Abstract
The six-membered heterocycle in the title compound, C18H16BrN3O4S, adopts a sofa conformation. Intramolecular N—H⋯N and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds stabilize the molecular conformation by forming a five- and a six-membered ring, respectively. The crystal packing is stabilized by intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For general background, see: Zia-ur-Rehman et al. (2009 ▶). For synthesis details, see: Ahmad et al. (2011 ▶). For graph-set notation of hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H16BrN3O4S
M r = 450.31
Monoclinic,
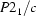
a = 14.692 (2) Å
b = 16.562 (2) Å
c = 7.5254 (10) Å
β = 104.820 (1)°
V = 1770.2 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.47 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.48 × 0.36 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Siemens SMART diffractometer equipped with a Bruker KappaCCD APEXII
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001 ▶) T min = 0.383, T max = 0.773
21408 measured reflections
4490 independent reflections
3600 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.034
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.070
S = 1.03
4490 reflections
292 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2001 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and X-SEED (Barbour, 2001 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035641/bt5633sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035641/bt5633Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035641/bt5633Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C17—H17C⋯O2i | 0.95 (3) | 2.38 (3) | 3.275 (2) | 158 (2) |
| C17—H17A⋯O4ii | 0.95 (3) | 2.54 (3) | 3.479 (2) | 171 (2) |
| N2—H2N⋯N1 | 0.84 (3) | 2.24 (3) | 2.690 (2) | 114 (2) |
| O1—H1O⋯O4 | 0.82 (3) | 1.86 (3) | 2.5979 (18) | 148 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 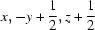 ; (ii)
; (ii) 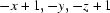 .
.
Acknowledgments
NA is grateful to the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan for the award of an HEC indigenous scholarship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In continuation of our on-going research on various biologically active benzothiazine derivatives (Zia-ur-Rehman et al., 2009; Ahmad et al., 2011) synthesis and crystal structure of the title molecule (I) is reported here.
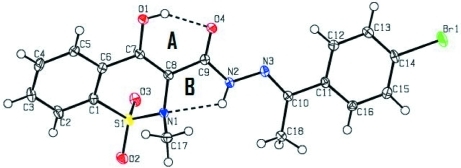
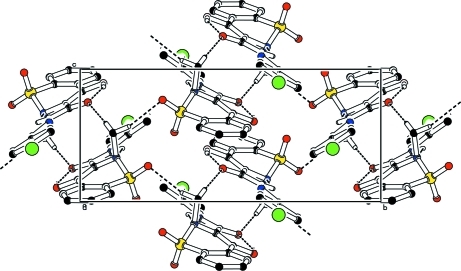
In the crystal structure of the title compound (I), two fused rings (benzene & thiazine) are twisted with a dihedral angle of 13.61 (10)° while the later (C1/C6/C7/C8/N1/S1) adopts half chair conformation [Nitrogen (0.3564 (10)Å and sulfur (-0.3114 (9) Å) atoms show maximum deviation from the least square plane]. The bromophenyl ring (C11—C16) is oriented almost at the same dihedral angle that measures 27.93 (7)° and 26.23 (8)° with respect to the thiazine and aromatic ring (C1—C6). Intramolecular hydrogen bonding through O—H···O and N—H···N interactions gives rise to two different rings S11(6) A and S11(5) B respectively (Figure 1). Rings generated from intramolecular hydrogen bondings are fused and twisted at dihedral angle of 5.01 (82)Å and both are inclined at 22.00 (47)Å and 18.83 (27)Å with respect to the thiazine ring. Molecules of the title compound (I) are involved in symmetry related C—H···O weak interactions which form inversion dimers and give rise to the formation of a twelve membered ring R22(12) (Bernstein et al., 1995). The dimers are further linked through another C—H···O interaction generating from N-methyl hydrogen and sulfone oxygen atoms giving rise to two dimensional polymeric network along bc plane (Figure 2., Table 1).
Experimental
A mixture of 4-hydroxy-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-3-carbohydrazide 1,1-dioxide (2.0 mmol), 4-bromo acetophenone (2.0 mmol), ortho phosphoric acid (2 drops) and methanol (50 ml) was refluxed for a period of seven hours. The content was cooled to 5°C in an ice bath, filtered and the solids were washed with cold methanol to get the pure compound. The product was crystallized from ethanol to get the suitable crystals. Yield: 82%.
Refinement
The coordinates of all H atoms were refined with U(H) set to 1.2Ueq for all N and aromatic C atoms and 1.5Ueq for O and Cmethyl.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The title molecule with the displacement ellipsoids plotted at 50% probability level (Farrugia, 1999).
Fig. 2.
The unit cell packing of the title compound; H bonds have been plotted with dashed lines and H-atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds have been excluded for clarity.
Crystal data
| C18H16BrN3O4S | F(000) = 912 |
| Mr = 450.31 | Dx = 1.690 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 6699 reflections |
| a = 14.692 (2) Å | θ = 2.9–28.6° |
| b = 16.562 (2) Å | µ = 2.47 mm−1 |
| c = 7.5254 (10) Å | T = 173 K |
| β = 104.820 (1)° | Block, light yellow |
| V = 1770.2 (4) Å3 | 0.48 × 0.36 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Siemens SMART diffractometer equipped with a Bruker KappaCCD APEXII | 4490 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3600 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.034 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.9°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001) | h = −19→19 |
| Tmin = 0.383, Tmax = 0.773 | k = −22→22 |
| 21408 measured reflections | l = −10→10 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.070 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0314P)2 + 1.043P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4490 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 292 parameters | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.74833 (13) | 0.08528 (11) | 0.1120 (2) | 0.0143 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.83074 (14) | 0.10149 (12) | 0.0597 (3) | 0.0192 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.87895 (14) | 0.03747 (13) | 0.0071 (3) | 0.0214 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.84550 (14) | −0.04104 (12) | 0.0080 (3) | 0.0191 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.76259 (13) | −0.05643 (11) | 0.0574 (3) | 0.0153 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.71272 (12) | 0.00689 (11) | 0.1115 (2) | 0.0125 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.62439 (12) | −0.00730 (10) | 0.1649 (2) | 0.0118 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.58824 (12) | 0.04814 (10) | 0.2620 (2) | 0.0126 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.49476 (12) | 0.03746 (10) | 0.2936 (2) | 0.0122 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.35797 (12) | 0.15959 (11) | 0.5072 (2) | 0.0126 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.25982 (12) | 0.16068 (11) | 0.5279 (2) | 0.0127 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.19684 (13) | 0.09850 (11) | 0.4527 (2) | 0.0143 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.10540 (13) | 0.09808 (12) | 0.4725 (3) | 0.0171 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.07621 (12) | 0.16057 (12) | 0.5683 (3) | 0.0168 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.13608 (13) | 0.22345 (12) | 0.6414 (3) | 0.0166 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.22758 (13) | 0.22328 (11) | 0.6209 (2) | 0.0146 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.70484 (14) | 0.11010 (12) | 0.5184 (3) | 0.0177 (4) | |
| C18 | 0.42638 (14) | 0.22228 (12) | 0.6057 (3) | 0.0179 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.63983 (10) | 0.12026 (9) | 0.3325 (2) | 0.0127 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.46422 (11) | 0.10249 (9) | 0.3728 (2) | 0.0132 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.37590 (10) | 0.10297 (9) | 0.4031 (2) | 0.0134 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.58057 (9) | −0.07719 (8) | 0.10541 (17) | 0.0144 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.74855 (9) | 0.22587 (8) | 0.26881 (19) | 0.0195 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.60735 (9) | 0.18640 (8) | 0.02540 (19) | 0.0185 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.44888 (9) | −0.02546 (7) | 0.25045 (17) | 0.0147 (3) | |
| S1 | 0.68413 (3) | 0.16496 (3) | 0.17764 (6) | 0.01416 (10) | |
| Br1 | −0.047586 (14) | 0.160120 (14) | 0.60056 (3) | 0.02823 (7) | |
| H1O | 0.530 (2) | −0.0778 (16) | 0.134 (4) | 0.042* | |
| H2 | 0.8547 (18) | 0.1523 (15) | 0.064 (3) | 0.034* | |
| H2N | 0.5020 (19) | 0.1414 (16) | 0.401 (3) | 0.034* | |
| H3 | 0.9330 (18) | 0.0479 (15) | −0.028 (3) | 0.034* | |
| H4 | 0.8796 (18) | −0.0832 (15) | −0.022 (3) | 0.034* | |
| H5 | 0.7398 (17) | −0.1094 (15) | 0.056 (3) | 0.034* | |
| H12 | 0.2183 (17) | 0.0564 (15) | 0.385 (3) | 0.034* | |
| H13 | 0.0610 (17) | 0.0546 (16) | 0.420 (3) | 0.034* | |
| H15 | 0.1165 (17) | 0.2691 (15) | 0.707 (3) | 0.034* | |
| H16 | 0.2668 (18) | 0.2657 (15) | 0.667 (3) | 0.034* | |
| H17A | 0.6686 (19) | 0.0859 (16) | 0.592 (4) | 0.042* | |
| H17B | 0.758 (2) | 0.0739 (16) | 0.512 (4) | 0.042* | |
| H17C | 0.727 (2) | 0.1614 (16) | 0.566 (4) | 0.042* | |
| H18A | 0.488 (2) | 0.2076 (17) | 0.624 (4) | 0.042* | |
| H18B | 0.4183 (18) | 0.2313 (16) | 0.732 (4) | 0.042* | |
| H18C | 0.4163 (19) | 0.2714 (17) | 0.549 (4) | 0.042* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0125 (8) | 0.0151 (9) | 0.0161 (9) | 0.0036 (7) | 0.0051 (7) | 0.0024 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0163 (9) | 0.0179 (10) | 0.0260 (10) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0100 (8) | 0.0032 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0145 (9) | 0.0274 (11) | 0.0252 (11) | 0.0027 (8) | 0.0101 (8) | 0.0029 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0178 (10) | 0.0220 (10) | 0.0188 (10) | 0.0065 (8) | 0.0072 (8) | −0.0013 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0162 (9) | 0.0125 (9) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0039 (7) | −0.0005 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0124 (8) | 0.0136 (8) | 0.0109 (8) | 0.0026 (7) | 0.0021 (7) | 0.0014 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0115 (8) | 0.0113 (8) | 0.0120 (8) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0021 (7) | 0.0026 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0119 (8) | 0.0125 (8) | 0.0135 (9) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0032 (7) | 0.0011 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0131 (8) | 0.0140 (8) | 0.0093 (8) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0025 (6) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0143 (8) | 0.0110 (8) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0025 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0115 (8) | 0.0159 (9) | 0.0111 (8) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0034 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0151 (9) | 0.0131 (9) | 0.0148 (9) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0042 (7) | 0.0012 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0138 (9) | 0.0170 (9) | 0.0200 (10) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0035 (7) | 0.0005 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0099 (8) | 0.0218 (9) | 0.0196 (9) | 0.0012 (7) | 0.0055 (7) | 0.0039 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0168 (9) | 0.0188 (9) | 0.0152 (9) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0057 (7) | −0.0006 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0162 (9) | 0.0148 (9) | 0.0132 (9) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0045 (7) | −0.0004 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0179 (10) | 0.0177 (10) | 0.0171 (10) | −0.0017 (8) | 0.0036 (8) | −0.0016 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0153 (9) | 0.0185 (10) | 0.0211 (10) | −0.0032 (7) | 0.0067 (8) | −0.0036 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0127 (7) | 0.0103 (7) | 0.0166 (8) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0064 (6) | 0.0000 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0103 (7) | 0.0151 (8) | 0.0150 (8) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0045 (6) | −0.0001 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0114 (7) | 0.0164 (8) | 0.0132 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0042 (6) | 0.0024 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0136 (6) | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0163 (7) | −0.0016 (5) | 0.0043 (5) | −0.0008 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0179 (7) | 0.0126 (6) | 0.0297 (8) | −0.0017 (5) | 0.0093 (6) | 0.0000 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0167 (7) | 0.0239 (7) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0069 (6) | 0.0058 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0141 (6) | 0.0146 (6) | 0.0160 (6) | −0.0021 (5) | 0.0048 (5) | 0.0004 (5) |
| S1 | 0.0124 (2) | 0.0112 (2) | 0.0204 (2) | 0.00122 (16) | 0.00694 (17) | 0.00262 (17) |
| Br1 | 0.01334 (10) | 0.03465 (13) | 0.03960 (14) | 0.00017 (8) | 0.01204 (9) | −0.00172 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.392 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.389 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.399 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.96 (3) |
| C1—S1 | 1.7646 (18) | C13—C14 | 1.390 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.388 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.98 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.91 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.383 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.391 (3) | C14—Br1 | 1.8956 (18) |
| C3—H3 | 0.91 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.392 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.385 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.99 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.92 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.92 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.398 (2) | C17—N1 | 1.488 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.94 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.95 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.472 (2) | C17—H17B | 1.00 (3) |
| C7—O1 | 1.344 (2) | C17—H17C | 0.95 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.363 (2) | C18—H18A | 0.92 (3) |
| C8—N1 | 1.441 (2) | C18—H18B | 1.00 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.463 (2) | C18—H18C | 0.91 (3) |
| C9—O4 | 1.239 (2) | N1—S1 | 1.6488 (15) |
| C9—N2 | 1.361 (2) | N2—N3 | 1.374 (2) |
| C10—N3 | 1.291 (2) | N2—H2N | 0.84 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.490 (2) | O1—H1O | 0.82 (3) |
| C10—C18 | 1.502 (3) | O2—S1 | 1.4326 (14) |
| C11—C16 | 1.400 (3) | O3—S1 | 1.4318 (14) |
| C11—C12 | 1.403 (2) | ||
| C2—C1—C6 | 122.01 (17) | C12—C13—H13 | 121.4 (14) |
| C2—C1—S1 | 120.07 (14) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.5 (14) |
| C6—C1—S1 | 117.92 (13) | C15—C14—C13 | 121.17 (17) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.53 (18) | C15—C14—Br1 | 119.05 (14) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.8 (16) | C13—C14—Br1 | 119.79 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 121.6 (16) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.24 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.41 (18) | C14—C15—H15 | 122.6 (14) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 118.7 (16) | C16—C15—H15 | 118.2 (14) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.8 (16) | C15—C16—C11 | 121.13 (17) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.63 (18) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.1 (16) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 (15) | C11—C16—H16 | 119.7 (16) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.5 (15) | N1—C17—H17A | 106.1 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.16 (18) | N1—C17—H17B | 110.2 (15) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.3 (15) | H17A—C17—H17B | 110 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 (15) | N1—C17—H17C | 109.3 (16) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.24 (16) | H17A—C17—H17C | 110 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.59 (16) | H17B—C17—H17C | 111 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.17 (15) | C10—C18—H18A | 113.8 (17) |
| O1—C7—C8 | 122.64 (16) | C10—C18—H18B | 110.2 (15) |
| O1—C7—C6 | 115.28 (15) | H18A—C18—H18B | 105 (2) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 122.03 (16) | C10—C18—H18C | 112.1 (17) |
| C7—C8—N1 | 121.02 (15) | H18A—C18—H18C | 110 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 121.10 (16) | H18B—C18—H18C | 106 (2) |
| N1—C8—C9 | 117.86 (15) | C8—N1—C17 | 113.77 (14) |
| O4—C9—N2 | 124.22 (16) | C8—N1—S1 | 112.18 (12) |
| O4—C9—C8 | 121.97 (16) | C17—N1—S1 | 116.15 (12) |
| N2—C9—C8 | 113.81 (15) | C9—N2—N3 | 120.56 (15) |
| N3—C10—C11 | 115.16 (16) | C9—N2—H2N | 116.5 (18) |
| N3—C10—C18 | 125.93 (16) | N3—N2—H2N | 123.0 (18) |
| C11—C10—C18 | 118.91 (16) | C10—N3—N2 | 116.92 (15) |
| C16—C11—C12 | 118.21 (16) | C7—O1—H1O | 108.1 (19) |
| C16—C11—C10 | 121.45 (16) | O3—S1—O2 | 119.83 (8) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.34 (16) | O3—S1—N1 | 107.72 (8) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 121.10 (17) | O2—S1—N1 | 108.04 (8) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 120.6 (15) | O3—S1—C1 | 109.24 (9) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 118.3 (15) | O2—S1—C1 | 109.01 (8) |
| C12—C13—C14 | 119.14 (17) | N1—S1—C1 | 101.43 (8) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.5 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.1 (3) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.37 (15) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.4 (3) | C12—C13—C14—Br1 | −178.89 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.4 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.6 (3) | Br1—C14—C15—C16 | 178.84 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.7 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.99 (17) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 1.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.3 (3) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −179.30 (17) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.21 (13) | C7—C8—N1—C17 | −88.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −178.95 (17) | C9—C8—N1—C17 | 93.45 (19) |
| S1—C1—C6—C7 | −0.1 (2) | C7—C8—N1—S1 | 46.2 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | −19.8 (2) | C9—C8—N1—S1 | −132.15 (14) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | 159.41 (16) | O4—C9—N2—N3 | −2.8 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 162.47 (17) | C8—C9—N2—N3 | 176.94 (15) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −18.3 (3) | C11—C10—N3—N2 | 176.67 (14) |
| O1—C7—C8—N1 | 176.41 (15) | C18—C10—N3—N2 | −3.4 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—N1 | −6.1 (3) | C9—N2—N3—C10 | 167.98 (16) |
| O1—C7—C8—C9 | −5.3 (3) | C8—N1—S1—O3 | 60.35 (14) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 172.21 (16) | C17—N1—S1—O3 | −166.41 (13) |
| C7—C8—C9—O4 | 7.4 (3) | C8—N1—S1—O2 | −168.87 (12) |
| N1—C8—C9—O4 | −174.25 (15) | C17—N1—S1—O2 | −35.63 (15) |
| C7—C8—C9—N2 | −172.33 (16) | C8—N1—S1—C1 | −54.33 (13) |
| N1—C8—C9—N2 | 6.0 (2) | C17—N1—S1—C1 | 78.91 (14) |
| N3—C10—C11—C16 | −173.38 (16) | C2—C1—S1—O3 | 98.82 (17) |
| C18—C10—C11—C16 | 6.6 (3) | C6—C1—S1—O3 | −80.10 (16) |
| N3—C10—C11—C12 | 6.2 (2) | C2—C1—S1—O2 | −33.83 (18) |
| C18—C10—C11—C12 | −173.73 (17) | C6—C1—S1—O2 | 147.26 (14) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | −1.1 (3) | C2—C1—S1—N1 | −147.64 (16) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 179.26 (16) | C6—C1—S1—N1 | 33.45 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C17—H17C···O2i | 0.95 (3) | 2.38 (3) | 3.275 (2) | 158 (2) |
| C17—H17A···O4ii | 0.95 (3) | 2.54 (3) | 3.479 (2) | 171 (2) |
| N2—H2N···N1 | 0.84 (3) | 2.24 (3) | 2.690 (2) | 114 (2) |
| O1—H1O···O4 | 0.82 (3) | 1.86 (3) | 2.5979 (18) | 148 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5633).
References
- Ahmad, N., Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Siddiqui, H. L., Fasih Ullah, M. & Pervez, M. (2011). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46, 2368–2377. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Barbour, L. J. (2001). J. Supramol. Chem pp. 189–191.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2001). SADABS, APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Choudary, J. A., Elsegood, M. R. J., Siddiqui, H. L. & Khan, K. M. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 1311–1316. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035641/bt5633sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035641/bt5633Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811035641/bt5633Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report