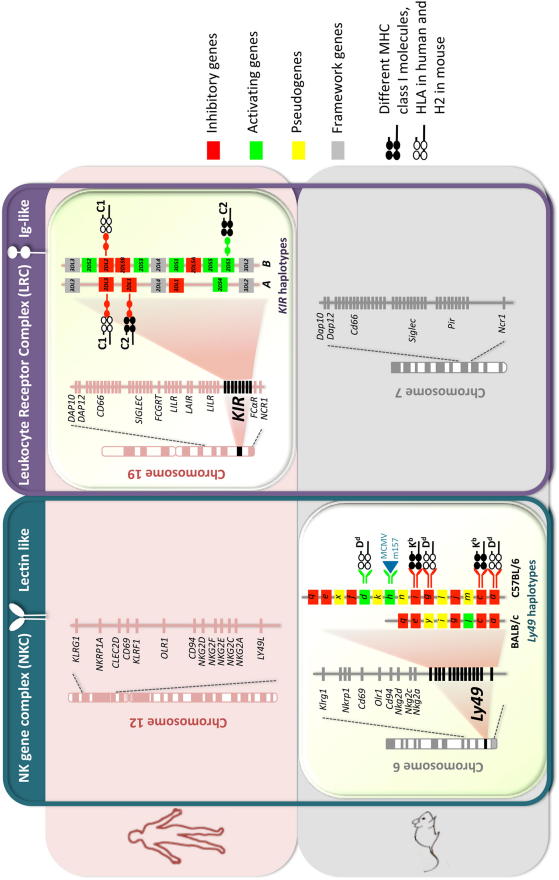
Fig. 2.
Comparative Genomics of NKC and LRC in human and mouse. A schematic map of the NKC and the LRC encompassing genes encoding for lectin-like and Ig-like NKR and emphasizes the functional homology of human KIR[18] and mouse Ly49[38] genes that arose by convergent evolution [37]. Two typical human KIR haplotypes (A and B) and mouse Ly49 haplotypes (BALB/c and C57BL/6) are shown. The MHC class I ligands for the cognate receptors are also depicted for both human and mouse. For clarity, only one MHC class I molecules is indicated for each of the Ly49 receptors, however individual Ly49 receptors can bind multiple MHC class I molecules. For example Ly49C can bind H2-Kb and H2-Kd[39]. The figure is not drawn to scale and not all genes that map to the NKC and the LRC are indicated. Additional information can be found in references [40–43].