Abstract
The equine alpha globin gene complex comprises two functional alpha genes and an alpha-like pseudogene arranged in the order 5'-alpha 2-(5kb)-alpha 1-(3kb)-psi alpha-3'. A single (embryonic) zeta-like sequence lies within a 12 kb region 5' to the alpha 2 gene. We have determined the sequence of the alpha 1 gene of the BII haplotype, one of two most common haplotypes (the other being BI) which encode alpha globins with either Tyr (BI) or Phe (BII) at codon 24 in both linked alpha genes. In BI and BII the non-allelic alpha 2 and alpha 1 genes respectively code for Gln or Lys at codon 60, thus accounting for the 4 alpha globin types seen in BI/BII heterozygotes. Genomic restriction enzyme maps of the BII alpha complex (24Phe/60Lys,Gln) and the allelic BI (24Tyr/60Lys,Gln) are identical to each other, and to those of a rarer normal haplotype, A, which encodes only alpha 24Tyr/60Gln globin, and a low expression mutant of BII which encodes only 24Phe/60Lys globin. These two latter haplotypes must therefore have a linked pair of alpha genes, as in BI and BII, but with identical coding properties, and it is suggested that this has arisen by gene conversion.
Full text
PDF








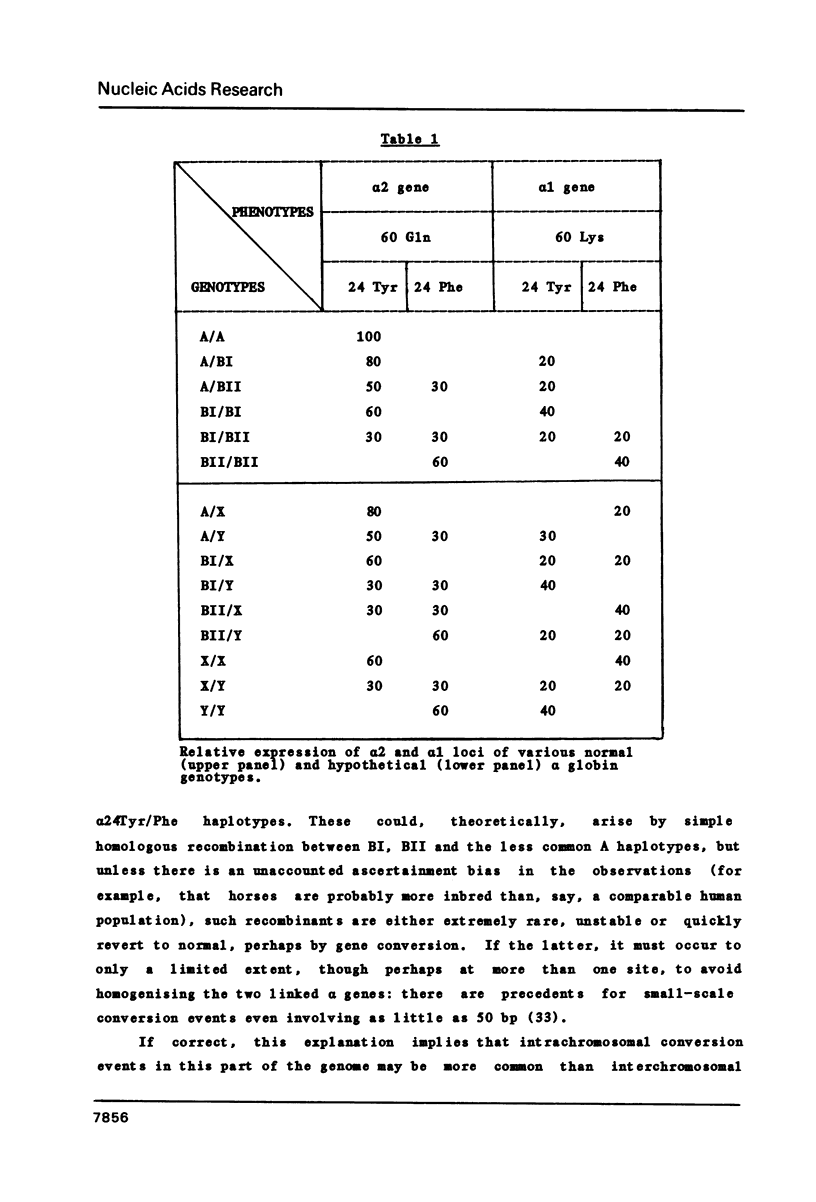


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANGHAM A. D., LEHMANN H. Multiple haemoglobins in the horse. Nature. 1958 Jan 24;181(4604):267–268. doi: 10.1038/181267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchetot A., Wilson V., Wood D., Jeffreys A. J. The seal myoglobin gene: an unusually long globin gene. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):732–734. doi: 10.1038/301732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braend M., Clegg J. B., Storset A. Inheritance of an abnormal haemoglobin haplotype in horses and its possible influence on blood values. Acta Vet Scand. 1983;24(4):384–391. doi: 10.1186/BF03546712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braend M. Genetic variation of horse hemoglobin. Hereditas. 1967;58(3):385–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1967.tb02163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braend M., Johansen K. E. Haemoglobin types in Norwegian horses. Anim Blood Groups Biochem Genet. 1983;14(4):305–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1983.tb01089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B. Horse hemoglobin polymorphism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Nov 29;241(0):61–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb21866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Fox M., Schmid C., Shen C. K. Molecular evolution of the human adult alpha-globin-like gene region: insertion and deletion of Alu family repeats and non-Alu DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5970–5974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Clegg J. B. Amino-acid replacements in horse haemoglobin. Nature. 1967 Jan 21;213(5073):269–271. doi: 10.1038/213269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauer J., Shen C. K., Maniatis T. The chromosomal arrangement of human alpha-like globin genes: sequence homology and alpha-globin gene deletions. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie H. Serum types of the Nordland horse and the Norwegian trotter. Nord Vet Med. 1973 Feb;25(2):83–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Goossens M., Kan Y. W. Homology and concerted evolution at the alpha 1 and alpha 2 loci of human alpha-globin. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):26–29. doi: 10.1038/290026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Brammar W. J. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning large DNA fragments made with several restriction enzymes. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda G., Maita T., Braunitzer G., Schrank B. Hämoglobine, XXXIII: Notiz zur Sequenz der Hämoglobine des Pferdes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Jul;361(7):1107–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Orkin S. H. Boundaries of gene conversion within the duplicated human alpha-globin genes. Concerted evolution by segmental recombination. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15245–15254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. The duplicated human alpha globin genes lie close together in cellular DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5950–5954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Genetic recombination: strand transfer and mismatch repair. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:847–880. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder O. A., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C., Clegg J. B. Hemoglobin polymorphism in Equus przewalskii and E. caballus analyzed by isoelectric focusing. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1979;62(4):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(79)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Telford J., Baldari C., Pirrotta V. Isolation of cloned genes differentially expressed at early and late stages of Drosophila embryonic development. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):438–447. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E. A., Wernke S. M., Lingrel J. B. Gene conversion of two functional goat alpha-globin genes preserves only minimal flanking sequences. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6825–6835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver S., Comer M. B., Jahn C. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. The adult beta-globin genes of the "single" type mouse C57BL. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Mellor A., Golden L., Fahrner K., Simpson E., Hurst J., Flavell R. A. The structure of a mutant H-2 gene suggests that the generation of polymorphism in H-2 genes may occur by gene conversion-like events. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):671–674. doi: 10.1038/301671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zassenhaus H. P., Butow R. A., Hannon Y. P. Rapid electroelution of nucleic acids from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;125(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer E. A., Martin S. L., Beverley S. M., Kan Y. W., Wilson A. C. Rapid duplication and loss of genes coding for the alpha chains of hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2158–2162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



