Abstract
Three polymorphs of the title compound, C15H12N2O2, were obtained accidentally as single crystals in the hydrothermal reaction of the title compound with manganese bromide in the presence of N,N′-dimethylformamide at 373 K. Here we report the structure of the first polymorph. The benzimidazole ring is almost planar, the maximum deviation from the mean plane being 0.016 (1) Å. The benzimidazole and benzene rings are approximately perpendicular, making a dihedral angle 85.56 (7)°, which is a reflection of the axial rotation of the flexible benzimidazolyl arm. In the crystal, adjacent molecules are connected through O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds into a chain along [100], and neighboring chains are further linked by via weak C—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding interactions, forming a two-dimensional network.
Related literature
For two other polymorphs of the title compound, see Kuai & Cheng (2011a
▶,b
▶). For the synthesis of 4-[(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzoic acid, see: Hua et al. (2010 ▶). For background to metal-organic hybrid materials, see: Das & Bharadwaj (2009 ▶); Kuai et al. (2011 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H12N2O2
M r = 252.27
Monoclinic,

a = 10.435 (2) Å
b = 14.360 (3) Å
c = 8.2922 (17) Å
β = 96.925 (3)°
V = 1233.5 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.20 × 0.20 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.982, T max = 0.985
6155 measured reflections
2157 independent reflections
1294 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.065
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.082
S = 0.82
2157 reflections
160 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1998 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039043/aa2023sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039043/aa2023Isup2.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039043/aa2023Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039043/aa2023Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H12⋯N12i | 0.82 | 1.83 | 2.652 (2) | 178 |
| C12—H7⋯O2ii | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.213 (3) | 135 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (BK2008195) for financial support of this work.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
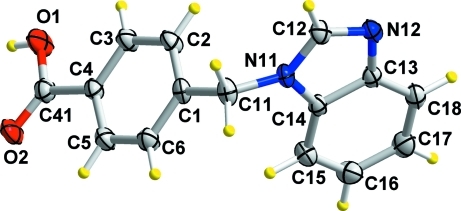
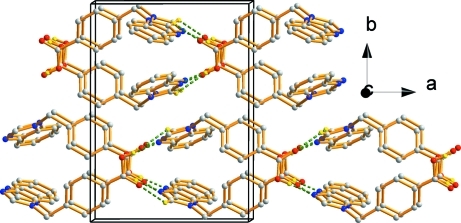
The title compound, 4-((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoic acid (HL), are usually regarded as an excellent candidate for building block in molecular self-assembly engineerings due to its variable conformations and coordination modes (Das et al., 2009). During assemblies of coordination polymers, we accidentally obtained three different kind of single crystals of the title compound, which can be proved by different unit cell parameters (or space group). Here, we will introduce one of them. The single crystals of the title compound, C15H12N2O2, were accidentally obtained by the hydrothermal reaction at 373 K of the HL with manganese bromide in the presence of N,N'-dimethylformamide as alkaline medium for the deprotonation. As shown in Fig. 1, the asymmetric unit consists of only one HL molecule. Interestingly, though crystallizing from alkaline solution, the HL remains the intact carboxylic group in the crystal structure. The flexible benzimidazolyl arm is apt to axially rotate. as a result, the benzimidazolyl ring and central benzene rings are approximately vertical, inclined at a dihedral angle of 85.56 (6) °; The torsion angles of N11-C11-C1-C2 and N11-C11-C1-C6 are -56.9 (3) ° and 125.4 (2) °, respectively. Adjacent molecules are connected through O-H···N hydrogen bonds into a one-dimensional chain along [100] deirction, and neighboring chains are further linked via C-H···O weak hydrogen bonding interaction to form a two-dimensional network (Fig. 2).
Experimental
Reaction mixture of MnBr2 (21.5 mg, 0.1 mmol), 4-((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoic acid (25.2 mg, 0.1 mmol) and 2 ml N,N'-dimethylformamide (DMF) in 8 ml H2O were sealed in a 16 ml Teflon-lined stainless steel container and keeped at 373 K for 3 days. After cooling to the room temperature, colourless block crystals of the title compound were obtained.
Refinement
All hydrogen atoms were located in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.93 and 0.97 Å, O—H = 0.82 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C, O).
Figures
Fig. 1.
: The crystal structure of the title compound showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
: The packing diagram of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C15H12N2O2 | F(000) = 528 |
| Mr = 252.27 | Dx = 1.358 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 961 reflections |
| a = 10.435 (2) Å | θ = 2.8–20.1° |
| b = 14.360 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 8.2922 (17) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 96.925 (3)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1233.5 (4) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.16 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 2157 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1294 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.065 |
| phi and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.982, Tmax = 0.985 | k = −17→14 |
| 6155 measured reflections | l = −9→9 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.082 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.82 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0242P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2157 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 160 parameters | Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N11 | 0.62238 (13) | 0.42913 (9) | 0.16767 (19) | 0.0384 (4) | |
| N12 | 0.43462 (14) | 0.36669 (10) | 0.06416 (19) | 0.043 | |
| O2 | 1.30575 (12) | 0.33153 (9) | 0.43647 (18) | 0.062 | |
| O1 | 1.19958 (12) | 0.20370 (10) | 0.49287 (19) | 0.0694 (5) | |
| H12 | 1.2729 | 0.1834 | 0.5165 | 0.083* | |
| C14 | 0.63655 (16) | 0.40473 (11) | 0.0100 (2) | 0.0362 (5) | |
| C4 | 1.07691 (16) | 0.33415 (13) | 0.3955 (2) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.73758 (18) | 0.41493 (12) | −0.0828 (3) | 0.0479 (5) | |
| H8 | 0.8156 | 0.4417 | −0.0406 | 0.057* | |
| C13 | 0.51859 (17) | 0.36548 (12) | −0.0533 (2) | 0.0383 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.84621 (17) | 0.33703 (13) | 0.3785 (2) | 0.0473 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.7693 | 0.3075 | 0.3939 | 0.057* | |
| C11 | 0.71733 (16) | 0.47882 (13) | 0.2797 (2) | 0.0469 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.6815 | 0.4900 | 0.3806 | 0.056* | |
| H5 | 0.7347 | 0.5388 | 0.2333 | 0.056* | |
| C1 | 0.84294 (16) | 0.42581 (13) | 0.3160 (2) | 0.0402 (5) | |
| C41 | 1.20563 (18) | 0.28995 (15) | 0.4421 (2) | 0.0468 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.50053 (17) | 0.40470 (12) | 0.1920 (2) | 0.0445 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.4671 | 0.4140 | 0.2898 | 0.053* | |
| C5 | 1.07310 (18) | 0.42162 (14) | 0.3297 (3) | 0.0515 (6) | |
| H3 | 1.1497 | 0.4503 | 0.3106 | 0.062* | |
| C18 | 0.49941 (19) | 0.33416 (13) | −0.2123 (3) | 0.0488 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.4214 | 0.3075 | −0.2550 | 0.059* | |
| C6 | 0.95772 (18) | 0.46810 (14) | 0.2912 (3) | 0.0523 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.9573 | 0.5280 | 0.2484 | 0.063* | |
| C17 | 0.5994 (2) | 0.34376 (13) | −0.3053 (3) | 0.0563 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.5888 | 0.3235 | −0.4126 | 0.068* | |
| C3 | 0.96226 (17) | 0.29079 (13) | 0.4188 (2) | 0.0506 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.9630 | 0.2309 | 0.4614 | 0.061* | |
| C16 | 0.7167 (2) | 0.38356 (13) | −0.2405 (3) | 0.0557 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.7827 | 0.3890 | −0.3060 | 0.067* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N11 | 0.0279 (9) | 0.0422 (10) | 0.0433 (11) | 0.0015 (7) | −0.0023 (8) | −0.0023 (8) |
| N12 | 0.032 | 0.044 | 0.053 | −0.002 | −0.001 | −0.001 |
| O2 | 0.029 | 0.070 | 0.085 | −0.006 | 0.001 | 0.011 |
| O1 | 0.0326 (8) | 0.0644 (11) | 0.1098 (14) | 0.0077 (7) | 0.0023 (8) | 0.0228 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0324 (11) | 0.0324 (11) | 0.0427 (13) | 0.0008 (8) | −0.0007 (9) | 0.0012 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0299 (11) | 0.0493 (13) | 0.0418 (13) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0014 (9) | 0.0007 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0392 (12) | 0.0494 (13) | 0.0543 (15) | −0.0065 (10) | 0.0027 (11) | −0.0049 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0350 (11) | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0474 (13) | 0.0020 (8) | −0.0033 (10) | 0.0027 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0282 (11) | 0.0524 (14) | 0.0612 (15) | −0.0028 (9) | 0.0046 (10) | −0.0005 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0361 (12) | 0.0481 (13) | 0.0539 (14) | 0.0039 (9) | −0.0054 (10) | −0.0101 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0323 (11) | 0.0425 (13) | 0.0435 (13) | 0.0008 (9) | −0.0046 (9) | −0.0076 (10) |
| C41 | 0.0355 (12) | 0.0548 (14) | 0.0494 (14) | 0.0029 (10) | 0.0021 (10) | 0.0018 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0339 (11) | 0.0472 (12) | 0.0523 (14) | 0.0060 (9) | 0.0048 (10) | 0.0027 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0338 (12) | 0.0566 (14) | 0.0634 (15) | −0.0062 (10) | 0.0022 (11) | 0.0068 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0425 (12) | 0.0451 (13) | 0.0553 (15) | −0.0032 (10) | −0.0078 (11) | −0.0021 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0415 (13) | 0.0460 (13) | 0.0668 (16) | −0.0013 (10) | −0.0032 (11) | 0.0092 (11) |
| C17 | 0.0699 (16) | 0.0486 (14) | 0.0492 (15) | −0.0045 (11) | 0.0024 (13) | −0.0046 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0354 (12) | 0.0473 (13) | 0.0683 (16) | 0.0006 (10) | 0.0035 (11) | 0.0103 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0605 (15) | 0.0514 (14) | 0.0574 (16) | −0.0101 (11) | 0.0164 (13) | −0.0028 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N11—C12 | 1.357 (2) | C2—C3 | 1.386 (2) |
| N11—C14 | 1.379 (2) | C2—H1 | 0.9300 |
| N11—C11 | 1.460 (2) | C11—C1 | 1.514 (2) |
| N12—C12 | 1.311 (2) | C11—H6 | 0.9700 |
| N12—C13 | 1.387 (2) | C11—H5 | 0.9700 |
| O2—C41 | 1.209 (2) | C1—C6 | 1.380 (2) |
| O1—C41 | 1.312 (2) | C12—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O1—H12 | 0.8200 | C5—C6 | 1.380 (2) |
| C14—C15 | 1.386 (2) | C5—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C14—C13 | 1.397 (2) | C18—C17 | 1.377 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.368 (2) | C18—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C3 | 1.383 (2) | C6—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C41 | 1.494 (2) | C17—C16 | 1.398 (3) |
| C15—C16 | 1.375 (3) | C17—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C15—H8 | 0.9300 | C3—H2 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C18 | 1.384 (3) | C16—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C1 | 1.375 (2) | ||
| C12—N11—C14 | 106.55 (15) | C2—C1—C11 | 121.50 (16) |
| C12—N11—C11 | 127.41 (16) | C6—C1—C11 | 119.67 (18) |
| C14—N11—C11 | 125.84 (15) | O2—C41—O1 | 123.63 (18) |
| C12—N12—C13 | 105.01 (15) | O2—C41—C4 | 122.30 (19) |
| C41—O1—H12 | 109.5 | O1—C41—C4 | 114.05 (16) |
| N11—C14—C15 | 132.49 (17) | N12—C12—N11 | 113.38 (17) |
| N11—C14—C13 | 105.55 (15) | N12—C12—H7 | 123.3 |
| C15—C14—C13 | 121.93 (18) | N11—C12—H7 | 123.3 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.02 (17) | C4—C5—C6 | 121.26 (17) |
| C5—C4—C41 | 118.38 (17) | C4—C5—H3 | 119.4 |
| C3—C4—C41 | 122.59 (18) | C6—C5—H3 | 119.4 |
| C16—C15—C14 | 116.72 (19) | C17—C18—C13 | 117.92 (19) |
| C16—C15—H8 | 121.6 | C17—C18—H11 | 121.0 |
| C14—C15—H8 | 121.6 | C13—C18—H11 | 121.0 |
| C18—C13—N12 | 129.94 (18) | C5—C6—C1 | 120.08 (19) |
| C18—C13—C14 | 120.54 (18) | C5—C6—H4 | 120.0 |
| N12—C13—C14 | 109.51 (17) | C1—C6—H4 | 120.0 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 121.09 (17) | C18—C17—C16 | 120.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—H1 | 119.5 | C18—C17—H10 | 119.6 |
| C3—C2—H1 | 119.5 | C16—C17—H10 | 119.6 |
| N11—C11—C1 | 112.67 (15) | C4—C3—C2 | 119.73 (18) |
| N11—C11—H6 | 109.1 | C4—C3—H2 | 120.1 |
| C1—C11—H6 | 109.1 | C2—C3—H2 | 120.1 |
| N11—C11—H5 | 109.1 | C15—C16—C17 | 121.99 (19) |
| C1—C11—H5 | 109.1 | C15—C16—H9 | 119.0 |
| H6—C11—H5 | 107.8 | C17—C16—H9 | 119.0 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.79 (17) | ||
| C12—N11—C14—C15 | 178.01 (19) | C3—C4—C41—O2 | −172.53 (19) |
| C11—N11—C14—C15 | 2.8 (3) | C5—C4—C41—O1 | −175.23 (18) |
| C12—N11—C14—C13 | −0.18 (18) | C3—C4—C41—O1 | 5.9 (3) |
| C11—N11—C14—C13 | −175.40 (16) | C13—N12—C12—N11 | 0.2 (2) |
| N11—C14—C15—C16 | −178.63 (19) | C14—N11—C12—N12 | 0.0 (2) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.7 (3) | C11—N11—C12—N12 | 175.12 (17) |
| C12—N12—C13—C18 | −179.09 (19) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.0 (3) |
| C12—N12—C13—C14 | −0.3 (2) | C41—C4—C5—C6 | −176.89 (19) |
| N11—C14—C13—C18 | 179.22 (16) | N12—C13—C18—C17 | 178.11 (18) |
| C15—C14—C13—C18 | 0.8 (3) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | −0.6 (3) |
| N11—C14—C13—N12 | 0.3 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.2 (3) |
| C15—C14—C13—N12 | −178.13 (16) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.4 (3) |
| C12—N11—C11—C1 | 124.04 (18) | C11—C1—C6—C5 | 177.53 (19) |
| C14—N11—C11—C1 | −61.7 (2) | C13—C18—C17—C16 | 0.3 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1—C6 | 1.1 (3) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | −1.3 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1—C11 | −176.76 (18) | C41—C4—C3—C2 | 177.59 (18) |
| N11—C11—C1—C2 | −56.8 (2) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.3 (3) |
| N11—C11—C1—C6 | 125.34 (19) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.4 (3) |
| C5—C4—C41—O2 | 6.3 (3) | C18—C17—C16—C15 | −0.2 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H12···N12i | 0.82 | 1.83 | 2.652 (2) | 178. |
| C12—H7···O2ii | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.213 (3) | 135. |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: AA2023).
References
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Das, M. C. & Bharadwaj, P. K. (2009). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 10942–10943. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hua, Q., Zhao, Y., Xu, G.-C., Chen, M.-S., Su, Z., Cai, K. & Sun, W.-Y. (2010). Cryst. Growth Des. 10, 2553–2562.
- Kuai, H.-W. & Cheng, X.-C. (2011a). Acta Cryst. E67, submitted (AA2024). [Google Scholar]
- Kuai, H.-W. & Cheng, X.-C. (2011b). Acta Cryst. E67, submitted (AA2025). [Google Scholar]
- Kuai, H.-W., Cheng, X.-C. & Zhu, X.-H. (2011). J. Coord. Chem. 64, 1636–1644.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039043/aa2023sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039043/aa2023Isup2.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039043/aa2023Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039043/aa2023Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report