Abstract
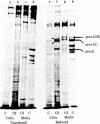
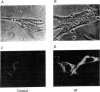
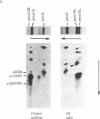
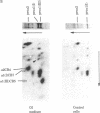
Osteogenesis imperfecta is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of inherited connective tissue disorders in which bone fragility is the predominant feature. Cultured dermal fibroblasts from one patient with the lethal perinatal form of osteogenesis imperfecta secrete type I procollagen at a rate half that of normal cells. Short-term labeling experiments and treatment with alpha,alpha'-dipyridyl (which prevents posttranslational prolyl and lysyl hydroxylation) demonstrated that these cells produce two distinct pro alpha 1(I) chains, which are synthesized at the same rate. Analysis of cyanogen bromide peptides indicated that the two chains differ in their primary structures. Thus, structural abnormalities in type I procollagen prevent this molecule from being secreted normally, resulting in an anomalously low ratio of type I procollagen to other extracellular matrix molecules. While the lethal perinatal form of osteogenesis imperfecta may be heterogeneous, we propose that the underlying pathogenesis of at least one form is decreased secretion of type I procollagen.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg R. A., Schwartz M. L., Crystal R. G. Regulation of the production of secretory proteins: intracellular degradation of newly synthesized "defective" collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4746–4750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowski R. S., Baum B. J., Crystal R. G. Fibroblasts degrade newly synthesised collagen within the cell before secretion. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):413–416. doi: 10.1038/276413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Structurally distinct collagen types. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:957–1003. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Holbrook K. A., Barsh G. S., Smith L. T., Bornstein P. Altered secretion of type III procollagen in a form of type IV Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Biochemical studies in cultured fibroblasts. Lab Invest. 1981 Apr;44(4):336–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetta G., Lenzi L., Rizzotti M., Ruggeri A., Valli M., Boni M. Osteogenesis imperfecta: morphological, histochemical and biochemical aspects. Modifications induced by (+)-catechin. Connect Tissue Res. 1977;5(1):51–58. doi: 10.3109/03008207709152612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvin E. E., Glorieux F. H., Lopez E. In vitro sulfate turnover in osteogenesis imperfecta congenita and tarda. Am J Med Genet. 1979;4(4):349–355. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320040406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engfeldt B., Hjerpe A. Glycosaminoglycans of cartilage and bone tissue in two cases of osteogenesis imperfecta congenita. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1976 Nov;84(6):488–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler J. H., Fessler L. I. Biosynthesis of procollagen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:129–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Smith R. Polymeric collagen of skin in osteogenesis imperfecta, homocystinuria and Ehlers-Danlos and Marfan syndromes. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(6):15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii K., Tanzer M. L. Osteogenesis imperfecta: biochemical studies of bone collagen. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977 May;(124):271–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood R., Grant M. E., Jackson D. S. The route of secretion of procollagen. The influence of alphaalpha'-bipyridyl, colchicine and antimycin A on the secretory process in embryonic-chick tendon and cartilage cells. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):81–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1560081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller R. H., Winn K. J., Heller R. M. The prenatal diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta congenita. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Feb 15;121(4):572–573. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao W. W., Prockop D. J., Berg R. A. Kinetics for the secretion of nonhelical procollagen by freshly isolated tendon cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2234–2243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. S., Salinas C. F., Jorgenson R. J. Classification of osteogenesis imperfecta by dental characteristics. Lancet. 1978 Feb 11;1(8059):332–333. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Williamson A. R. Structural mutations in a mouse immunoglobulin light chain resulting in failure to be secreted. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A. C., Pope F. M., Schloon H. Biochemical heterogeneity of osteogenesis imperfecta: New variant. Lancet. 1979 Jun 2;1(8127):1193–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91872-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Davidson J. M., Gagnon J., Rowe D. W., Bornstein P. NH2-terminal sequence of the chick proalpha1(I) chain synthesized in the reticulocyte lysate system. Evidence for a transient hydrophobic leader sequence. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1433–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson C. R. Heterogeneity of osteogenesis imperfecta congenita. Lancet. 1980 Apr 12;1(8172):821–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen L., Palotie A., Prockop D. J. A defect in the structure of type I procollagen in a patient who had osteogenesis imperfecta: excess mannose in the COOH-terminal propeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6179–6183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttinen R. P., Lichtenstein J. R., Martin G. R., McKusick V. A. Abnormal collagen metabolism in cultured cells in osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):586–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillence D. O., Senn A., Danks D. M. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1979 Apr;16(2):101–116. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann B. U., Martin G. R., Baum B. I., Crystal R. G. Synthesis and degradation of collagen by skin fibroblasts from controls and from patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 15;101(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Rubin D., Gross J. Osteogenesis imperfecta congenita: evidence for a generalized molecular disorder of collagen. Lab Invest. 1977 May;36(5):501–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turakainen H., Larjava H., Saarni H., Penttinen R. Synthesis of hyaluronic acid and collagen in skin fibroblasts cultured from patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 3;628(4):388–397. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. D., Harper P. S. Recurrence risk in osteogenesis imperfecta congenita. Lancet. 1980 Feb 23;1(8165):432–432. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90988-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]