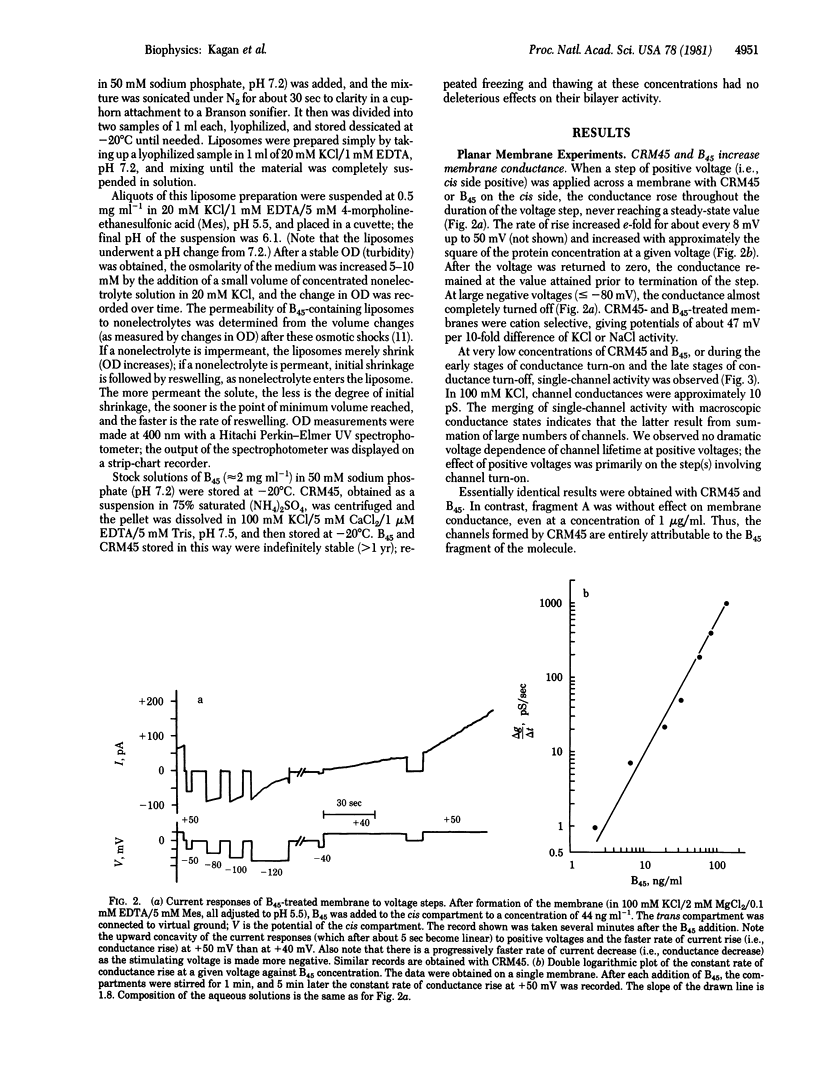
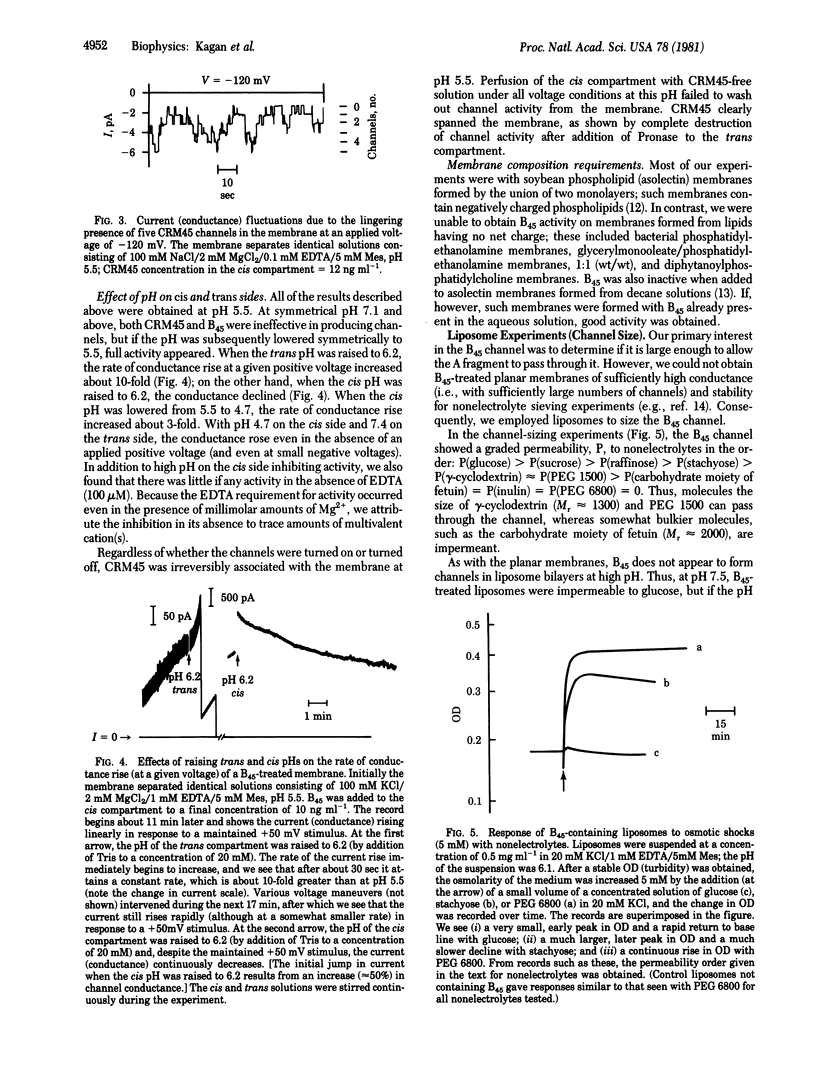
Abstract
The cytotoxic effect of diphtheria toxin requires the entry of its enzymatic A fragment (Mr approximately 21,000) into the cytosol of sensitive cells. We show that the B45 fragment (Mr approximately 24,000) forms, in lipid bilayers, pores that are large enough (diameter greater than or equal to 18 A) to allow the passage of extended fragment A. Pore formation is maximal when the B45-containing side is at low pH (4.7) and the opposite side is at high pH (7.4). These conditions resemble the pH gradient existing across lysosomal membranes. We suggest that fragment A passes through these pores from acidic endocytotic vesicles (lysosomes?) to the cytosol.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boquet P. Interaction of diphtheria toxin fragments A, B and protein crm 45 with liposomes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):483–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P., Silverman M. S., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Vernon W. B. Binding of triton X-100 to diphtheria toxin, crossreacting material 45, and their fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4449–4453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. J., Simon M. I., Draper R. K., Montal M. Diphtheria toxin forms transmembrane channels in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):172–176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R., Kandel J., Collier R. J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. II. Attack by trypsin at a specific site within the intact toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1504–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ermishkin L. N., Kasumov K. M., Potseluyev V. M. Properties of amphotericin B channels in a lipid bilayer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 1;470(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R., Finkelstein A. The water and nonelectrolyte permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):125–145. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Groman N. B. Mode of inhibition of diphtheria toxin by ammonium chloride. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1557–1562. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1557-1562.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S., Dorland R. B., Middlebrook J. L. Inhibition of diphtheria toxin degradation and cytotoxic action by chloroquine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2247–2250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Racker E. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles reconstituted with cytochrome c oxidase and mitochondrial hydrophobic protein. J Membr Biol. 1976 May;26(4):319–333. doi: 10.1007/BF01868880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:545–554. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Ultrastructural analysis of toxin binding and entry into mammalian cells. Nature. 1974 Oct 18;251(5476):628–630. doi: 10.1038/251628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes J., Latorre R. Effect of the anesthetics benzyl alcohol and chloroform on bilayers made from monolayers. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):259–279. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85175-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Diphtheria toxin entry into cells is facilitated by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):828–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Colombini M., Finkelstein A. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a voltage-dependent anion-selective channel obtained from paramecium mitochondria. J Membr Biol. 1976 Dec 28;30(2):99–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01869662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Konisky J. Effect of colicins Ia and E1 on ion permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6167–6171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. Protein conformation in biomembranes: optical rotation and absorption of membrane suspensions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):115–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


