Abstract
We present the primary structure of a chloroplast tRNAArgACG gene of the plant, Pelargonium zonale, and its faithful expression in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. This tRNAArg gene is located 250 bp downstream of a 5S RNA gene within a cloned 5kb long ribosomal DNA segment (Fig. 1). The Pelargonium tRNAArg gene shares 97% and 86% sequence homology with tRNAArgACG genes of Spirodela oligorhiza and Euglena gracilis chloroplasts, respectively, and also extensive homology (70%) with the corresponding gene of E. coli. It lacks an intervening sequence and, like eukaryotic tRNA genes, does not code for the 3' terminal CCA nucleotides. Moreover, the chloroplast tRNAArg gene carries all the sequence elements essential for transcription by vertebrate RNA polymerase III since it is efficiently expressed in Xenopus oocyte nuclei, even in the presence of 1 microgram/ml alpha-amanitin. In Xenopus oocyte nuclei, no transcripts of the chloroplast 5S RNA gene were detected.
Full text
PDF








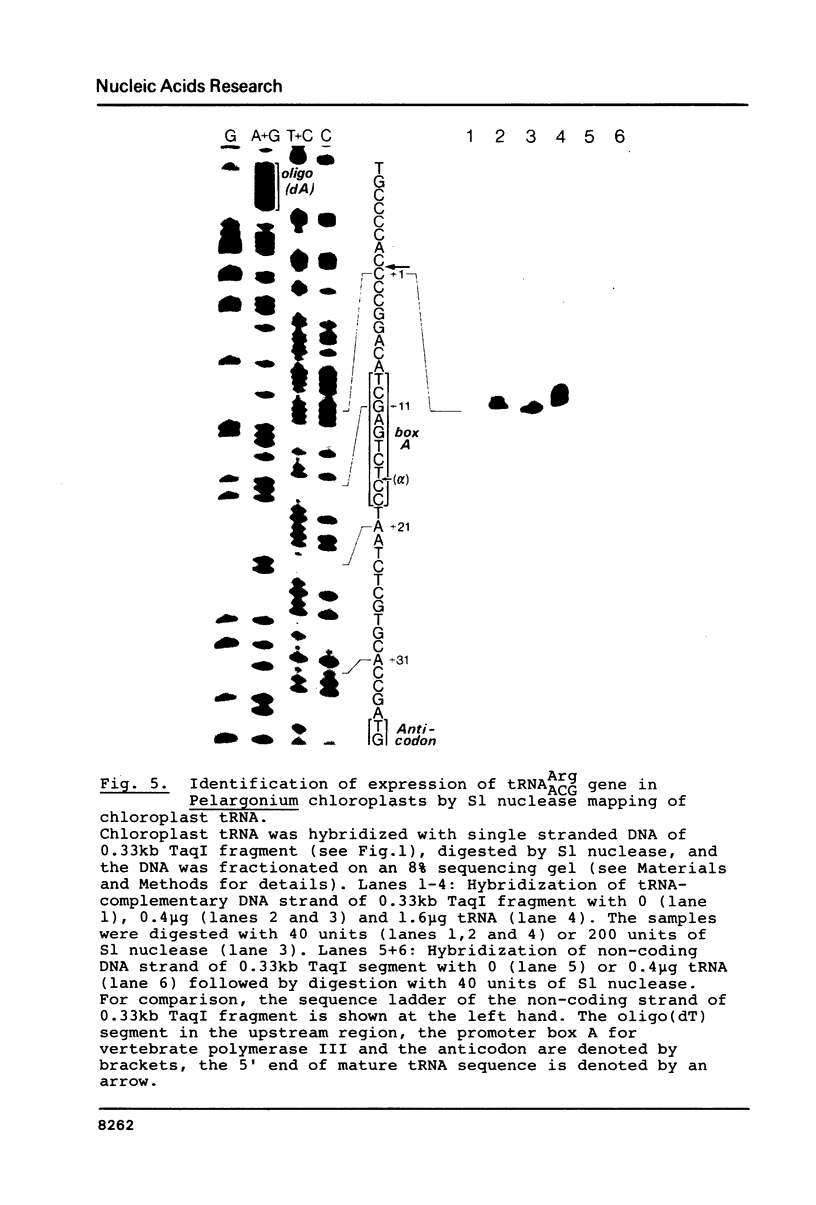






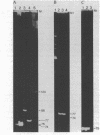
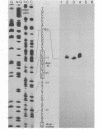
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartnik E., de Robertis E. M. Mitochondrial transfer RNA genes from fungi (Aspergillus nidulans) and plants (Lupinus luteus) are transcribed in Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 5;168(2):439–444. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Melton D. A., Cortese R. Promoter of a eukaryotic tRNAPro gene is composed of three noncontiguous regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1195–1199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Raugei G., Costanzo F., Dente L., Cortese R. Common and interchangeable elements in the promoters of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase iii. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Traboni C., Cortese R. Relationship between the two components of the split promoter of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1921–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J., Sprouse H. M., Dudock B. The nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast 5S ribosomal RNA from spinach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2801–2805. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Fasano O., Costanzo F., Traboni C., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. A prokaryotic tRNATyr gene, inactive in Xenopus laevis oocytes, is activated by recombination with an eukaryotic tRNAPro gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):817–820. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01253.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards K., Kössel H. The rRNA operon from Zea mays chloroplasts: nucleotide sequence of 23S rDNA and its homology with E.coli 23S rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2853–2869. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Hofstetter H. A detailed mutational analysis of the eucaryotic tRNAmet1 gene promoter. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Some bacterial tRNA genes are transcribed by eukaryotic RNA polymerase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7153–7162. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Sprinzl M. Compilation of sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):r55–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):r1–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Greenberg B. M., Zurawski G., Prescott D. M., Hallick R. B. Biosynthesis of chloroplast transfer RNA in a spinach chloroplast transcription system. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):815–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Prescott D. M., Greenberg B. M., Hallick R. B. Transcription of E. coli and Euglena chloroplast tRNA gene clusters and processing of polycistronic transcripts in a HeLa cell-free system. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley M. R., Head C. The synthesis of chloroplast high-molecular-weight ribosomal ribonucleic acid in spinach. Eur J Biochem. 1979 May 15;96(2):301–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haumont E., Fournier M., de Henau S., Grosjean H. Enzymatic conversion of adenosine to inosine in the wobble position of yeast tRNAAsp: the dependence on the anticodon sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2705–2715. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R. G., Bohnert H. J., Kowallik K. V., Schmitt J. M. Size, conformation and purity of chloroplast DNA of some higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 20;378(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato A., Shimada H., Kusuda M., Sugiura M. The nucleotide sequences of two tRNAAsn genes from tobacco chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5601–5607. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keus R. J., Stam N. J., Zwiers T., de Heij H. T., Groot G. S. The nucleotide sequences of the genes coding for tRNAArgUCU, tRNAArgACG and tRNAAsnGUU on Spirodela oligorhiza chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5639–5646. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Edwards K., Kössel H. Sequencing of the 16S-23S spacer in a ribosomal RNA operon of Zea mays chloroplast DNA reveals two split tRNA genes. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Clarkson S. G., Telford J. L., Birnstiel M. L. Transcription of xenopus tDNAmet1 and sea urchin histone DNA injected into the Xenopus oocyte nucleus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1077–1082. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J., Appel B., Schaack J., Sharp S., Yamada H., Söll D. The 5S RNA genes of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):487–500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., De Robertis E. M., Cortese R. Order and intracellular location of the events involved in the maturation of a spliced tRNA. Nature. 1980 Mar 13;284(5752):143–148. doi: 10.1038/284143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Gurdon J. B. Purified DNAs are transcribed after microinjection into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murao K., Tanabe T., Ishii F., Namiki M., Nishimura S. Primary sequence of arginine transfer RNA from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1332–1337. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., De Robertis E. M. RNA processing in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. Sequential addition of base modifications in the spliced transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 15;145(2):405–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast transfer RNA transcription units. II. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a tRNAVal-tRNAAsn-tRNAArg-tRNALeu gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3265–3275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. C., Doering J. L., Brown D. D. Characterization of two xenopus somatic 5S DNAs and one minor oocyte-specific 5S DNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Sugiura M. Nucleotide sequence of the 16S - 23S spacer region in an rRNA gene cluster from tobacco chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2665–2676. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboni C., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. A novel method for site-directed mutagenesis: its application to an eukaryotic tRNAPro gene promoter. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):415–420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Nazar R. N. Nucleotide sequence of wheat chloroplastid 4.5 S ribonucleic acid. Sequence homologies in 4.5 S RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11896–11900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]