Abstract
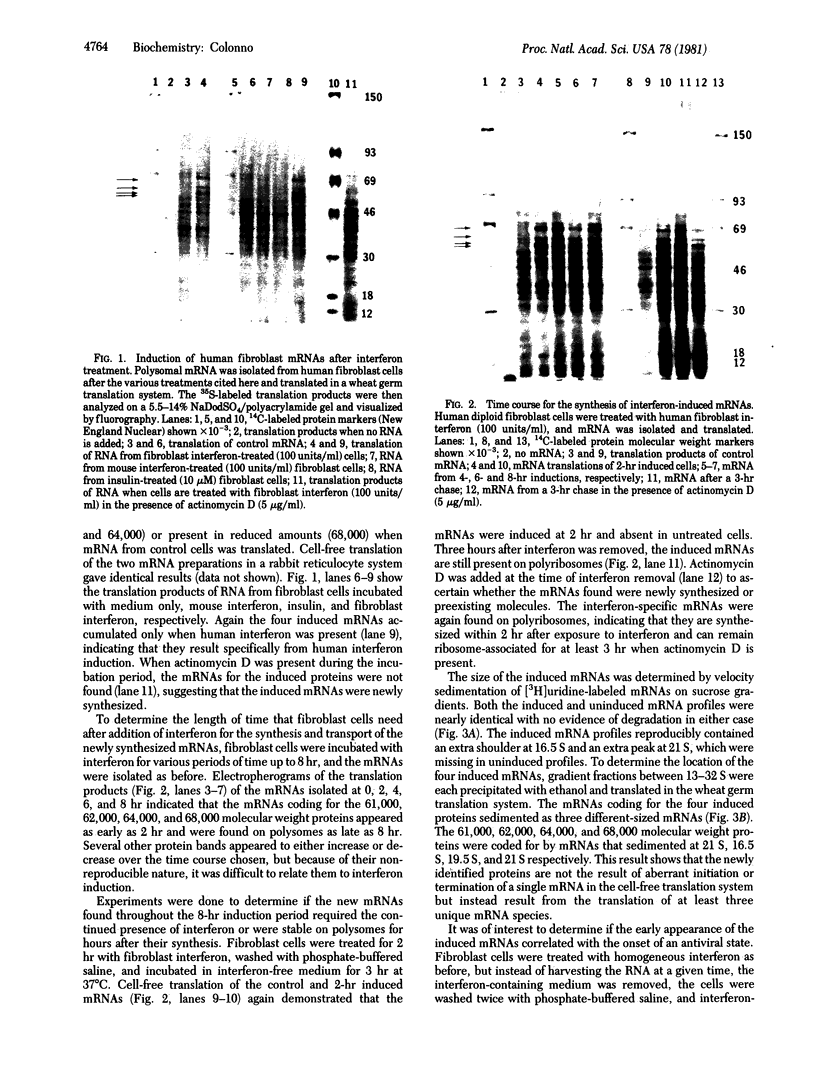
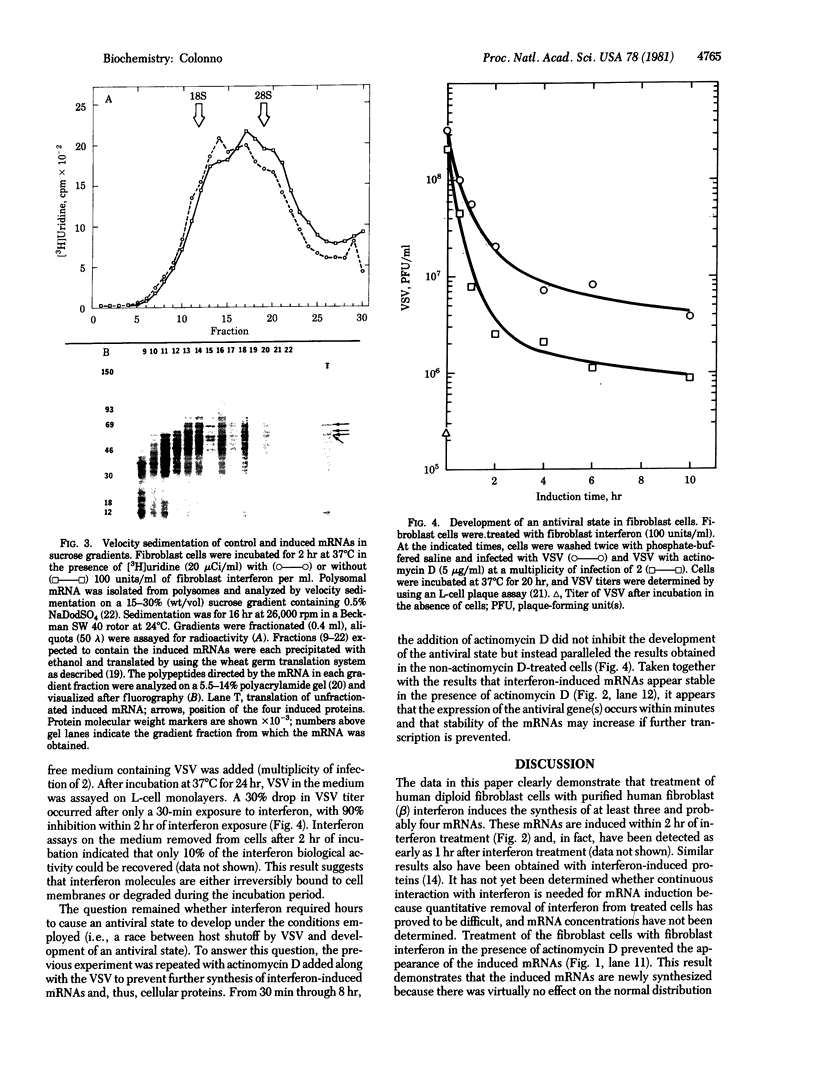
Treatment of human fibroblast cells with human fibroblast (beta)interferon for up to 8 hr resulted in the accumulation of at least four mRNAs. The mRNAs were isolated from cellular polysomes and characterized by stimulation of translation in a wheat germ cell-free protein synthesis system. The mRNAs appear as early as 2 hr after exposure to interferon and can be translated in vitro into proteins having molecular weights of 61,000, 62,000, 64,000, and 68,000. The response is not elicited by mouse interferon or insulin and does not occur in the presence of actinomycin D. Chase experiments indicated that the induced mRNAs remain ribosome-associated for at least 3 hr after their synthesis. The appearance of the induced mRNAs correlated directly with the onset of an antiviral state. Velocity sedimentation of the induced mRNAs on sucrose gradients demonstrated that each of the four induced proteins are encoded by different-sized mRNAs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A., White C. N. Nuclease activation by double-stranded RNA and by 2',5'-oligoadenylate in extracts of interferon-treated chick cells. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):348–356. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Moyer S. A., Rhodes D. P. Studies on the in vitro adenylation of RNA by vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):547–558. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90289-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chany C., Fournier F., Rousset S. Potentiation of the antiviral activity of interferon by actinomycin D. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):113–114. doi: 10.1038/newbio230113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K. Mapping and initiation studies on the leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):260–268. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Lazzarini R. A., Keene J. D., Banerjee A. K. In vitro synthesis of messenger RNA by a defective interfering particle of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1884–1888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Broeze R. J., Lengyel P. Accumulation of an mRNA and protein in interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):523–525. doi: 10.1038/279523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Sen G. C., Dubois M. F., Ratner L., Slattery E., Lengyel P. Interferon action: two distinct pathways for inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5893–5897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Rubin B. Y., Holmes S. L. Interferon action: induction of specific proteins in mouse and human cells by homologous interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4817–4821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter A. R., Farrell P. J., Jackson R. J., Hunt T. The role of polyamines in cell-free protein synthesis in the wheat-germ system. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):149–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Zilberstein A., Schmidt A., Shulman L., Revel M. The interferon-induced protein kinase PK-i from mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9846–9853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Hunkapiller M. W., Korant B. D., Hardy R. W., Hood L. E. Human fibroblast interferon: amino acid analysis and amino terminal amino acid sequence. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):525–526. doi: 10.1126/science.7352259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Korant B. D. Fibroblast interferon induces synthesis of four proteins in human fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1824–1827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minks M. A., West D. K., Benvin S., Greene J. J., Ts'o P. O., Baglioni C. Activation of 2',5'-oligo(A) polymerase and protein kinase of interferon-treated HeLa cells by 2'-O-methylated poly (inosinic acid) . poly(cytidylic acid), Correlations with interferon-inducing activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6403–6407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Gupta S. L. Interferon-induced proteins in human fibroblasts and development of the antiviral state. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):446–454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.446-454.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Chernajovsky Y., Shulman L., Federman P., Berissi H., Revel M. An interferon-induced phosphodiesterase degrading (2'-5') oligoisoadenylate and the C-C-A terminus of tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4788–4792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Shaila S., Lebleu B., Brown G. E., Desrosiers R. C., Lengyel P. Impairment of reovirus mRNA methylation in extracts of interferon-treated Ehrilich ascites tumor cells: further characteristics of the phenomenon. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):69–83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.69-83.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slattery E., Ghosh N., Samanta H., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and RNA degradation: activation of an endonuclease by (2'-5')An. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4778–4782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. Inhibition of interferon action by actinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West D. K., Baglioni C. Induction of interferon in HeLa cells of a protein kinase activated by double-stranded RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov;101(2):461–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb19740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]