Abstract
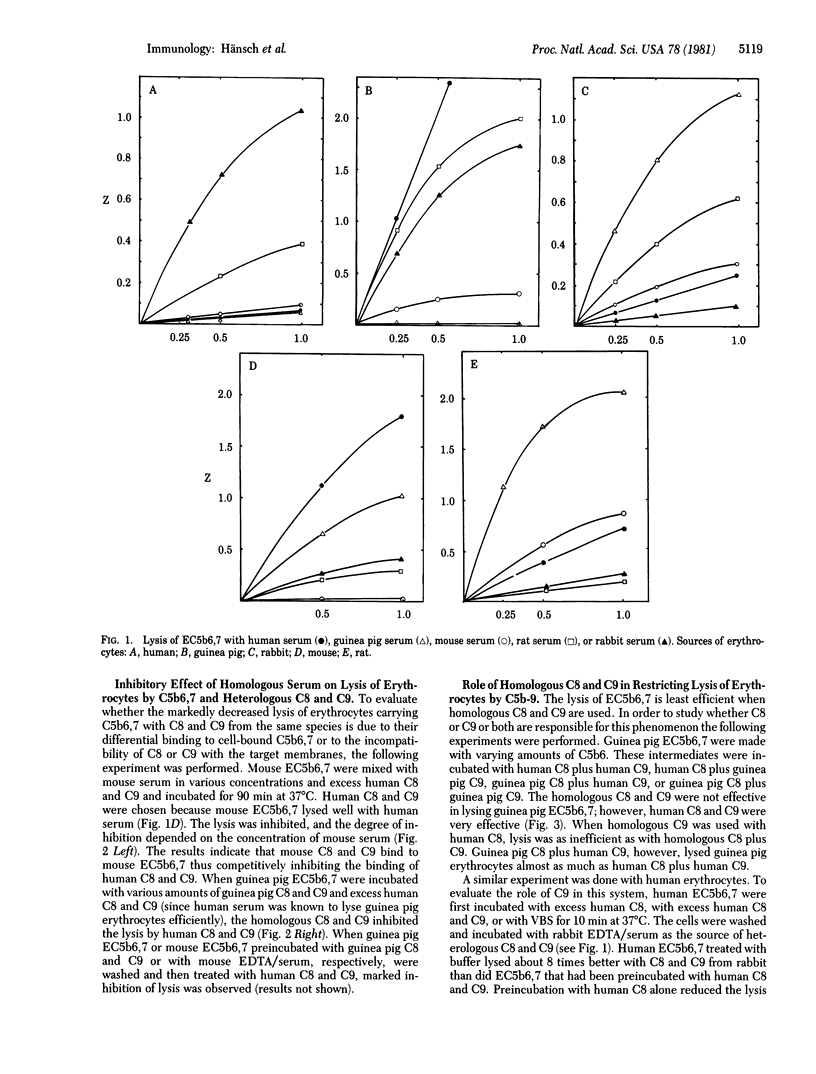
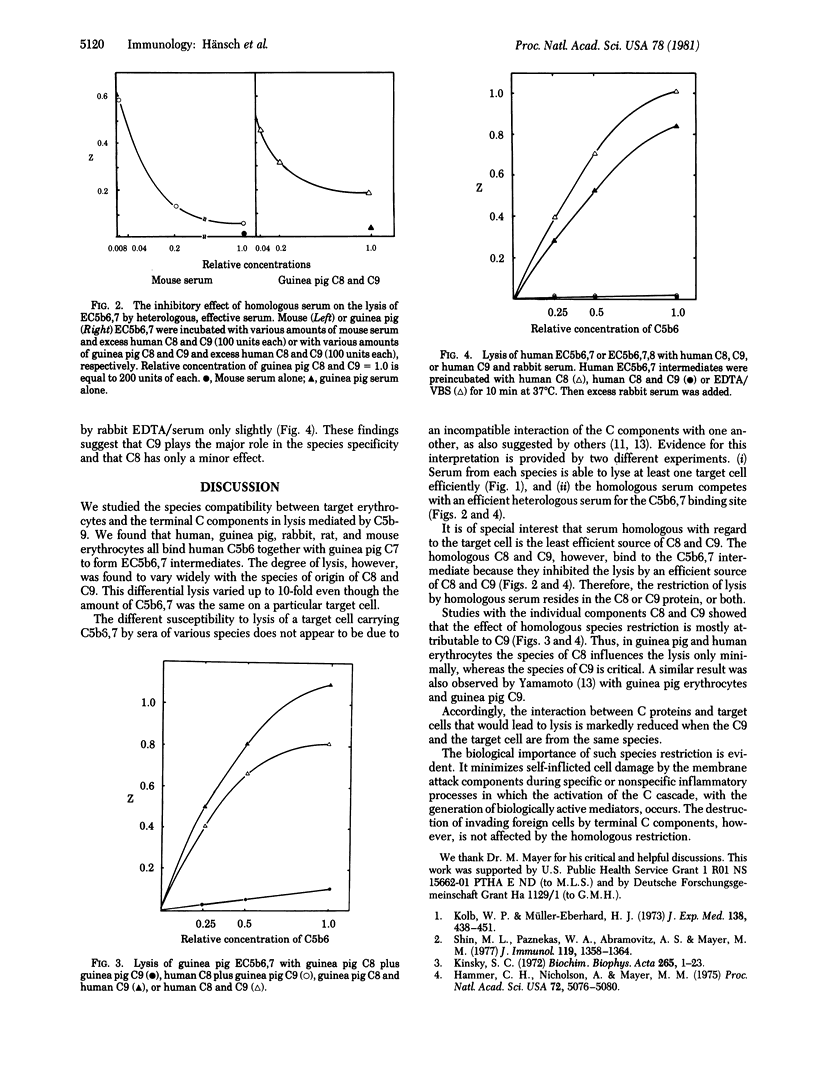
The cytolytic efficiency of the terminal complement protein complex, C5b-9, varies with the species of origin of C8 and C9. In the present study, we explored the susceptibility of erythrocytes from various species to lysis by C5b6,7 plus C8 and C9 from different species. EC5b6,7 intermediates were prepared on human, guinea pig, rabbit, mouse, and rat erythrocytes with human C5b6 and guinea pig C7. The degree of lysis of these intermediates by C8 and C9 was found to vary widely depending on the species of the proteins and the target cells. In all cases, lysis was least efficient when C8 and C9 were homologous with respect to the target cell species. This effect was mostly attributable to C9. The inefficient lysis in a homologous system is not due to a failure of C9 binding. Rather, the poor lysis in the homologous system may be attributable to inefficient insertion or channel formation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle M. D., Langone J. J., Borsos T. Studies on the terminal stages of immune hemolysis. III. Distinction between the insertion of C9 and the formation of a transmembrane channel. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1721–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldlust M. B., Shin H. S., Hammer C. H., Mayer M. M. Studies of complement complex C5b,6 eluted from--EAC-6: reaction of C5b,6 with EAC4b,3b and evidence on the role of C2a and C3b in the activation of C5. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):998–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Nicholson A., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of cytolysis by complement: evidence on insertion of C5b and C7 subunits of the C5b,6,7 complex into phospholipid bilayers of erythrocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5076–5080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Shin M. L., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of cell membrane damage by complement: evidence on insertion of polypeptide chains from C8 and C9 into the lipid bilayer of erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibody-complement interaction with lipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura H., Inai S. Molecular analysis of the reaction of C9 with EAC1-8: reaction of C9 with EAC1-8. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1992–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Verification of a stable C5-9 complex in free solution. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):438–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thompson R. A. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. II. The characterization of activated reactor as C56 and the participation of C8 and C9. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):643–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Packman C. H., Jenkins D. E., Jr, Countryman J. K., Leddy J. P. Complement lysis of human erythrocytes. III. Differing effectiveness of human and guinea pig C9 on normal and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2063–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin H. S., Pickering R. J., Mayer M. M. The fifth component of the guinea pig complement system. 3. Dissociation and transfer of C5b, and the probable site of C5b fixation. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):480–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin M. L., Paznekas W. A., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of membrane damage by C: exposure of hydrophobic sites on activated C proteins. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1358–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Shin H. S., Phillips J. K., Gewurz H., Mergenhagen S. E. A neutrophil chemotatic factor derived from C'5 upon interaction of guinea pig serum with endotoxin. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):413–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura N., Shimada A. The ninth component of guinea-pig complement. Isolation and identification as an alpha 2-globulin. Immunology. 1971 Mar;20(3):415–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Lachmann P. J. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. I. The characterization of the indicator factor and its identification as C7. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):629–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. I., Gewurz G. The complex of C5b and C6: isolation, characterization, and identification of a modified form of C5b consisting of three polypeptide chains. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2008–2015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. I. Lytic activity of C5-9 complexes for erythrocytes from the species other than sheep: C9 rather than C8-dependent variation in lytic activity. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1482–1485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



