Abstract
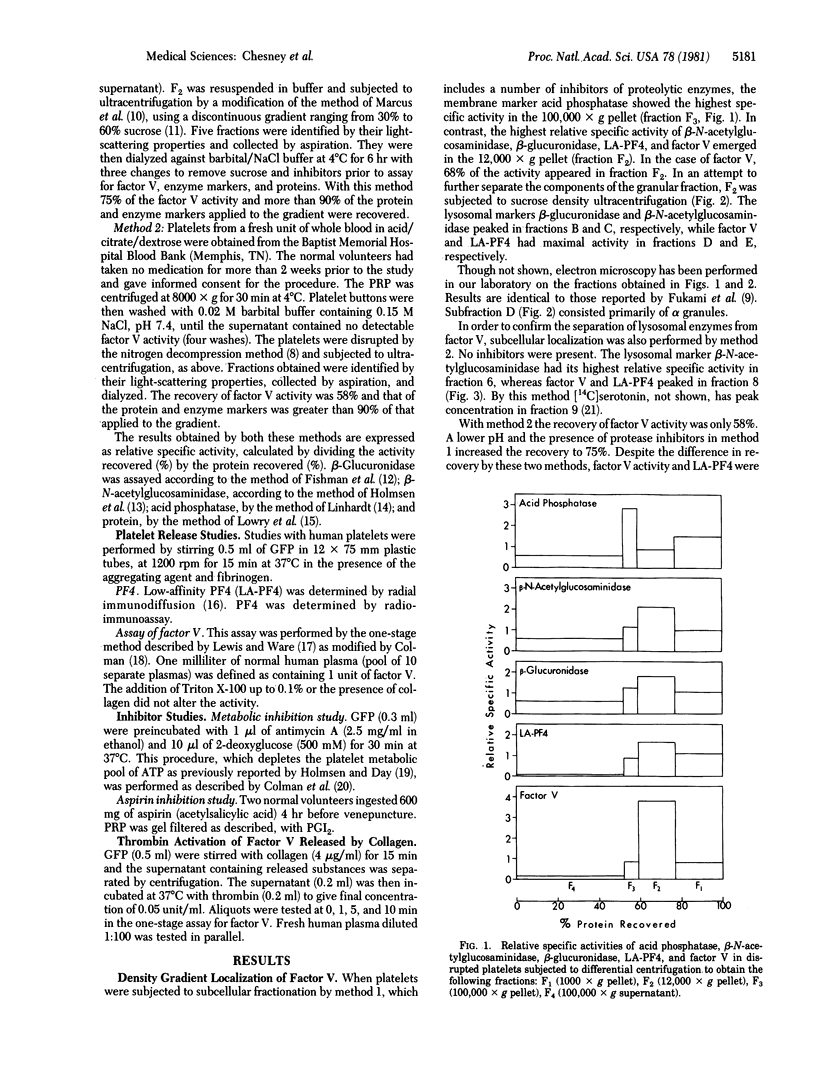
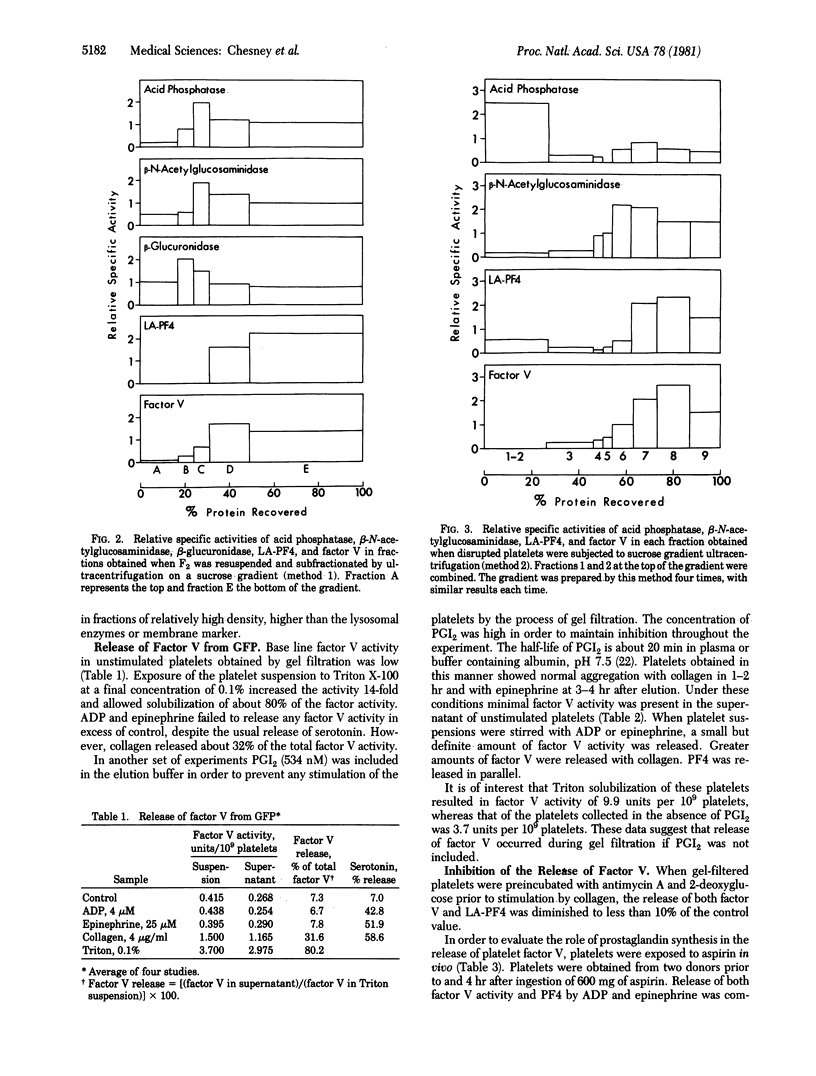
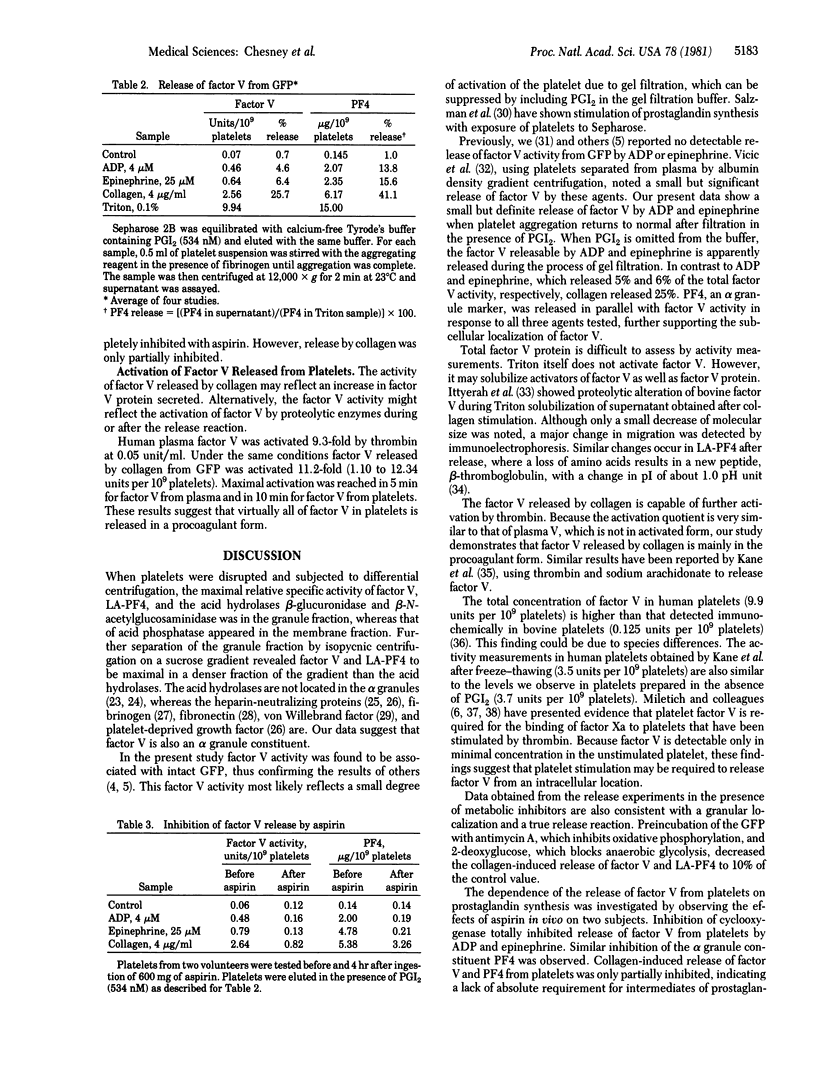
Factor V, a plasma protein cofactor necessary for optimal conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, is also present in considerable concentration in blood platelets (9.9 units per 10(9) platelets). Subcellular fractionation by two methods has localized factor V in the alpha granules of unstimulated platelets. ADP and epinephrine cause release of 4.6% and 6.4%, respectively, of the total factor V, a process completely inhibited by cyclooxygenase alkylation by aspirin. In contrast, collagen causes release of 25% of platelet factor V, a process only partially suppressed by aspirin. Secretion of factor V depends on the availability of metabolic energy, because antimycin A, an inhibitor of aerobic metabolism, and 2-deoxyglucose, an inhibitor of anaerobic glycolysis, together almost totally inhibited the secretion of factor V induced by collagen. The data establish that factor V is not normally available on unstimulated platelets but can be secreted from alpha granules upon stimulation with physiological agents such as ADP, epinephrine, and collagen. Because factor V is known to serve as a receptor for factor Xa, the exposure of factor V on platelets consequent to release would accelerate the process of blood coagulation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentfeld M. E., Bainton D. F. Cytochemical localization of lysosomal enzymes in rat megakaryocytes and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1635–1649. doi: 10.1172/JCI108246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breederveld K., Giddings J. C., ten Cate J. W., Bloom A. L. The localization of factor V within normal human platelets and the demonstration of a platelet-factor V antigen in congenital factor V deficiency. Br J Haematol. 1975 Mar;29(3):405–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Handin R. I., Cohen P. Distribution of fibrinogen, and platelet factors 4 and XIII in subcellular fractions of human platelets. Br J Haematol. 1975 Sep;31(1):51–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Westmoreland N. P., Cohen P. An improved method for isolating alpha granules and mitochondria from human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):507–519. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney C. M., Harper E., Colman R. W. Critical role of the carbohydrate side chains of collagen in platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2693–2701. doi: 10.1172/JCI107088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney C. M., Harper E., Colman R. W. Human platelet collagenase. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1647–1654. doi: 10.1172/JCI107715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Kuchibhotla J., Schreiber A. D. Effect of heterologous antiplatelet antibody on human platelets: a new pathway to platelet alteration. Blood. 1977 Oct;50(4):575–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. The effect of proteolytic enzymes on bovine factor V. I. Kinetics of activation and inactivation by bovine thrombin. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1438–1445. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami M. H., Bauer J. S., Stewart G. J., Salganicoff L. An improved method for the isolation of dense storage granules from human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):389–399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami M. H., Niewiarowski S., Rucinski B., Salganicoff L. Subcellular localization of human platelet antiheparin proteins. Thromb Res. 1979 Feb-Mar;14(2-3):433–443. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJORT P., RAPAPORT S. I., OWREN P. A. Evidence that platelet accelerator (platelet factor 1) is adsorbed plasma proaccelerin. Blood. 1955 Nov;10(11):1139–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Day H. J. Adenine nucleotides and platelet function. Ser Haematol. 1971;4(1):28–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Setkowsky C. A., Lages B., Day H. J., Weiss H. J., Scrutton M. C. Content and thrombin-induced release of acid hydrolases in gel-filtered platelets from patients with storage pool disease. Blood. 1975 Jul;46(1):131–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Lindhout M. J., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Factor Va-dependent binding of factor Xa to human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1170–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Lindhout M. J., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Factor Va-dependent binding of factor Xa to human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1170–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. L., Broekman M. J., Chernoff A., Lesznik G. R., Drillings M. Platelet alpha-granule proteins: studies on release and subcellular localization. Blood. 1979 Apr;53(4):604–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS M. L., WARE A. G. A simple procedure for separation of prothrombin and accelerator globulin from citrated human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):636–640. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L. Studies on human platelet granules and membranes. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):14–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI105318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Interaction of coagulation factor Xa with human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Majerus D. W., Majerus P. W. Patients with congenital factor V deficiency have decreased factor Xa binding sites on their platelets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):824–831. doi: 10.1172/JCI109194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Jaffe E. A. Subcellular platelet factor VIII antigen and von Willebrand factor. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1101–1113. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Lowery C. T., Hawiger J., Millman M., Timmons S. Immunoassay of human platelet factor 4(PF4, antiheparin factor) by radial immunodiffusion. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Apr;87(4):720–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I., Lavine K. K. Factor V activity of platelets: evidence for an activated factor V molecule and for a platelet activator. Blood. 1977 May;49(5):819–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer D. D., Cagen L. M., Chesney C. M. Stability of prostaglandin I2 in human blood. Prostaglandins. 1981 Feb;21(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucinski B., Niewiarowski S., James P., Walz D. A., Budzynski A. Z. Antiheparin proteins secreted by human platelets. purification, characterization, and radioimmunoassay. Blood. 1979 Jan;53(1):47–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W., Lindon J. N., Rodvien R. Cyclic AMP in human blood platelets: relation to platelet prostaglandin synthesis induced by centrifugation or surface contact. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1976;2(1):25–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel A., Lüscher E. F. Non-identity of the alpha-granules of human blood platelets with typical lysosomes. Nature. 1967 Aug 12;215(5102):745–747. doi: 10.1038/215745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangen O., Berman H. J., Marfey P. Gel filtration. A new technique for separation of blood platelets from plasma. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Jun 30;25(2):268–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Peterson J. M., Nesheim M. E., McDuffie F. C., Mann K. G. Interaction of coagulation factor V and factor Va with platelets. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10354–10361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicic W. J., Lages B., Weiss H. J. Release of human platelet factor V activity is induced by both collagen and ADP and is inhibited by aspirin. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):448–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Mosesson M. W., Broekman M. J., Kaplan K. L. Release of platelet fibronectin (cold-insoluble globulin) from alpha granules induced by thrombin or collagen; lack of requirement for plasma fibronectin in ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Blood. 1979 Jul;54(1):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



