 0.14228 (11) | 0.0488 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.6794 | 1.0968 | 0.1382 | 0.059* | |
| C3 | 0.66431 (13) | 0.8654 (2) | 0.17072 (12) | 0.0541 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.7420 | 0.8486 | 0.1863 | 0.065* | |
| C4 | 0.58737 (14) | 0.7403 (2) | 0.17652 (11) | 0.0509 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.6148 | 0.6412 | 0.1961 | 0.061* | |
| C5 | 0.47145 (13) | 0.75842 (17) | 0.15415 (10) | 0.0442 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.4203 | 0.6739 | 0.1581 | 0.053* | |
| C6 | 0.43434 (11) | 0.90840 (16) | 0.12546 (9) | 0.0356 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.33085 (13) | 1.12984 (17) | 0.07792 (10) | 0.0429 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.44359 (12) | 1.17348 (17) | 0.08955 (9) | 0.0412 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.22868 (16) | 1.2312 (2) | 0.05301 (14) | 0.0655 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.2527 | 1.3399 | 0.0472 | 0.098* | |
| H9B | 0.1747 | 1.2233 | 0.1012 | 0.098* | |
| H9C | 0.1929 | 1.1958 | −0.0053 | 0.098* | |
| C10 | 0.48781 (17) | 1.3321 (2) | 0.07368 (12) | 0.0559 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.4355 | 1.4109 | 0.0545 | 0.067* | |
| C11 | 0.13200 (11) | 0.92243 (17) | 0.19354 (9) | 0.0395 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.18938 (12) | 0.90248 (19) | 0.27999 (10) | 0.0457 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.2640 | 0.8624 | 0.2845 | 0.055* | |
| C13 | 0.13415 (16) | 0.9431 (2) | 0.35933 (11) | 0.0569 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.1717 | 0.9313 | 0.4180 | 0.068* | |
| C14 | 0.02338 (16) | 1.0010 (2) | 0.35188 (13) | 0.0624 (4) | |
| H14 | −0.0138 | 1.0270 | 0.4058 | 0.075* | |
| C15 | −0.03304 (14) | 1.0211 (2) | 0.26584 (13) | 0.0613 (4) | |
| H15 | −0.1078 | 1.0608 | 0.2618 | 0.074* | |
| C16 | 0.02108 (12) | 0.9824 (2) | 0.18524 (11) | 0.0516 (4) | |
| H16 | −0.0163 | 0.9964 | 0.1267 | 0.062* | |
| N1 | 0.32271 (9) | 0.96653 (14) | 0.09734 (8) | 0.0411 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.23308 (10) | 0.69878 (14) | 0.10309 (9) | 0.0575 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.13304 (10) | 0.91043 (19) | 0.01249 (8) | 0.0667 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.58819 (13) | 1.36833 (15) | 0.08380 (10) | 0.0742 (4) | |
| S1 | 0.20015 (3) | 0.86138 (5) | 0.09314 (2) | 0.04468 (12) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0448 (6) | 0.0379 (7) | 0.0289 (6) | −0.0030 (5) | 0.0030 (5) | −0.0032 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0440 (7) | 0.0547 (9) | 0.0472 (8) | −0.0074 (6) | −0.0017 (6) | −0.0046 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0436 (7) | 0.0656 (11) | 0.0522 (9) | 0.0079 (7) | −0.0060 (6) | −0.0027 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0571 (8) | 0.0483 (9) | 0.0471 (8) | 0.0133 (7) | 0.0004 (6) | 0.0037 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0496 (7) | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0446 (7) | 0.0006 (6) | 0.0056 (6) | 0.0048 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0385 (6) | 0.0379 (7) | 0.0307 (6) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0045 (5) | 0.0004 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0510 (7) | 0.0415 (7) | 0.0364 (7) | 0.0070 (6) | 0.0045 (6) | 0.0049 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0537 (8) | 0.0364 (7) | 0.0336 (6) | −0.0022 (6) | 0.0026 (5) | −0.0003 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0608 (10) | 0.0607 (11) | 0.0750 (12) | 0.0181 (8) | 0.0052 (9) | 0.0158 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0760 (11) | 0.0397 (8) | 0.0511 (9) | −0.0074 (7) | −0.0044 (8) | 0.0027 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0338 (6) | 0.0439 (7) | 0.0407 (7) | −0.0018 (5) | 0.0020 (5) | 0.0007 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0411 (7) | 0.0510 (8) | 0.0445 (8) | 0.0027 (6) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0027 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0653 (10) | 0.0651 (11) | 0.0400 (8) | 0.0036 (8) | 0.0012 (7) | 0.0007 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0630 (10) | 0.0713 (12) | 0.0545 (10) | 0.0056 (9) | 0.0169 (8) | −0.0067 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0439 (8) | 0.0717 (12) | 0.0690 (11) | 0.0132 (8) | 0.0091 (7) | −0.0060 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0385 (7) | 0.0648 (10) | 0.0508 (8) | 0.0050 (6) | −0.0042 (6) | 0.0012 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0372 (5) | 0.0421 (7) | 0.0442 (6) | −0.0003 (4) | 0.0050 (4) | 0.0063 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0532 (6) | 0.0470 (6) | 0.0737 (8) | −0.0101 (5) | 0.0156 (5) | −0.0129 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0536 (6) | 0.1042 (11) | 0.0411 (6) | −0.0050 (7) | −0.0075 (5) | −0.0038 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0809 (9) | 0.0546 (8) | 0.0847 (10) | −0.0268 (7) | −0.0179 (7) | 0.0078 (7) |
| S1 | 0.03861 (17) | 0.0548 (2) | 0.0407 (2) | −0.00535 (14) | 0.00263 (13) | −0.00445 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.3962 (19) | C9—H9C | 0.96 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3988 (18) | C10—O3 | 1.207 (2) |
| C1—C8 | 1.4404 (19) | C10—H10 | 0.93 |
| C2—C3 | 1.370 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.3835 (19) |
| C2—H2 | 0.93 | C11—C16 | 1.3841 (19) |
| C3—C4 | 1.386 (2) | C11—S1 | 1.7552 (14) |
| C3—H3 | 0.93 | C12—C13 | 1.378 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.377 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.93 |
| C4—H4 | 0.93 | C13—C14 | 1.376 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3871 (19) | C13—H13 | 0.93 |
| C5—H5 | 0.93 | C14—C15 | 1.374 (3) |
| C6—N1 | 1.4246 (16) | C14—H14 | 0.93 |
| C7—C8 | 1.363 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.383 (2) |
| C7—N1 | 1.4046 (19) | C15—H15 | 0.93 |
| C7—C9 | 1.490 (2) | C16—H16 | 0.93 |
| C8—C10 | 1.451 (2) | N1—S1 | 1.6753 (12) |
| C9—H9A | 0.96 | O1—S1 | 1.4242 (13) |
| C9—H9B | 0.96 | O2—S1 | 1.4190 (12) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.32 (13) | O3—C10—C8 | 124.15 (17) |
| C2—C1—C8 | 133.15 (13) | O3—C10—H10 | 117.9 |
| C6—C1—C8 | 107.53 (12) | C8—C10—H10 | 117.9 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.80 (14) | C12—C11—C16 | 121.52 (13) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.6 | C12—C11—S1 | 118.64 (10) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.6 | C16—C11—S1 | 119.77 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.88 (14) | C13—C12—C11 | 118.90 (14) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C13—C12—H12 | 120.6 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.6 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.96 (15) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.02 (15) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.0 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.0 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 117.02 (14) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.82 (15) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 121.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 121.5 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 122.02 (12) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.14 (15) |
| C5—C6—N1 | 131.25 (12) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C1—C6—N1 | 106.74 (12) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C8—C7—N1 | 108.28 (12) | C15—C16—C11 | 118.59 (14) |
| C8—C7—C9 | 128.68 (14) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.7 |
| N1—C7—C9 | 123.01 (14) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.7 |
| C7—C8—C1 | 108.71 (12) | C7—N1—C6 | 108.71 (11) |
| C7—C8—C10 | 125.09 (14) | C7—N1—S1 | 125.08 (10) |
| C1—C8—C10 | 126.20 (14) | C6—N1—S1 | 126.14 (10) |
| C7—C9—H9A | 109.5 | O2—S1—O1 | 119.54 (8) |
| C7—C9—H9B | 109.5 | O2—S1—N1 | 107.77 (7) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 | O1—S1—N1 | 106.19 (6) |
| C7—C9—H9C | 109.5 | O2—S1—C11 | 109.16 (7) |
| H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 | O1—S1—C11 | 109.24 (7) |
| H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 | N1—S1—C11 | 103.76 (6) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.2 (3) |
| C8—C1—C2—C3 | 178.78 (15) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.3 (2) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (2) | S1—C11—C16—C15 | 176.34 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.1 (2) | C8—C7—N1—C6 | 2.23 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.2 (2) | C9—C7—N1—C6 | −175.57 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 179.63 (14) | C8—C7—N1—S1 | 179.33 (10) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.6 (2) | C9—C7—N1—S1 | 1.5 (2) |
| C8—C1—C6—C5 | −178.94 (12) | C5—C6—N1—C7 | 178.03 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6—N1 | −179.26 (12) | C1—C6—N1—C7 | −2.08 (14) |
| C8—C1—C6—N1 | 1.17 (14) | C5—C6—N1—S1 | 1.0 (2) |
| N1—C7—C8—C1 | −1.48 (16) | C1—C6—N1—S1 | −179.15 (9) |
| C9—C7—C8—C1 | 176.15 (15) | C7—N1—S1—O2 | 41.89 (14) |
| N1—C7—C8—C10 | 178.30 (13) | C6—N1—S1—O2 | −141.51 (11) |
| C9—C7—C8—C10 | −4.1 (3) | C7—N1—S1—O1 | 171.10 (11) |
| C2—C1—C8—C7 | −179.31 (15) | C6—N1—S1—O1 | −12.30 (13) |
| C6—C1—C8—C7 | 0.18 (15) | C7—N1—S1—C11 | −73.79 (13) |
| C2—C1—C8—C10 | 0.9 (2) | C6—N1—S1—C11 | 102.82 (12) |
| C6—C1—C8—C10 | −179.60 (13) | C12—C11—S1—O2 | −172.81 (12) |
| C7—C8—C10—O3 | −179.51 (16) | C16—C11—S1—O2 | 10.03 (16) |
| C1—C8—C10—O3 | 0.2 (3) | C12—C11—S1—O1 | 54.80 (13) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.2 (2) | C16—C11—S1—O1 | −122.36 (13) |
| S1—C11—C12—C13 | −176.90 (13) | C12—C11—S1—N1 | −58.13 (13) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.6 (3) | C16—C11—S1—N1 | 124.72 (13) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.8 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5—H5···O1 | 0.93 | 2.28 | 2.8723 (19) | 121 |
| C12—H12···O3i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.1664 (19) | 131 |
| C16—H16···O2ii | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.388 (2) | 167 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x, −y+2, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CI5199).
References
- Andreani, A., Granaiola, M., Leoni, A., Locatelli, A., Morigi, R., Rambaldi, M., Giorgi, G., Salvini, L. & Garaliene, V. (2001). Anti-Cancer Drug Des. 16, 167–174. [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chai, H., Zhao, C. & Gong, P. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14, 911–917. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chakkaravarthi, G., Dhayalan, V., Mohanakrishnan, A. K. & Manivannan, V. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Chakkaravarthi, G., Ramesh, N., Mohanakrishnan, A. K. & Manivannan, V. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3564.
- Ramathilagam, C., Saravanan, V., Mohanakrishnan, A. K., Chakkaravarthi, G., Umarani, P. R. & Manivannan, V. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singh, U. P., Sarma, B. K., Mishra, P. K. & Ray, A. B. (2000). Folia Microbiol. (Prague), 45, 173–176. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035665/ci5199sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035665/ci5199Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035665/ci5199Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report