Abstract
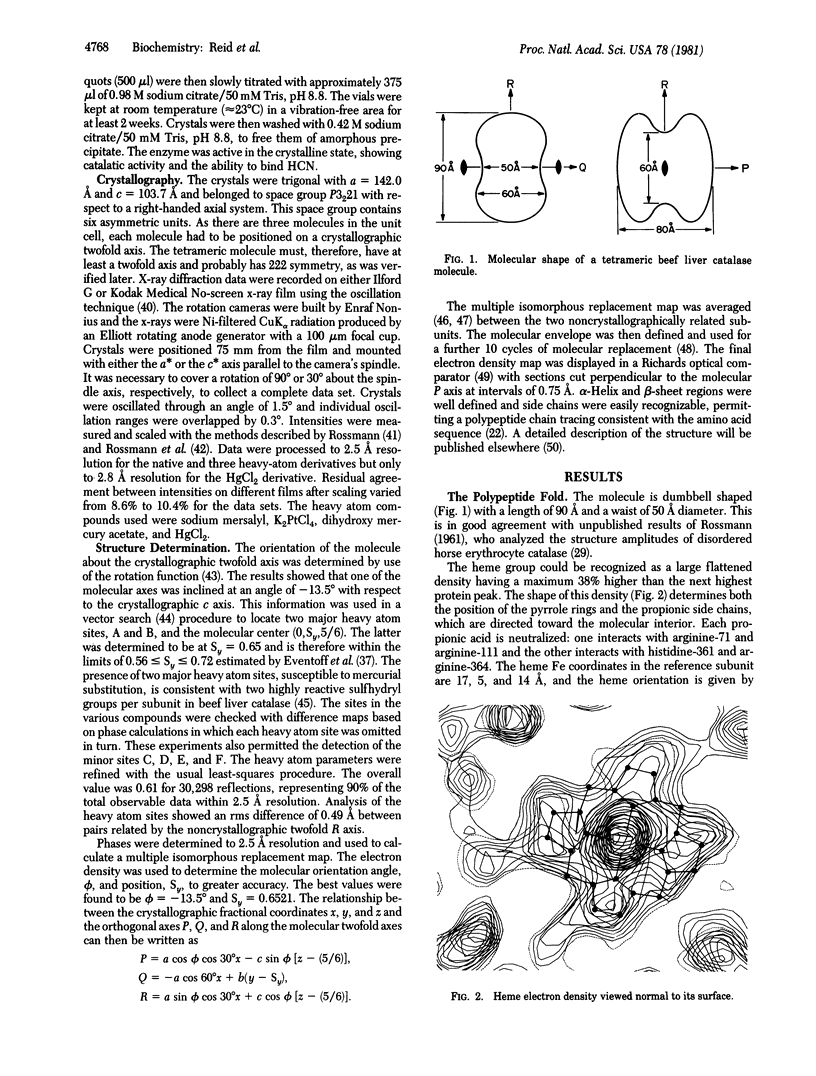
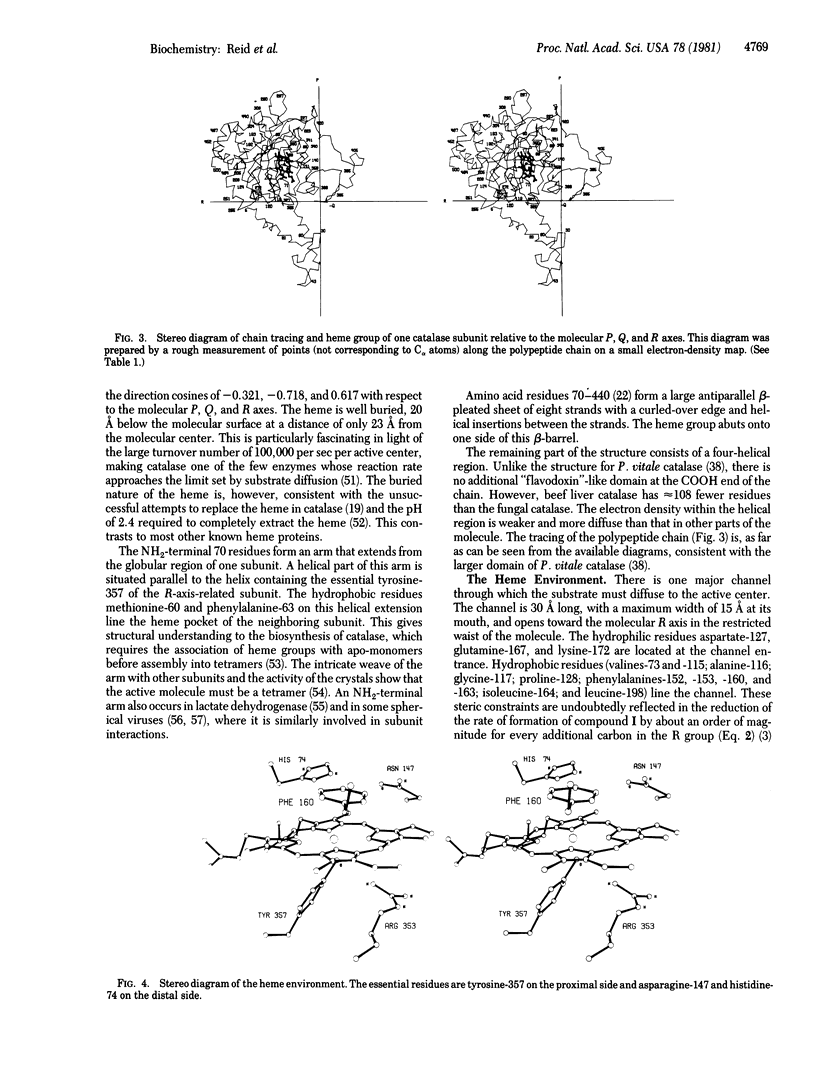
Most of the amino acid side chains of beef liver catalase were clearly identifiable in the 2.5 A resolution electron-density map, and the results are in good agreement with the sequence [Schroeder, W. A., Shelton, J. R., Shelton, J. B., Roberson, B. & Apell, G. (1969) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 131, 653-655]. The tertiary structure of one subunit consists of a large antiparallel beta-pleated sheet domain with helical insertions, followed by a smaller domain containing four alpha-helices. The heme group is buried at least 20 A below the molecular surface and is accessible by a channel lined with hydrophobic residues. The proximal ligand is tyrosine-357, while histidine-74 and asparagine-147 re the important residues on the distal side of the heme. The inhibitor 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, which has been shown to covalently bond to histidine-74, can be built into the heme cavity with its N(2) atom coordinated to the heme iron.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. J., Ford G. C., Koekoek R., Lentz P. J., McPherson A., Jr, Rossmann M. G., Smiley I. E., Schevitz R. W., Wonacott A. J. Structure of lactate dehydrogenase at 2-8 A resolution. Nature. 1970 Sep 12;227(5263):1098–1103. doi: 10.1038/2271098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow G. H., Margoliash E. Sedimentation studies on catalase Complex II using photoelectric scanning optics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 12;188(1):159–161. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudhuin P., Beaufay H., De Duve C. Combined biochemical and morphological study of particulate fractions from rat liver. Analysis of preparations enriched in lysosomes or in particles containing urate oxidase, D-amino acid oxidase, and catalase. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jul;26(1):219–243. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill A. S., Sandberg H. E. Spectral studies of iron coordination in hemeprotein complexes: difference spectroscopy below 250 millimicrons. Biophys J. 1968 Jun;8(6):669–690. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(68)86514-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill A. S., Williams R. J. The absorption spectra, magnetic moments and the binding of iron in some haemoproteins. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78(2):246–253. doi: 10.1042/bj0780246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buehner M., Ford G. C., Moras D., Olsen K. W., Rossmann M. G. Structure determination of crystalline lobster D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 5;82(4):563–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkey D. J., McPherson A. Crystallographic evidence for the structural isomorphism of deer and beef catalase. Experientia. 1977 Jul 15;33(7):880–881. doi: 10.1007/BF01951258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. The effect of pH upon the equilibria of catalase compounds. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):483–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. The spectra of the enzyme-substrate complexes of catalase and peroxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Dec;41(2):404–415. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisseroth A., Dounce A. L. Catalase: Physical and chemical properties, mechanism of catalysis, and physiological role. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jul;50(3):319–375. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin D., Forman A., Borg D. C., Fajer J., Felton R. H. Compounds I of catalase and horse radish peroxidase: pi-cation radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eventoff W., Tanaka N., Rossmann M. G. Crystalline bovine liver catalase. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 5;103(4):799–801. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90210-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George P., Lyster R. L. CREVICE STRUCTURES IN HEMOPROTEIN REACTIONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1013–1029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer J. Three-dimensional structure of abnormal human haemoglobins M Hyde Park and M Iwate. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):107–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL C. E. Electron microscopy of crystalline catalase. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):749–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager L. P., Doubek D. L., Silverstein R. M., Hargis J. H., Martin J. C. Chloroperoxidase. IX. The structure of compound I. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 14;94(12):4364–4366. doi: 10.1021/ja00767a068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEILIN D., HARTREE E. F. Reaction of methaemoglobin with hydrogen peroxide. Nature. 1950 Sep 23;166(4221):513–514. doi: 10.1038/166513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiselev N. A., Shpitzberg C. L., Vainshtein B. K. Crystallization of catalase in the form of tubes with monomolecular walls. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90196-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS U. J. Acid cleavage of heme proteins. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jan;206(1):109–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanir A., Schejter A. On the sixth coordination position of beef liver catalase. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):254–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemberg R., Legge J. W. Liver catalase. Biochem J. 1943 Apr;37(1):117–127. doi: 10.1042/bj0370117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley W. The crystal structure of bovine liver catalase: a combined study by x-ray diffraction and electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):323–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMON A. G. Small angle x-ray scattering studies of the size, shape, and hydration of catalase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Nov;26(2):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E., NOVOGRODSKY A., SCHEJTER A. Irreversible reaction of 3-amino-1:2:4-triazole and related inhibitors with the protein of catalase. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:339–348. doi: 10.1042/bj0740339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marie A. L., Parak F., Hoppe W. Unit cell and space group of catalase from Micrococcus luteus. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):675–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson A., Jr, Rich A. Crystallographic study of beef liver catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jul;157(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90384-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLLS P. The role of the protein in haem enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:217–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Kraut J. The stereochemistry of peroxidase catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8199–8205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulsinelli P. D., Perutz M. F., Nagel R. L. Structure of hemoglobin M Boston, a variant with a five-coordinated ferric heme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3870–3874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. The matching of physical models to three-dimensional electron-density maps: a simple optical device. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruis H. The biosynthesis of catalase. Can J Biochem. 1979 Sep;57(9):1122–1130. doi: 10.1139/o79-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. R., Shelton J. B., Robberson B., Apell G. The amino acid sequence of bovine liver catalase: a preliminary report. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 May;131(2):653–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90441-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Glaeser R. M. Electron diffraction of frozen, hydrated protein crystals. Science. 1974 Dec 13;186(4168):1036–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4168.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torii K., Iizuka T., Ogura Y. Magnetic susceptibility and EPR measurements of catalase and its derivatives. A thermal equilibrium between the high- and low-spin states in the catalase-azide compound. J Biochem. 1970 Dec;68(6):837–841. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N. Beef liver catalase structure: interpretation of electron micrographs. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



