Abstract
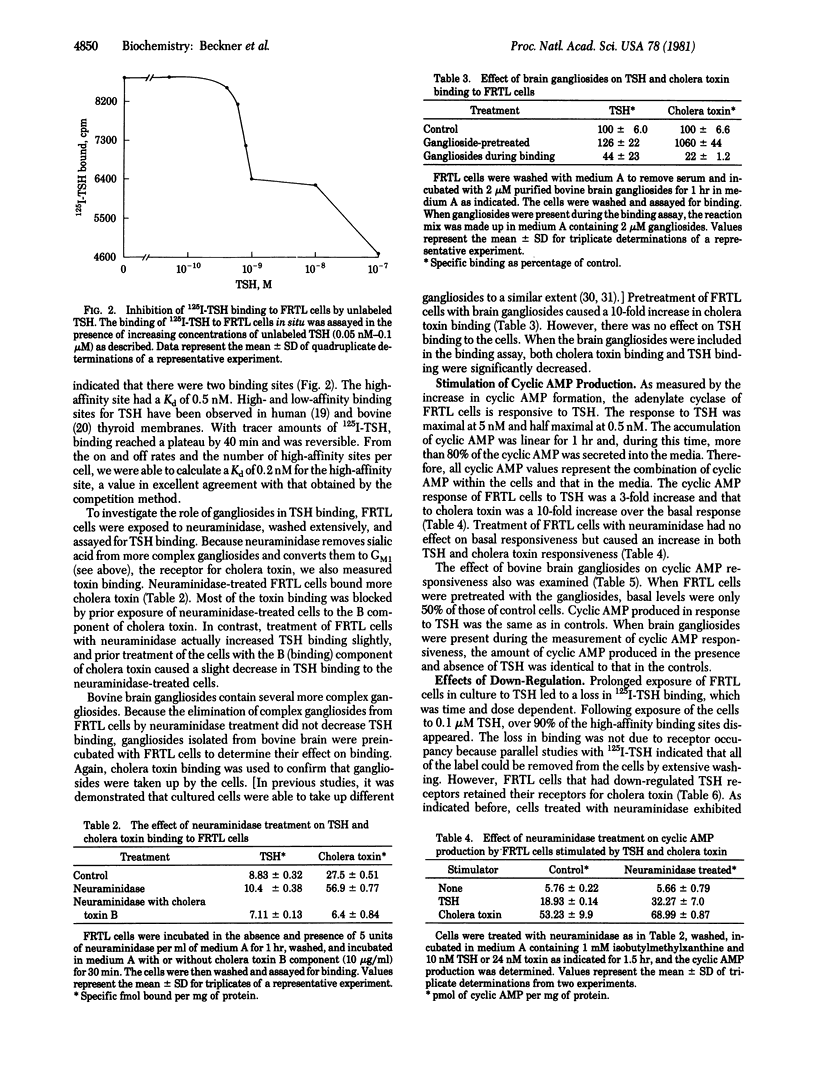
A cloned line of normal rat thyroid cells, FRTL, contained a small number of high-affinity binding sites for thyrotropin (TSH) when measured under physiological conditions. The cells also bound small amounts of cholera toxin, and both hormone and toxin stimulated cyclic AMP production by the cells. The major ganglioside of FRTL cells was N-acetylneuraminylgalactosylglucosylceramide (GM3), with minor amounts of gangliosides corresponding to galactosyl-N-acetylgalactosaminyl-[N-acetyl-neuraminyl]-galactosylglucosylceramide (GM1) and N-acetylneuraminylgalactosyl-N-acetylgalactosaminyl-[N-acetylneuraminyl]-galactosylglucosylceramide (GD1a). Treatment of these cells with neuraminidase (acylneuraminyl hydrolase, EC 3.2.1.18) converted most of the GD1a to GM1. After neuraminidase treatment, the binding of cholera toxin, which binds to GM1, was increased, but there was no change in the binding of TSH. Preincubation of neuraminidase-treated FRTL cells with the B (binding) component of cholera toxin completely prevented cholera toxin binding but had no effect on the binding of TSH. Neuraminidase treatment also somewhat enhanced, rather than decreased, the cyclic AMP response to TSH. Pretreatment of FRTL cells with mixed brain gangliosides resulted in a 10-fold increase in cholera toxin binding. Again there was no enhancement of TSH binding or adenylate cyclase stimulation. Finally, prolonged exposure of FRTL cells to TSH induced down-regulation of TSH receptors but had no effect on gangliosides or cholera toxin receptors. The results indicate that more complex gangliosides do not serve as a component of the TSH receptor nor are they involved in the transmission of the hormone signal across the cell membrane of these cultured rat thyroid cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloj S. M., Kohn L. D., Lee G., Meldolesi M. F. The binding of thyrotropin to liposomes containing gangliosides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91624-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloj S. M., Lee G., Consiglio E., Formisano S., Minton A. P., Kohn L. D. Dansylated thyrotropin as a probe of hormone-receptor interactions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9030–9039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloj S. M., Lee G., Grollman E. F., Beguinot F., Consiglio E., Kohn L. D. Role of phospholipids in the structure and function of the thyrotropin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9040–9049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambesi-Impiombato F. S., Parks L. A., Coon H. G. Culture of hormone-dependent functional epithelial cells from rat thyroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amir S. M., Goldfine I. D., Ingbar S. H. Properties of the interaction between bovine thyrotropin and bovine thyroid plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4693–4699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Aloj S. M., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O. Relationship of gangliosides to the structure and function of thyrotropin receptors: their absence on plasma membranes of a thyroid tumor defective in thyrotropin receptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4060–4064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin: studies on the lag period. J Membr Biol. 1980;54(1):61–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01875377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Moss J., Manganiello V. C. Synthesis and uptake of gangliosides by choleragen-responsive human fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1871–1875. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Moss J., Vaughan M. Uptake and metabolism of gangliosides in transformed mouse fibroblasts. Relationship of ganglioside structure to choleragen response. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4490–4494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman Y., Hladis P., Babiarz-Crowell D., Burke G. Effects of cholera toxin on thyroid cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and ornithine decarboxylase activities. Endocr Res Commun. 1979;6(1):71–92. doi: 10.3109/07435807909070885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes S. D., Titus G., Chou M., Field J. B. Effects of thyrotropin and cholera toxin on the thyroidal adenylate cyclase-adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate system. Endocrinology. 1980 Dec;107(6):2076–2081. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-6-2076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D., Mullin B. R., Lee G., Aloj S. M., Fishman P. H., Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O., Kohn L. D. Sequence similarity between cholera toxin and glycoprotein hormones: implications for structure activity relationship and mechanism of action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 19;69(4):852–859. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90452-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Grollman E. F., Aloj S. M., Kohn L. D., Winand R. J. Abnormal adenylate cyclase activity and altered membrane gangliosides in thyroid cells from patients with Graves' disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi M. F., Fishman P. H., Aloj S. M., Ledley F. D., Lee G., Bradley R. M., Bradley R. M., Brady R. O., Kohn L. D. Separation of the glycoprotein and ganglioside components of thyrotropin receptor activity in plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 11;75(3):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91512-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. V., Feldman L. Thyroid-stimulating hormone binding to beef thyroid membranes. Role of N-acetylneuraminic acid. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4247–4253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Fishman P. H., Richards R. L., Alving C. R., Vaughan M., Brady R. O. Choleragen-mediated release of trapped glucose from liposomes containing ganglioside GM1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3480–3483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Manganiello V. C., Fishman P. H. Enzymatic and chemical oxidation of gangliosides in cultured cells: effects of choleragen. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1876–1881. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Richards R. L., Alving C. R., Fishman P. H. Effect of the A and B protomers of choleragen on release of trapped glucose from liposomes containing or lacking ganglioside GM1. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):797–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Aloj S. M., Fishman P. H., Lee G., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O. Cholera toxin interactions with thyrotropin receptors on thyroid plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1679–1683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Fishman P. H., Lee G., Aloj S. M., Ledley F. D., Winand R. J., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O. Thyrotropin-ganglioside interactions and their relationship to the structure and function of thyrotropin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):842–846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Pacuszka T., Lee G., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O., Fishman P. H. Thyroid gangliosides with high affinity for thyrotropin: potential role in thyroid regulation. Science. 1978 Jan 6;199(4324):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4324.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omodeo-Sale F., Brady R. O., Fishman P. H. Effect of thyroid phospholipids on the interaction of thyrotropin with thyroid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5301–5305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacuszka T., Osborne J. C., Jr, Brady R. O., Fishman P. H. Interaction of human chorionic gonadotropin with membrane components of rat testes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):764–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Roth J., Macchia V. Binding of hormone to tissue: the first step in polypeptide hormone action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1802–1809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekonen F. Role of carbohydrates in thyrotropin binding sites. Horm Metab Res. 1980 Jul;12(7):310–314. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-996277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekonen F., Weintraub B. D. Thyrotropin receptors on bovine thyroid membranes: two types with different affinities and specificities. Endocrinology. 1979 Aug;105(2):352–359. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-2-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poss A., Deleers M., Ruysschaert J. M. Evidence for a specific interaction between GT1 ganglioside incorporated into bilayer membranes and thyrotropin. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 15;86(2):160–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80553-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell-Jones C. H., Thomas C. G., Jr, Nayfeh S. N. Thyrotropin receptors in normal human thyroid. Nonclassical binding kinetics not explained by the negative cooperativity model. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4001–4010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Powell-Jones C. H., Thomas C. G., Jr, Nayfeh S. N. Apparent "negative cooperativity" kinetics in the absence of a nonlinear Scatchard plot of thyrotropin-receptor interaction in a human thyroid adenoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 16;95(1):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90751-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate R. L., Holmes J. M., Kohn L. D., Winand R. J. Characteristics of a solubilized thyrotropin receptor from bovine thyroid plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6527–6533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Tosteson D. C. Bilayers containing gangliosides develop channels when exposed to cholera toxin. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):142–144. doi: 10.1038/275142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]