Abstract
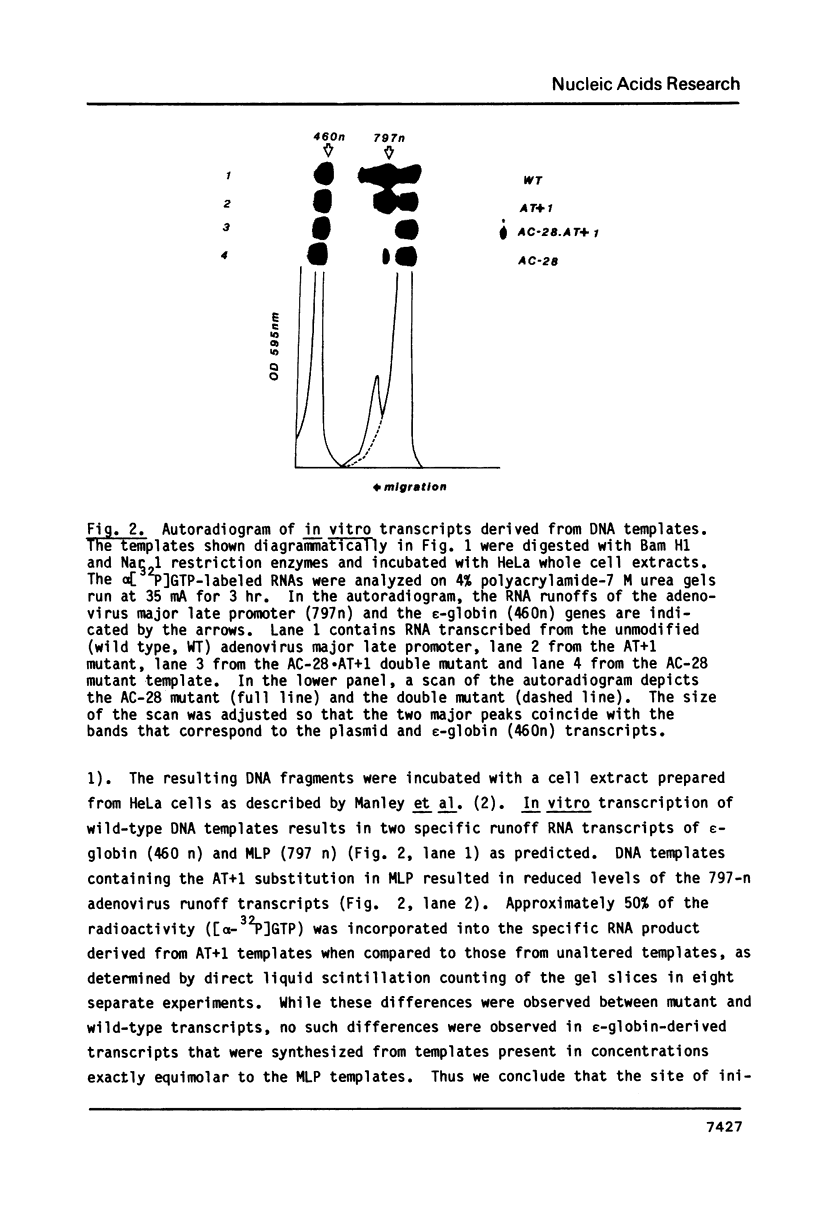
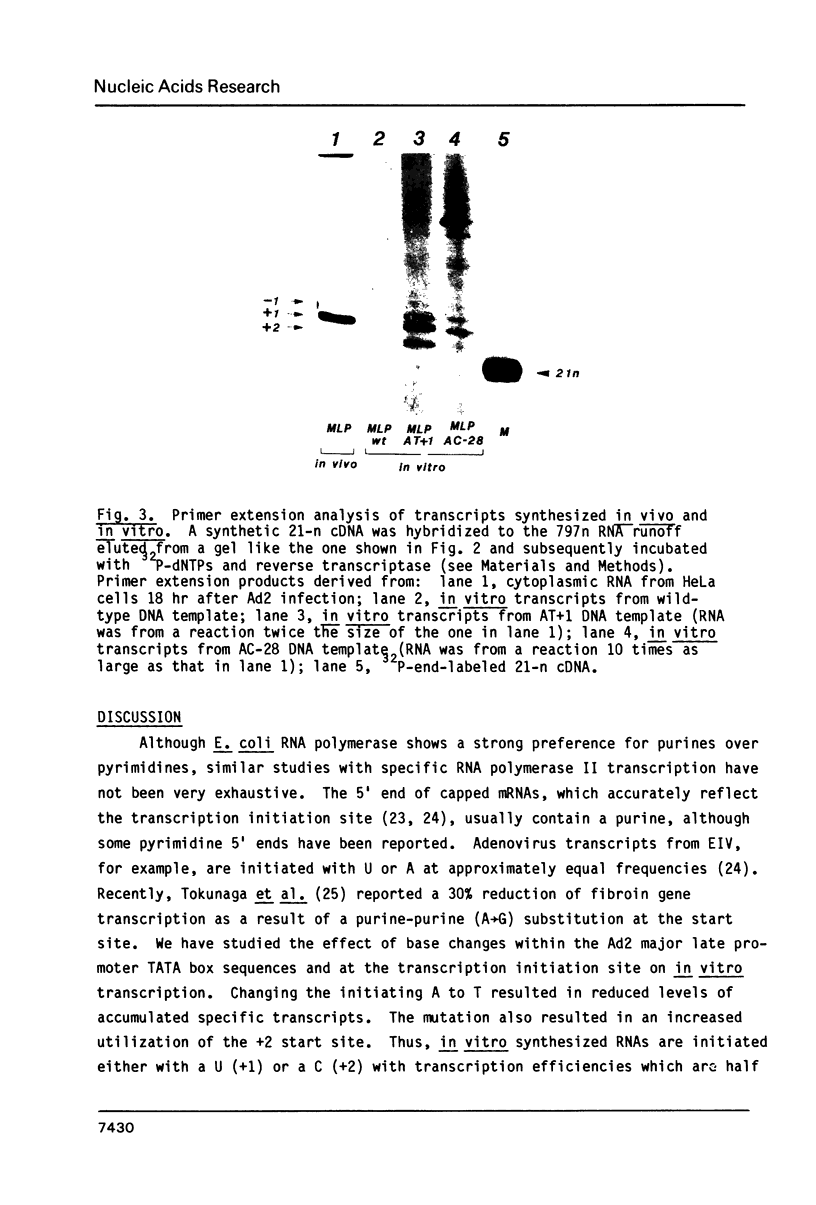
Mutagenized DNA templates and HeLa whole cell extracts were used to study the effects of promoter-specific base changes on in vitro transcription. DNA templates where the initiating adenine (+1) was changed to thymidine (AT+1) in the adenovirus 2 major late transcription unit were transcribed with 50% efficiency of the unaltered template. We have described a mutant at the TATA box, where the A at position -28 was changed to a C (AC-28). Transcription efficiency was reduced to less than 20% of control in the AC-28 mutant (Concino et al., 1983, J. Biol. Chem. 258: 8493-8496). Primer extension analysis revealed increased 5' end heterogeneity for in vitro transcripts derived from AC-28 and AT+1 DNA templates. Specific transcription was completely abolished from AT+1 DNA templates when a second change was introduced within the TATA sequence, creating a double mutant (AC-28 . AT+1). Neither the AC-28 nor the AT+1 change alone had such an effect, suggesting a coordinated interaction in transcription initiation involving both the TATA box and the initiation site.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K. L., Brunstedt J., Noyes B. E. A general method for detection and characterization of an mRNA using an oligonucleotide probe. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1023–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunick D., Zandomeni R., Ackerman S., Weinmann R. Mechanism of RNA polymerase II--specific initiation of transcription in vitro: ATP requirement and uncapped runoff transcripts. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):877–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90449-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concino M., Goldman R. A., Caruthers M. H., Weinmann R. Point mutations of the adenovirus major late promoter with different transcriptional efficiencies in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8493–8496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Field A. S., Luse D. S. Promoter-proximal pausing by RNA polymerase II in vitro: transcripts shorter than 20 nucleotides are not capped. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1251–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Manley J. L. DNA sequence required for initiation of transcription in vitro from the major late promoter of adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Manley J. L. In vitro transcription from the adenovirus 2 major late promoter utilizing templates truncated at promoter-proximal sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8513–8521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Energy requirement for specific transcription initiation by the human RNA polymerase II system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5321–5326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington C. A., Leder P. Rescuing the in vitro function of a globin pseudogene promoter. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):192–195. doi: 10.1038/298192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Hirose S., Suzuki Y. In monkey COS cells only the TATA box and the cap site region are required for faithful and efficient initiation of the fibroin gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1543–1558. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., Kops L. E., Minghetti P. P., O'Malley B. W. Transcription factors from oviduct and HeLa cells are similar. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13055–13059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]