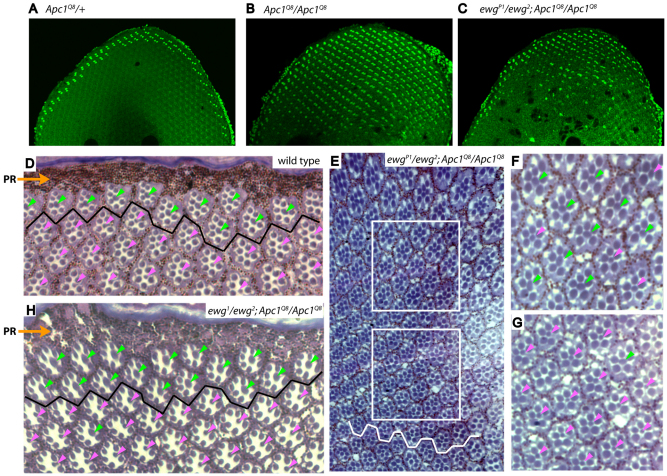
Fig. 2.
Ewg is required for aberrant photoreceptor cell fate specification in response to Apc1 loss. (A-H) Confocal images of 35-40 hour pupal retinas stained with Homothorax (Hth) antiserum (A-C) and cross-sections through adult retinas (D-H). In all panels, dorsal is towards the top. (A,D) In wild-type and Apc1 heterozygous retinas, inner photoreceptors (PRs) with DRA fate are restricted to one or two rows of ommatidia at dorsal retinal periphery, as indicated by Hth staining in pupae (A) and enlarged rhabdomeres located close to pigment rim (PR) in adults (D, ommatidia above black line, green arrowheads). (B) In Apc1Q8 mutants, constitutive activation of Wingless signaling induces all inner PRs in entire dorsal retinal half to aberrantly express Hth. (C,E-G) In ewgP1/ewg2; Apc1Q8 double mutants, partial reduction of Ewg activity leads to a reduction in the number of inner PRs expressing Hth and displaying enlarged rhabdomeres, which is most evident near dorsal-ventral equator (C,E). Higher magnifications of the upper and lower boxed areas in E are shown in F and G, respectively. Inner PRs closer to retinal dorsal edge mostly retain DRA fate, as indicated by enlarged rhabdomeres (green arrowheads in F); ommatidia closest to equator (white jagged line in E) mostly adopt a normal cell fate, as indicated by small rhabdomeres (pink arrowheads in G). (E) A montage of photographs compiled in Adobe Photoshop. (H) In ewg1/ewg2; Apc1Q8 double mutants, inner PRs adopting a DRA fate (green arrowheads) is further reduced to only two ommatidial rows adjacent to the dorsal rim (above solid black line), indicating attenuation of Ewg activity prevents ectopic Wingless signaling in Apc1 mutants.