Abstract
Epidemiology, disease patterns, immunology, diagnosis, treatment and control measures of leishmaniasis are described. Various issues relating to leishmaniasis are highlighted: the relative lack of importance given to this disease compared with other infections, climate change and its possible impact on extension of endemicity of this infection, and new diagnostic tests which are improving diagnosis, especially in resource poor areas. Other important aspects discussed include the potential for newer oral therapy to change the way this disease is managed; Leishmania–HIV coinfection and groups at risk; and development of an effective vaccine.
Keywords: Leishmania, antimonial, amphotericin, miltefosine, HIV
Publisher's apology.
This article is being reprinted as there were a number of errors in the original version. The publisher apologises unreservedly to the authors and readers for any confusion these errors may have caused.
Infectious diseases steal the headlines on a regular basis and are ranked high among other major news items like natural disasters, conflict situations and terrorism. Emerging infectious diseases with wide threatening potential such as severe acute respiratory syndrome and pandemic influenza, are usually the ones which get best coverage and consequently better funding. Diseases with high prevalence such as HIV/AIDS and malaria (table 1) should bring better financial returns from investing research into new treatments and developing vaccinations than similar investment into lower prevalence infections. Leishmaniasis is one such infection which rarely shares this limelight and thus remains largely a neglected disease.1 2
Table 1 Epidemiology of different infectious diseases .
| Disease | Annual incidence (global) | Mortality: no of deaths per year (global) | Prevalence: total no of infected persons (global) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIV/AIDS | 5.6 million | 2.6 million | 34 million |
| Malaria | 300 million | 1–2.7 million | – |
| Tuberculosis | 7.8 million | 1.8 million | 1.7 billion |
| Visceral leishmaniasis | 500 000 | 80 000 | 12 million |
| Cutaneous leishmaniasis | 1.5–2 million3 | – | – |
Source: www.who.int; www.cdc.gov; www.hopkins-id.edu.
Despite this, several issues regarding leishmaniasis merit discussion: resistance to conventional drug treatment has developed in certain areas of the world, necessitating a change of first-line agents; rapid, less invasive diagnostic procedures have been developed which are most useful in poorly resourced parts of the world; despite advances in the understanding of the immunology of the disease and the unravelling of the Leishmania genome, a vaccine has not yet been developed; and the extent of disease in different individuals stresses the complex immunology of leishmaniasis, brought to the fore more recently with the advent of HIV–Leishmania coinfection, and its difficult eradication in this scenario.
This review is based on information from bibliographic research, Entrez-Pubmed searches on leishmaniasis, review articles and papers in their reference lists, and from the authors' personal archives.
Epidemiology
Leishmaniasis is endemic in more than 60 countries worldwide,1 including Southern Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, Central and South America and the Indian subcontinent. It is not endemic in South East Asia and Australia.4 The burden of disease (90% of cases) is borne by Afghanistan, Pakistan, Syria, Saudi Arabia, Algeria, Iran, Brazil, and Peru in the case of cutaneous leishmaniasis, and by India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sudan, and Brazil in the case of visceral leishmaniasis.3 Recently the number of reported cases and geographical areas have increased,5 and this has sparked concern regarding the contribution that global warming might have on this observation.6 7
One of the causative organisms of leishmaniasis, Leishmania donovani, was first described in 1903 by Leishman and Donovan almost simultaneously.4 Leishmania is a protozoon, able to infect animals, humans and sandflies. There are at least 20 species of Leishmania. Each may cause a disease specific to the species and the host response. Organism prevalence differs by geographical distribution. Thus disease patterns differ by geographical area (table 2).
Table 2 Disease patterns and organisms prevalent in different geographical locations4 8 9 12 .
| Disease patterns | Old World organisms | New World organisms |
|---|---|---|
| Visceral leishmaniasis | L donovani (India, Kenya) | L chagasi |
| L infantum (Southern Europe and North Africa) | L amazonensis | |
| L tropica | ||
| Post-kala azar dermal leishmaniasis | L donovani sensu stricto | |
| Viscerotropic leishmaniasis | L tropica | |
| Cutaneous leishmaniasis | L tropica | L mexicana species complex |
| L major | L mexicana | |
| L aethiopica | L amazonensis | |
| L infantum | L venezuelensis | |
| L donovani | Viannia subgenus | |
| L (V) braziliensis | ||
| L (V) panamensis | ||
| L (V) guyanensis | ||
| L (V) peruviana) | ||
| L major-like organisms | ||
| L chagasi | ||
| Mucosal leishmaniasis | Viannia subgenus | |
| L (V) braziliensis | ||
| L (V) panamensis | ||
| L (V) guyanensis) | ||
| L amazonensis (see text) | ||
| Leishmaniasis recidivans | L tropica | |
| L major | ||
| Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis | L aethiopica | L mexicana species complex |
(V): refers to the Viannia subgenus. The leishmanias were classified into the subgenera Leishmania sensu stricto (Old and New World) and Viannia (New World) by Lainson and Shaw in 1987.9
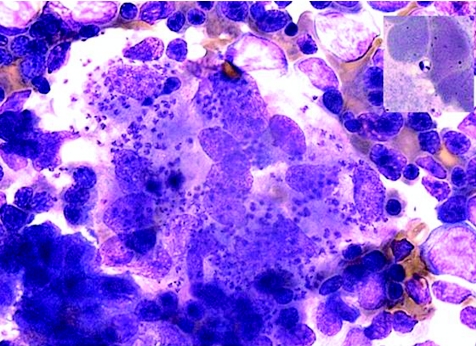
The reservoirs of the disease are animals like canines and rodents (zoonotic cycle) and, in countries such as Sudan, humans (anthroponotic cycle).10 The sandfly is the vector of the disease and ingests the organism, as an amastigote, into its digestive tract when feeding on an infected animal. The amastigote develops into a promastigote in its digestive tract, and will then be injected into the susceptible host at the next feed. The promastigote then infects macrophages and develops into amastigotes (fig 1).
Figure 1 Abundant amastigotes of Leishmania in a bone marrow aspirate. Inset photo showing amastigote with its nucleus and kinetoplast (specialised mitochondria containing DNA) (photograph courtesy of Dr Alicia Grochowska, Consultant Haematologist, St Luke's Hospital, Malta).
About 70 different species of sandfly can transmit leishmaniasis.11 The species are mainly Lutzomyia in the Americas and Phlebotomous elsewhere.12 The sandfly characteristically feeds at dusk, and being a weak flier, tends to remain close to its breeding area, not too high from the ground. Different species have different feeding and resting patterns. These different characteristics are important in formulating control strategies (see below).
The incidence and prevalence can be seen in table 1. Infection is more common in men than in women, but this may reflect increased exposure to sandflies. Although disease occurs irrespective of age, children aged 1–4 years are particularly at risk of infection in the Mediterranean regions, and childhood infection may account for more than half of all cases in some of these countries.13 Untreated visceral leishmaniasis carries a mortality of 75–95%, while cutaneous leishmaniasis can disseminate to involve the mucosa, resulting in death from secondary infection.8
Disease patterns
Three main types of disease patterns occur: visceral, cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis (table 3). The type of disease expressed depends both on the type of Leishmania species and on the zymodeme (electrophoretic isoenzyme pattern) expressed on that species. Thus one zymodeme may cause visceral leishmaniasis while another zymodeme of the same species may cause cutaneous leishmaniasis.14
Table 3 Leishmaniasis disease patterns .
| Disease type | Incubation period | Clinical features |
|---|---|---|
| Visceral leishmaniasis | 3– 8 months (range 10 days to 34 months) | Fever, weight loss, hepatosplenomegaly lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia and hypergammaglobulinaemia, skin pigmentation |
| Post-kala azar dermal leishmaniasis | Variable; develops after resolution of visceral leishmaniasis | Skin lesions around mouth and other parts of body |
| Cutaneous leishmaniasis | 2 weeks to several months (rarely up to 3 years) | Papule at the site of a sandfly bite increases in size, crusts, and ulcerates |
| Leishmaniasis recidivans | Tuberculoid lesions develop around scars of healed cutaneous ulcers; low parasite count on biopsy | |
| Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis | Rare. Dissemination of skin lesions occurs over face and extremities; high parasite numbers due to poor cell-mediated immune response | |
| Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis | 1–3 months (may occur many years after the initial cutaneous ulcer has healed) | Mainly in South America. Involves the nose, oral cavity and pharynx resulting in difficulty with eating |
Visceral leishmaniasis
The incubation period varies from 3 to 8 months15 16 (range 10 days17 to 34 months18). Features include fever, weight loss, hepatosplenomegaly (usually spleen much larger than liver), lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia and hypergammaglobulinaemia.10 Skin pigmentation may be a feature (“kala azar”: black disease). It may be asymptomatic and self-resolving, but usually runs a chronic course and may be fatal without or despite treatment.19 Death usually occurs because of severe secondary bacterial infections in advanced disease.
Some cases of visceral leishmaniasis present atypically and cases have been reported which involve the lungs, pleura, oral mucosa, larynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, skin and bone marrow .12
Box 1: Current issues in Leishmania infection
Leishmania is given less importance than other more prevalent infectious diseases.
Climate change may be responsible for the extension of endemicity of leishmaniasis to previously non-endemic countries.
New diagnostic tests should improve diagnosis, especially in the field in resource-poor areas.
Leishmania may relapse in HIV patients and is difficult to eradicate, if at all in this setting. There have been calls for Leishmania infection to be officially recognised as an AIDS-defining illness.
Anthroponotic transmission may occur in intravenous drug users who share needles.
The Leishmania genome has been unravelled, but an effective vaccine is not yet available.
Variations of visceral leishmaniasis
Post-kala azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL) develops after resolution of visceral leishmaniasis. The time interval to development of PKDL is variable. PKDL occurs in a small percentage of patients in Africa and India.12 This is usually due to infection by the L donovani sensu stricto cluster.20 The skin lesions are macular, maculo-papular or nodular, and usually spread from the perioral area to other areas of the body.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
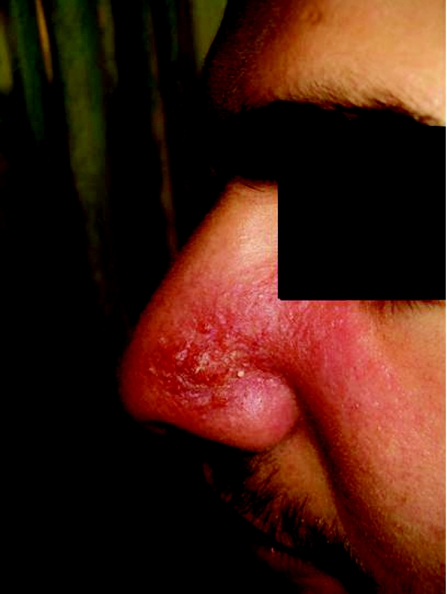
This initially starts as a papule at the site of a sandfly bite which then increases in size, crusts (fig 2), and eventually ulcerates. It may take 3–18 months to heal in over 90% of cases.12 The incubation period lasts from 2 weeks to several months and cases up to 3 years have been reported in Old World cutaneous leishmaniasis.17 21 In New World cutaneous leishmaniasis, the incubation period is usually 2–8 weeks.22
Figure 2 Cutaneous leishmaniasis at crusting stage, Malta (informed consent was obtained from the patient to publish this photograph).
Variations of cutaneous leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis recidivans is characterised by tuberculoid lesions developing around scars of healed cutaneous ulcers, revealing a low parasite count on biopsy. Infections tend to be resistant to treatment.
In diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis, dissemination of skin lesions rarely occurs over the face, hands and feet, revealing high parasite numbers due to poor cell-mediated immune response. This is more common in the New World Leishmania but also occurs with L aethiopica in East Africa.23
Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis
The incubation period is 1–3 months, but mucocutaneous leishmaniasis may occur many years after the initial cutaneous ulcer has healed. Mucosal involvement occurs in South American cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis (espundia) involving the nose, oral cavity and pharynx. This causes difficulty with eating and an increased risk of secondary infection which carries a significant mortality.
Immunology
The immune response (box 2) to Leishmania infection is cell mediated. The organism lies exclusively intracellularly, mainly inside macrophages as replicating amastigotes. The outcome of infection will depend on whether the host mounts primarily a T-helper (Th)-1 or Th2 response.24 Studies in animals suggest that the same parasite epitope can induce a Th1 response in animals with resolving infection or a Th2 response in others with disease progression.25 Other animal studies have shown that Th1 and natural-killer cells produce interferon γ (IFNγ), which mediates resistance, whilst interleukin (IL)4-producing Th2 cells confer susceptibility to infection.26 Human studies have also shown that IL4, a component of the Th2 response, may also be associated with disease progression.27
In the Th1 response, promastigotes attach to reticuloendothelial cells and T helper CD4 cells produce IL2, IL3 and IFNγ which activate macrophages. IL12 and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) are also important in this type of response. The promastigotes are then phagocytosed by the activated macrophages into vacuoles which then fuse with lysosomes.
Host genetics inevitably influence the type of immune response. Studies in mice and humans have shown that genes such as those coding for natural resistance associated macrophage protein 1 (NRAMP1), TNF or the major histocompatibility complex are thought to play a major role in the outcome of infection.28 The parasite itself can affect the macrophage and dendritic cell responses. Specific gene loci such as the A2 gene can code for products which promote L donovani infectivity.11 Thus the interplay between the host-determined delayed-type hypersensitivity, antigen-specific T-cell reactivity, and cytokine secretion, and the type and virulence of the particular infecting Leishmania species determine what type of disease expression develops in the host.
Box 2: The immune response
Th1 immune response
T-helper CD4 cells producing IL2, IL3, IFNγ
Will promote immune responses that are primarily cell mediated/inflammatory by activating cytotoxic T cells, natural killer cells and macrophages
In leishmaniasis, associated with disease resolution
Th2 immune response
Th2 cells produce IL4, IL5, IL6, IL10 which favour induction of antibody responses by B cells
In leishmaniasis, associated with disease progression
Some cases are believed to harbour Leishmania organisms for indefinite periods before the disease is expressed, suggesting latent infection.29 Parasites have also been detected in lymph nodes after clinical cure.30 This is probably the basis of recrudescence of leishmaniasis which can occur decades after the initial infection, if cell-mediated immunity becomes disturbed. It is thought that “sterile” immunity—that is, complete eradication of the organism, probably rarely develops in visceral infection.
Diagnosis
Visceral leishmaniasis
Diagnosis in visceral leishmaniasis is usually based on microscopic detection of amastigotes in smears of tissue aspirates or biopsy samples. Bone marrow aspirates or biopsy are frequently the tissues of choice with sensitivities in the 55–97% range (fig 1). Lymph node aspirate smears (sensitivity 60%) or biopsy, and splenic aspirates (sensitivity >97%)11 may also be taken for diagnosis, though the latter may give rise to life-threatening haemorrhage (table 4).
Table 4 Diagnostic methods .
| Diagnostic test | Comments |
|---|---|
| Visceral leishmaniasis | |
| Microscopic detection of amastigotes in smears of tissue aspirates or biopsy samples | Bone marrow aspirates or biopsy: sensitivity 55–97% |
| Lymph node aspirate smears (sensitivity 60%) or biopsy | |
| Splenic aspirates (sensitivity >97%): risk of life-threatening haemorrhage | |
| Tissue culture | On special media like Novy, McNeal, Nicolle (NNN) medium or inoculated into animals such as hamsters |
| Leishmania antibody (DAT) | Sensitivity 72%, specificity 94% |
| Some cross-reactions in leprosy, Chagas disease, malaria, and schistosomiasis | |
| In HIV, may be falsely negative | |
| Anti-K39 antibody in blood droplet | Sensitivity 90–100% in symptomatic patients |
| Useful in clinical management in resource-poor areas | |
| Leishmania DNA detection in tissue aspirates and peripheral blood by PCR | Sensitivity 70–93% in peripheral blood |
| Detection of Leishmania antigen and antibody in the urine | High sensitivity and specificity |
| Cutaneous leishmaniasis | |
| Microscopic examination of skin scrapings or biopsy specimens taken from the edge of lesions | Rapid and low-cost |
| Limited sensitivity, especially in chronic lesions | |
| A practical guide to diagnostic techniques in cutaneous leishmaniasis can be found at: http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140673698101782/fulltext#abstract | |
| Cultures of the lesions | More sensitive than microscopy |
| May become contaminated | |
| Different species have different growth requirements | |
| Antibody detection | Poorly sensitive |
| In American cutaneous leishmaniasis there have been reports of cross-reactivity | |
| Montenegro (leishmanin) skin test | Unable to distinguish between current and past infection |
| Reports of false positivity in other skin infections |
DAT, direct agglutination test; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
Sometimes the parasite can be cultured from microscopy negative tissue samples on special media like Novy, McNeal, Nicolle (NNN) medium or inoculated into animals such as hamsters.
Leishmania antibody (direct agglutination test) may be detected with a sensitivity of 72% and a specificity of 94%.10 Some cross-reactions in leprosy, Chagas disease, malaria, and schistosomiasis may occur. In HIV, antibodies to Leishmania may become undetectable.
Immunochromatographic strip testing of blood from a finger prick for leishmanial anti-K39 antibody has been used successfully in field serodiagnosis31 with a sensitivity of 90–100% in symptomatic patients. This test is useful in clinical management in resource-poor areas.1
Leishmania DNA can also be detected in tissue aspirates and peripheral blood by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), with some series giving a sensitivity of 70–93% in peripheral blood.10 High sensitivities down to the level of one parasite have been recorded.32 Newer methods with high sensitivity and specificity include the detection of Leishmania antigen and antibody in the urine.33 34
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
Diagnosis is usually based on microscopic examination of skin scrapings or biopsy specimens, usually taken from the edge of lesions. This is rapid and low-cost, but has limited sensitivity, especially in chronic lesions.35
Cultures of the lesions, while more sensitive, may become contaminated by bacterial and fungal elements in the biopsy specimen itself. Also, different species have different growth requirements. Leishmania species may be identified using isoenzyme electrophoresis, but this is lengthy and expensive and necessitates cultivation of parasites on a large scale. Monoclonal antibodies can also be used for identification of species in cultured strains, but direct analysis of clinical specimens is better achieved by using PCR, which is rapid, with high specificity and sensitivity. Detection and genetic characterisation of Leishmania can also be accomplished simultaneously.35. One study on American cutaneous leishmaniasis yielded a PCR sensitivity rate of 100%.36
Antibody detection is poorly sensitive due to a lack of significant antibody production in cutaneous leishmaniasis. Moreover, in American cutaneous leishmaniasis there have been reports of cross-reactivity of leishmanial antigens with antibodies induced by other kinetoplastids such as Trypanosoma cruzi.37
Other available means of diagnosing cutaneous leishmaniasis include the Montenegro (leishmanin) skin test which detects specific cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity. It involves intradermal injection of Leishmania antigen, for example L Mexicana, and monitoring for a local reaction.38 Limitations of this test include its inability to distinguish between current and past infection, as well as reports of false positivity in other skin infections.39
Treatment
Recommended treatment regimens are summarised in table 5.
Table 5 Summary of recommended treatment regimens* .
| Disease pattern | Drug | Dose | Comments† |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visceral leishmaniasis | Pentavalent antimony (as stibogluconate or meglumine antimonate) | 20 mg/kg/day IM or IV ×28 days | Some experts advise not to exceed 850 mg daily42 Not effective in North Bihar, India |
| Liposomal amphotericin BMiltefosine | 2 mg/kg/day IV ×5 days2.5 mg/kg/day PO (od or bd) ×28 days | (A)(A) | |
| Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis | As with visceral leishmaniasis | ||
| Amphotericin B | 1 mg/kg IV qod ×20–30 doses | This may be better than antimonials in mucosal disease | |
| Cutaneous leishmaniasis | Observation alone | L major (A) and L mexicana (B) | |
| Pentavalent antimony (as stibogluconate or meglumine antimonate) | 20 mg/kg/day IM or IV ×20 days (×10 days in L major, L tropica and L mexicana) | Some experts advise not to exceed 850 mg daily | |
| Fluconazole | 200 mg PO od | vsL major (A) | |
| Ketoconazole | 600 mg PO od ×28 days | vsL panamensis (A) | |
| vs L mexicana (A) | |||
| Miltefosine | 2.5 mg/kg PO od ×28 days | vsL panamensis (A) | |
| Pentavalent antimony | Intralesional: 1 ml per lesion qod ×8–15 times | vsL major every 1–2 weeks ×3–8 times (A) | |
| vsL tropica weekly ×8–11 times (D) | |||
| Pentamidine | 2–4 mg/kg od or every 2 days IV ×15 doses | vsL panamensis and L braziliensis | |
| vs L guyanensis (C) | |||
| Paromomycin | Topical bd | vsL major ×4 weeks (A) | |
| vsL mexicana ×20 days (B) |
bd, twice daily; IM, intramuscular; IV, intravenous; od, once daily; PO, orally; qod, every other day.
*Adapted from The Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy, 2005 (35th edition), Murray et al12 and Blum et al.56
†Level of evidence, when available, in brackets. Grades of recommendations based on best available evidence: (A) Randomised, controlled trial in representative collective. (B) Randomised, controlled trial in partially representative (small patient number, different species included) collective. Cohort trial or case control study in representative collective. (C) Cohort trial or case–control study in partially representative collective, series of cases in representative collective. (D) Series of cases in partially representative (small patient number, different species included) collective, informal expert opinion, other information.
Visceral leishmaniasis
Treatment is largely based on pentavalent antimonials. Increasing resistance to antimonials is a major problem, and this is most evident in North Bihar, India, where the failure rate for this treatment is more than 50%.11 40 Pentavalent antimony (Sb(V)) can take the form of sodium stibogluconate (Sb(V) 100 mg/ml) or meglumine antimonate (Sb(V) 85 mg/ml). These can be given intravenously or intramuscularly with equal efficacy. It is usually administered at a dose of Sb(V) 20 mg/kg for 28 days, depending on the species and the clinical syndrome. A recent randomised trial in US military personnel showed a shorter, 10-day course to be equally effective.41 A maximum dose of 850 mg daily has been recommended42 in order to minimise side effects such as arrhythmias. Some experts, however, feel that this might predispose to resistance, and advocate higher doses. In some resistant cases of both visceral leishmaniasis and cutaneous leishmaniasis, IFN-gamma has been added successfully to Sb(V) to induce remission.43
Amphotericin B is an effective treatment used in Sb(V)-resistant cases. It is toxic and needs to be given for a prolonged period on an inpatient basis. The alternative is to use the liposomal form, which is highly effective and less toxic, although up to now prohibitively expensive. The trend in Southern Europe is shifting towards using liposomal amphotericin B as first-line treatment, even though the response rate is still around 90% for antimonials. However, a recent trend in increasing resistance to pentavalent antimonials in this area has been recorded, possibly attributed to using meglumine antimonate to treat infected dogs.44 The effectiveness of short courses of this liposomal amphotericin B is resulting in improved cost-benefits.40 45 Studies using lower doses of this agent are also showing promise to improve cost-effective treatment in resource poor areas with high antimonial resistance.46
Miltefosine is the first effective orally active drug against leishmaniasis. Studies of treatment with this drug for 3 or 4 weeks have shown a cure rate of 95–100%.47 48 It has also compared very well (cure rate of 94%) with amphotericin B (cure rate 97%) at 6 months' follow-up. It has the added benefit of a very good safety profile.49 The potential for this drug for treatment of large numbers of patients as outpatients in resource-poor areas is high, though concerns about compliance and eventual resistance have been expressed.11
Other effective drugs have been used in treating leishmaniasis. Pentamidine can be used in treatment-resistant cases of visceral leishmaniasis.50 Its use is limited by its substantial toxicity, necessitating close inpatient monitoring.51 Paromomycin (aminosidine) has been used effectively in resistant cases in North Bihar.52 Pending commercial availability, this treatment should offer cost savings, though issues of potential toxicity such as nephrotoxicity or ototoxicity may need further evaluation.53 Sitamaquine, another oral agent, is currently being evaluated in phase II studies in India.11 This drug has been associated with a 50–67% cure rate.54 55 The imidazole and triazole drugs are not recommended for use in visceral leishmaniasis.
In PKDL, treatment is indicated only for those who have severe and prolonged disease. Pentavalent antimonials (2-month course usually sufficient) and liposomal amphotericin B are both effective.20
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
In deciding the best mode of treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis, some facts need to be considered. Old World cutaneous leishmaniasis is not a life threatening disease and >90% of patients heal spontaneously within 3–18 months. The outcome of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the New World depends on the infecting species and may vary from benign to more severe manifestations. It is thus important to try to identify the infecting species, either by knowing the endemic species of the specific geographical area, or by means of diagnostic procedures. This can throw light on the prognosis and management options.
Treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis will accelerate cure and reduce scarring. This is especially important at cosmetically important sites. Options in the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis include local or systemic treatment. Criteria in favour of local treatment56 include: Old World cutaneous leishmaniasis; small, single lesions; lack of risk of development of mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, lack of lymph node metastases; and L mexicana lesions. New World lesions except L mexicana, mucosal or lymph node involvement and lesions refractory to local treatment would be indications for systemic treatment.
Local treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis
Physical modes of treatment including cryotherapy have been employed with success ranging from 77% to 100% at 4 weeks.57 58 Local infrared heat lamps have also produced good results, although invariably accompanied by skin bulla formation.59
Paromomycin (aminosidine) ointment is produced in two different formulations. When combined with methylbenzethonium chloride, it gives cure rates of 74–85%, which is more effective than when combined with urea.60 However, paromomycin-methylbenzethonium causes more severe local inflammatory reactions than paromomycin-urea.61
Intralesional infiltration of the dermis and base of the lesion with pentavalent antimony may be performed. This is a relatively painful procedure which needs to be performed regularly every 1–2 weeks for about 3–8 times. The cure rate with this procedure is about 75%.11 If this is not effective, systemic therapy should be considered.
Imiquimod, a topical immunomodulator has been successfully used in combination with meglumine antimonate in cases resistant to meglumine alone.62
Systemic treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis
Systemic treatment with antimonials in general requires a 20-day course. L major, L tropica and L mexicana usually respond to a 10-day course.11 Pentamidine has been used as first line therapy in L guyanensis infection, but studies with L panamensis, L brasiliensis and L mexicana have also given a cure rate of 96%, comparable to 91% with meglumine antimonate.63 64
Of the imidazole/triazole drugs, oral fluconazole and has been found useful in L major infections, with a cure rate of 79%.65 Ketoconazole has been studied in L braziliensis panamensis with efficacy (74%) similar to that of stibogluconate (68%).66
Oral miltefosine has been studied in Colombia and Guatemala, with short-term cure rates of 91% in areas where L (V) panamensis is common. In areas where L (V) braziliensis and L mexicana mexicana are common, the cure rate fell to 53%.67
Liposomal amphotericin B has not been extensively studied in cutaneous leishmaniasis, but isolated reports of its use in resistant cases show its effectiveness.68 69 Similarly, systemic aminosidine has not been commonly used, and a study comparing it to antimonials for L braziliensis cutaneous leishmaniasis was not in favour of its use in this form.70
Allopurinol has shown some enhancing of antimonial activity, but its use alone has not shown any significant benefit.71
Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis
Treatment of mucocutaneous leishmaniasis with antimonials is unsatisfactory, especially in severe disease.72 Amphotericin B73 and more recently liposomal amphotericin B have been used in difficult cases with success.74 Steroids may have to be used in cases where respiratory compromise is possible.
Leishmania–HIV coinfection
There needs to be a high index of suspicion in patients with HIV with the typical presentations of visceral leishmaniasis such as pyrexia, pancytopenia and hepatosplenomegaly. However, splenomegaly may be absent in HIV.75 Uncommon sites of infection, such as the gastrointestinal tract or the upper respiratory tract, are more frequent. Diagnosis is reached as for non-HIV patients except that the Leishmania antibody test (direct agglutination test) is frequently (42.6%) negative.76 77 The highest prevalence of coinfection occurs in southwestern Europe, mostly in Spain.76 The main risk group is intravenous drug users and an anthroponotic cycle has been suggested where Leishmania organisms present in used syringes78 are inoculated intravenously.
The importance of cell-mediated immunity in controlling leishmaniasis in the long term is best illustrated in Leishmania–HIV coinfection. When visceral leishmaniasis occurs in a known HIV-positive patients or when someone with a history of visceral leishmaniasis acquires HIV, there is a high risk that the Leishmania infection will become intractable. Even after appropriate treatment of visceral leishmaniasis, Leishmania–HIV is associated with a high relapse rate of 52% after 1 month to 3 years.76 Visceral leishmaniasis in HIV infection is being proposed for inclusion in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC clinical category C for the definition of AIDS as an indicator disease.79
Although treatment of coinfection has not been adequately studied, pentavalent antimonials are still used widely. The relapse rate does not appear to be affected by the type of treatment given according to a head-to-head study between meglumine antimonate and amphotericin B.80 Meglumine antimonate and liposomal amphotericin have only been compared in smaller studies; no differences were found.81 One study suggested a role for oral miltefosine when the above treatments have failed in coinfected individuals.82
Secondary prophylaxis prevents relapse and improves survival.79 83 Both pentavalent antimonials administered once every 28 days84 and liposomal amphotericin B every 21 days may be used;83 no differences in efficacy have been found. Secondary prophylaxis should be continued at CD4 counts below 200/μl. It may be safe to stop secondary prophylaxis at CD4 counts above 350/μl and possibly even above 200/μl while on effective antiretroviral treatment.84 Antiretroviral treatment has been effective in decreasing relapses of visceral leishmaniasis.85
Control
Control of leishmaniasis depends on the prevalent local epidemiological characteristics. Thus in areas where sandflies are mostly endophilic (rest mostly indoors after feeding), spraying houses with insecticide is effective in reducing the likelihood of contracting cutaneous leishmaniasis.86 87 Treated and untreated bed nets have been used effectively in environments where sandflies are endophagic (feed mainly indoors).88 In some areas where the disease is transmitted anthroponotically, nets have also been used to prevent transmission from infected patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis. Other control strategies, including insecticide impregnated curtains, and insecticide treatment of dogs and dog collars have been used with good effect.89
Key references
Murray HW, Berman JD, Davies CR, et al. Advances in leishmaniasis. Lancet 2005;366:1561–77.
Davies CR, Kaye P, Croft SL, et al. Leishmaniasis: new approaches to disease control. BMJ 2003;326:377–82.
Guerin PJ, Olliaro P, Sundar S, et al. Visceral leishmaniasis: current status of control, diagnosis, and treatment, and a proposed research and development agenda. Lancet Infect Dis 2002;2:494–501.
Herwaldt BL. Leishmaniasis. Lancet 1999;354:1191–9.
Paredes R, Munoz J, Diaz I, et al. Symposium: Leishmaniasis in HIV infection. J Postgrad Med 2003;49:39–49.
In Brazil, dogs are culled if they test positive for Leishmania, but this strategy has not been effective.90 In southwestern Europe, where leishmaniasis is closely linked with intravenous drug abuse and HIV, control of HIV has yielded positive results.91 Needle-exchange interventions should have similar results.
In India, where anthroponotic transmission is important, effective treatment of patients, especially those with PKDL (who may act as long-term reservoirs), has been found to be effective in controlling transmission when combined with vector control.2
There is no effective vaccine for prevention of leishmaniasis. The closest effective alternative to vaccination follows from the traditional “leishmanisation” technique adopted in the Middle East and Eastern Europe. This involved the encouragement of sandfly bites on traditionally unexposed areas of skin, such as the buttocks. The resulting lesion would heal spontaneously, in the process providing immunity against cutaneous leishmaniasis in less acceptable areas, such as the face. Early studies recommended using L tropica inoculations to induce immunity.92 This technique has been further developed in Iran, where scientists have produced standardised and stable L major populations which can produce more consistent and acceptable iatrogenically-induced lesions.89
The safety and efficacy of live-attenuated and killed vaccines has been debated and shifts in favour of development some of these has been recorded in recent years. Killed vaccines were favoured in the 1990s because of safety problems with live-attenuated vaccines; however, recent advances in manipulation of the Leishmania genome may make development of a live attenuated vaccine more feasible.93
Work on recombinant DNA derived antigen vaccines and protein or peptide-based vaccines is a more recent approach, made possible by the Leishmania Genome Project (www.sanger.ac.uk/Projects/L_major/). The realisation that CD8 cells are as important as CD4 cells in inducing resistance94 and maintaining immunity has led to a shift in vaccine research.95 Most vaccine research is targeted against cutaneous leishmaniasis; any effectiveness against visceral leishmaniasis is uncertain. Work on a vaccine against human visceral leishmaniasis has been less successful,96 but should be boosted following success with a cutaneous leishmaniasis vaccine. Work on a canine visceral leishmaniasis vaccine seems to be more advanced.97
Conclusion
Leishmaniasis remains a problematic infection requiring either potentially toxic treatments or less toxic, but expensive drugs. However, the availability of newer oral agents may change the way this disease is managed. Relapse may occur, especially in situations where immunosuppression is present; secondary prophylaxis needs to be given in this setting. The combination of Leishmania, HIV and anthroponotic transmission between injecting drug users heralds a potential for higher incidence rates in endemic countries with severe drug abuse problems. In the absence of an effective vaccine, and with extension of endemicity, possibly due to climate change, these problems may become worse.
Multiple choice questions (true/false (T/F); answers at end of references)
1. Epidemiology
Leishmania is endemic in Australasia
Leishmania can be transmiited through infected syringes
The epidemiology of Leishmania is tightly knit with the epidemiology of the sandfly
The sandfly usually bites during the day
The number of countries where Leishmania is endemic is set to increase with global warming
2. Visceral leishmaniasis
Is characterised by splenomegaly and pancytopenia
Carries a low mortality if not treated
The organism is characteristically extracellular
Fatalities are usually the result of secondary bacterial infections
Almost always responds to antimony products
3. Immunology
An effective vaccine is available
The body's response to infection is T-cell mediated
The disease manifestation depends on Leishmania species and host response
Immunosuppression predisposes to Leishmania infection
Leishmania organisms can remain dormant for years in the reticulo-endothelial system
4. Treatment
Liposomal amphotericin is effective but very expensive
There are no oral medications to effectively treat Leishmania
Oral miltofisine is very effective in the treatment of kala azar
Cutaneous Leishmania can be treated both by physical and pharmacological means
Leishmania in the immunosuppressed usually necessitates secondary prophylaxis
5. Diagnosis
Identification of amastigotes in tissue smears or histology are commonly used methods of diagnosis
Antibody towards K39 antigen is proving useful, especially in field diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis
Tissue cultures are used routinely
Splenic aspirates are very sensitive and usually safe
Leishmania PCR is useless on blood samples
Acknowledgement
We are grateful to Dr Paul Cuschieri, Consultant Microbiologist St Luke's Hospital, Malta, for his helpful comments during production of this review.
Abbreviations
IFN - interferon
PCR - polymerase chain reaction
PKDL - post-kala azar dermal leishmaniasis
Th - T helper
Answers
1. (A) F, (B) T, (C) T, (D) F, (E) T; 2. (A) T, (B) F, (C) F, (D) T, (E) F; 3. (A) F, (B) T, (C) T, (D) T, (E) T; 4. (A) T, (B) F, (C) T, (D) T, (E) T; 5. (A) T, (B) T, (C) F, (D) F, (E) F.
Footnotes
Competing interests: None.
References
- 1. Murray H W. Kala-azar—progress against a neglected disease. N Engl J Med 2002. 22 1793 1794 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Guerin P J, Olliaro P, Sundar S. et al Visceral leishmaniasis: current status of control, diagnosis, and treatment, and a proposed research and development agenda. Lancet Infect Dis 2002. 2 494 501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Desjeux P. Leishmaniasis: current situation and new perspectives. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 2004. 27 305 318 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Herwaldt B L. Leishmaniasis. Lancet 1999. 354 1191 1199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Arias J R, Monteiro P S, Zicker F. The re-emergence of visceral leishmaniasis in Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 1996. 2 145 146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Desjeux P. The increase in risk factors for leishmaniasis worldwide. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2001. 95 239 243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Kuhn K G. Global warming and leishmaniasis in Italy. Bull Trop Med Int Health 1999. 7 1 2 [Google Scholar]
- 8. Hsia R. Leishmaniasis. 2005. http://www.emedicine.com/emerg/topic296.htm
- 9. Lainson R, Shaw J J. Evolution, classification and geographic distribution. In: Peters W, Killick-Kendrick R, eds. The leishmaniases in biology and medicine. V.1. London: Academic Press, 1987. 1 120
- 10. Zijlstra E E, El-Hassan A M. Visceral leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2001. 95 Suppl 1 S27 S58 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Murray H W, Berman J D, Davies C R. et al Advances in leishmaniasis. Lancet 2005. 366 1561 1577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Mandell G L, Bennett J E, Dolin R. Mandell, Douglas and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases, 6th edn. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2005. 2428 2442
- 13. Grech V, Mizzi J, Mangion M. et al Visceral leishmaniasis in Malta—an 18 year paediatric, population based study. Arch Dis Child 2000. 82 381 385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Gradoni L, Gramiccia M, Léger N. et al Isoenzyme characterization of Leishmania from man, dog and sandflies in the Maltese islands. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1991. 85 217 219 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. De Alencar J E, Neves J. Leishmaniose visceral (calazar). In: Veronesi R, ed. Doencas Infecciosas e Parasitarias, 7th edn. Rio de Janeiro: Editora Guanabara Koogan SA, 1982. 724
- 16. Manson-Bahr P E C, Southgate B A, Harvey A E C. Development of kala-azar in man after inoculation with a leishmania from a Kenyo sandfly. BMJ 1963. 1 1208 1210 [Google Scholar]
- 17. Manson-Bahr P E C, Apted F I C. Leishmaniasis. In: Manson-Bahr PEC, Apted FIC, eds. Manson's tropical diseases, 18th edn. London: Bailliere Tindall, 1982. 93 115
- 18. Stone H H, Tool C D, Pugsley W S. Kala-azar (visceral leishmanisis): report of a case with 34 month incubation period and positive Doan-Wright test. Ann Intern Med 1952. 36 686 693 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Wilson M E, Streit J A. Visceral leishmaniasis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1996. 25 535 551 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Zijlstra E E, El-Hassan A M. Post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2001. 95 Supp 1 S59 S76 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Smith P A J. Long incubation period in leishmaniasis. BMJ 1955. 2 1143 519334 [Google Scholar]
- 22. Marsden P D, Nonata R R. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis—a review of clinical aspects. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 1975. 9 309 326 [Google Scholar]
- 23. Stark C G, Wortmann G. Leishmaniasis. http://www.emedicine.com/MED/topic1275.htm
- 24. Heinzel F P, Sadick M D, Holaday B J. et al Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med 1989. 169 59 72 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Reiner S L, Wang Z E, Hatam F. et al TH1 and TH2 cell antigen receptors in experimental leishmaniasis. Science 1993. 259 1457 1460 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Reed S G, Scott P. T-cell and cytokine responses in leishmaniasis. Curr Opin Immunol 1993. 5 524 531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Sundar S, Reed S G, Sharma S. et al Circulating T helper 1 (TH1) cell- and TH2 cell-associated cytokines in Indian patients with visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1997. 56 522 525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Roberts L J, Handman E, Foote S J. Leishmaniasis. BMJ 2000. 321 801 804 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Costa C H N, Stewart J M, Gomes R B B. et al Asymptomatic human carriers of Leishmania chagasi. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2002. 66 334 337 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Dereure J, Duong Thanhb H. et al Visceral leishmaniasis. Persistence of parasites in lymph nodes after clinical cure. J Infect 2003. 47 77 81 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Sundar S, Sahu M, Mehta H. et al Noninvasive management of Indian visceral leishmaniasis: clinical application of diagnosis by K39 antigen strip testing at a kala-azar referral unit. Clin Infect Dis 2002. 35 581 586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Salotra P, Sreenivas G, Pogue G P. et al Development of a species-specific PCR assay for detection of Leishmania donovani in clinical samples from patients with kala-azar and post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis. J Clin Microbiol 2001. 39 849 854 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Sundar S, Agrawal S, Pai K. et al Detection of leishmanial antigen in the urine of patients with visceral leishmaniasis by latex agglutination test. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2005. 73 268 271 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Islam M Z, Itoh M, Mirza R. et al Direct agglutination test with urine samples for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2004. 70 78 82 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Belli A. Simplified polymerase chain reaction detection of new world Leishmania in clinical specimens of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1998. 58 102 109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. de Oliveira C I, Bafica A, Oliveira F. et al Clinical utility of polymerase chain reaction-based detection of Leishmania in the diagnosis of American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Clin Infect Dis 2003. 37 e149 e153 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Camargo M E, Rebonato C. Cross-reactivity in immuno-fluorescence test for Trypanosoma and Leishmania antibodies. A simple inhibition procedure to ensure specific results. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1969. 18 500 505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Lugo de yarbuh A. Studies of the leishmanin skin test positivity in cases with treatment anti-leishmania. Parasitol Día 1997. 21 3–4 76 80 [Google Scholar]
- 39. de Lima Barros M B, Schubach A, Francesconi-do-Valle A C. et al Positive Montenegro skin test among patients with sporotrichosis in Rio De Janeiro. Acta Trop 2005. 93 41 47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Sundar S, Jha T K, Thakur C P. et al Single-dose liposomal amphotericin B in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis in India: a multicenter study. Clin Infect Dis 2003. 37 800 804 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Wortmann G, Miller R S, Oster C. et al A randomized, double-blind study of the efficacy of a 10- or 20-day course of sodium stibogluconate for treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis in United States military personnel. Clin Infect Dis 2002. 35 261 267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. World Health Organization Control of the leishmaniasis. WHO Technical Report Series, 293. Geneva: WHO, 1990.
- 43. Gallin J I, Farber J M, Holland S M. et al Interferon-gamma in the management of infectious diseases. Ann Intern Med 1995. 123 216 224 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Gradoni L, Gramiccia M, Scalone A. Visceral leishmaniasis treatment, Italy. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003 Dec. http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol9no12/03-0178.htm [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 45. Syriopoulou V, Daikos G L, Theodoridou M. et al Two doses of a lipid formulation of amphotericin B for the treatment of Mediterranean visceral leishmaniasis. Clin Infect Dis 2003. 36 560 566 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Sundar S, Agrawal G, Rai M. et al Treatment of Indian visceral leishmaniasis with single or daily infusions of low dose liposomal amphotericin B: randomised trial. BMJ 2001. 323 419 422 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Sundar S, Makharia A, More D K. et al Short-course of oral miltefosine for treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. Clin Infect Dis 2000. 31 1110 1113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Jha T K, Sundar S, Thakur C P. et al Miltefosine, an oral agent, for the treatment of Indian visceral leishmaniasis. N Engl J Med 1999. 341 1795 1800 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Sundar S, Jha T K, Thakur C P. et al Oral miltefosine for Indian visceral leishmaniasis. N Engl J Med 2002. 347 1739 1746 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Sinha P K, Ranjan A, Singh V P. et al Visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar)—the Bihar (India) perspective. J Infect 2005;doi;10.1016/j.jinf.2005.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 51. Jha T K. Evaluation of diamidine compound (pentamidine isethionate) in the treatment resistant cases of kala-azar occurring in North Bihar, India. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1983. 77 167 170 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Jha T K. Randomised controlled trial of aminosidine (paromomycin) v sodium stibogluconate for treating visceral leishmaniasis in North Bihar, India. BMJ 1998. 316 1200 1205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Rosenthal E, Marty P. Recent understanding in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. J Postgrad Med. 2003;49 1 61 68 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Sherwood J A, Gachihi G S, Muiggai R K. et al Phase 2 efficacy trial of an oral 8–aminoquinoline (WR6026) for treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. Clin Infect Dis 1994. 19 1034 1039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Dietze R, Carvalho S F, Valli L C. et al Phase 2 trial of WR6026, an orally administered 8-aminoquinoline, in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania chagasi. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2001. 65 685 689 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Blum J, Desjeux, Schwartz E. et al Treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis among travellers. J Antimicrob Chemother 2004. 53 158 166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Bassiouny A, El Meshad M, Talaat M. et al Cryosurgery in cutaneous leishmaniasis. Br J Dermatol 1982. 107 467 474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Gurei M S, Tatli N, Ozbilge H. et al Efficacy of cryotherapy and intralesional pentostam in treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 2000. 30 169 176 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Junaid A J. Treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis with infrared heat. Int J Dermatol 1986. 25 470 472 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Garnier T, Croft L. Topical treatment for cutaneous leishmaniasis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2002. 3 538 544 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Bryceson A D, Murphy A, Moody A H. Treatment of ‘Old World' cutaneous leishmaniasis with aminosidine ointment: results of an open study in London. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1994. 88 226 228 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Arevalo I, Ward B, Miller R. et al Successful treatment of drug-resistant cutaneous leishmaniasis in humans by use of imiquimod, an immunomodulator. Clin Infect Dis 2001. 33 1847 1851 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Soto-Mancipe J, Grogl M, Berman J D. Evaluation of pentamidine for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Colombia. Clin Infect Dis 1993. 16 417 425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Soto J, Buffet P, Grogl M. et al Successful treatment of Colombian cutaneous leishmaniasis with four injections of pentamidine. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1994. 50 107 111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Alrajhi A A, Ibrahim E A, De Vol E B. et al Fluconazole for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania major. N Engl J Med 2002. 346 891 895 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Saenz R E, Paz H, Berman J D. Efficacy of ketoconazole against Leishmania braziliensis panamensis cutaneous leishmaniasis. Am J Med 1990. 89 147 155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Soto J, Arana B A, Toledo J. et al Miltefosine for New World cutaneous leishmaniasis. Clin Infect Dis 2004. 38 1266 1272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Brown M, Noursadeghi M, Boyle J. et al Successful liposomal amphotericin B treatment of Leishmania braziliensis cutaneous leishmaniasis. Br J Dermatol 2005. 153 203 205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Devlin R K, Parsonnet J, Klaus S N. Treatment of relapsed cutaneous Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis infection with liposomal amphotericin B. Infect Dis Clin Pract 2005. 13 84 86 [Google Scholar]
- 70. Hepburn N C, Tidman M J, Hunter J A A. Aminosidine (paromomycin) versus sodium stibogluconate for the treatment of American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1994. 88 700 703 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Martinez S, Marr J J. Allopurinol in the treatment of American cutaneous leishmaniasis. N Engl J Med 1992. 326 741 744 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Franke E D, Wignall F S, Cruz M E. et al Efficacy and toxicity of sodium stibogluconate for mucosal leishmaniasis. Ann Intern Med 1990. 113 934 940 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Sampaio S A P, Castro R M, Dillon N L. et al Treatment of mucocutaneous (American) leishmaniasis with amphotericin B: a report of 70 cases. Int J Dermatol 1971. 10 179 181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Amato V S, Nicodemo A C, Amato J G. et al Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis associated with HIV infection treated successfully with liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome). J Antimicrob Chemother 2000. 46 341 342 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Paredes R, Munoz J, Diaz I. et al Leishmaniasis in HIV infection. J Postgrad Med 2003. 49 39 49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. World Health Organization The leishmaniasis and Leishmania/HIV co-infections. WHO Fact Sheet no 116. WHO, May 2000.
- 77. Alvar J, Canavata C, Gutierreez-Solar B. et al Leishmania and human immunodeficiency virus co-infection: the first 10 years. Clin Microbiol Rev 1997. 10 298 319 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Cruz I, Morales M A, Noguer I. et al Leishmania in discarded syringes from intravenous drug users. Lancet 2002. 359 1124 1125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Pasquau F, Ena J, Sanchez R, Leishmania HIV Mediterranean Co-operative Group et al Leishmaniasis as an opportunistic infection in HIV-infected patients: determinants of relapse and mortality in a collaborative study of 228 episodes in a Mediterranean region. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2005. 24 411 418 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Laguna F, López-Vélez R, Pulido F. et al Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis in HIV-infected patients: a randomized trial comparing meglumine antimoniate with amphotericin B. AIDS 1999. 13 1063 1070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Goldsmith D R, Perry C M. Amphotericin B lipid complex: in visceral leishmaniasis. Drugs 2004. 64 1905 1913 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Sindermann H, Engel K R, Fischer C. et al The Miltefosine Compassionate Use Program. Oral miltefosine for leishmaniasis in immunocompromised patients: compassionate use in 39 patients with HIV infection. Clin Infect Dis 2004. 39 1520 1523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Lopez-Velez R, Videla S, Marquez M. et al Spanish HIV-Leishmania Study Group. Amphotericin B lipid complex versus no treatment in the secondary prophylaxis of visceral leishmaniasis in HIV-infected patients. J Antimicrob Chemother 2004. 53 540 543 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Berenguer J, Cosín J, Miralles P. et al Discontinuation of secondary anti-Leishmania prophylaxis in HIV-infected patients who have responded to highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2000. 14 2946 2948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Russo R, Nigro L, Panarello G. et al Clinical survey of Leishmania/HIV co-infection in Catania, Italy: the impact of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Ann Trop Med Parasitol 2003. 97 Suppl 1 149 155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Reyburn H, Ashford R, Mohsen M. et al A randomized controlled trial of insecticide-treated bednets and chaddars or top sheets, and residual spraying of interior rooms for the prevention of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Kabul, Afghanistan. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2000. 94 361 366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Davies C R, Llanos-Cuentas E A, Campos P. et al Spraying houses in the Peruvian Andes with lambda-cyhalothrin protects residents against cutaneous leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2000. 94 631 636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Bern C, Joshi A B, Jha S N. et al Factors associated with visceral leishmaniasis in Nepal: bed-net use is strongly protective. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2000. 63 184 188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Davies C R, Kaye P, Croft S L. et al Leishmaniasis: new approaches to disease control. BMJ 2003. 326 377 382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Carlos H N, Costa J M, Stewart R B B. et al Asymptomatic human carriers of Leishmania chagasi. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2002. 66 334 337 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. del Giudice P, Mary-Krause M, Pradier C. et al Impact of highly active antiretroviral therapy on the incidence of visceral leishmaniasis in a French cohort of patients infected with HIV. J Infect Dis 2002. 186 1366 1370 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Berberian D A. Vaccination and immunity against oriental sore. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1939. 33 87 88 [Google Scholar]
- 93. Handman E. Leishmaniasis: current status of vaccine development. Clin Microbiol Rev 2001. 14 229 243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Belkaid Y, Von Stebut E, Mendez S. et al CD8+ T cells are required for primary immunity in C57BL/6 mice following low-dose, intradermal challenge with Leishmania major. J Immunol 2002. 168 3992 4000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Rhee E G, Mendez S, Shah J A. et al Vaccination with heat-killed Leishmania antigen or recombinant leishmanial protein and CpG oligodeoxynucleotides induces long-term memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses and protection against Leishmania major infection. J Exp Med 2002. 195 1565 1573 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Khalil E A G, El Hassan A M, Zijlstra E E. et al Autoclaved Leishmania major vaccine for prevention of visceral leishmaniasis: a randomised, double-blind, BCG-controlled trial in Sudan. Lancet 2000. 356 1565 1569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Gradoni L. An update on antileishmanial vaccine candidates and prospects for a canine Leishmania vaccine. Vet Parasitol 2001. 100 87 103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]