Abstract
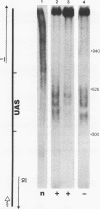
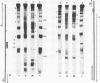
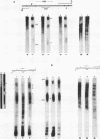
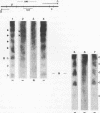
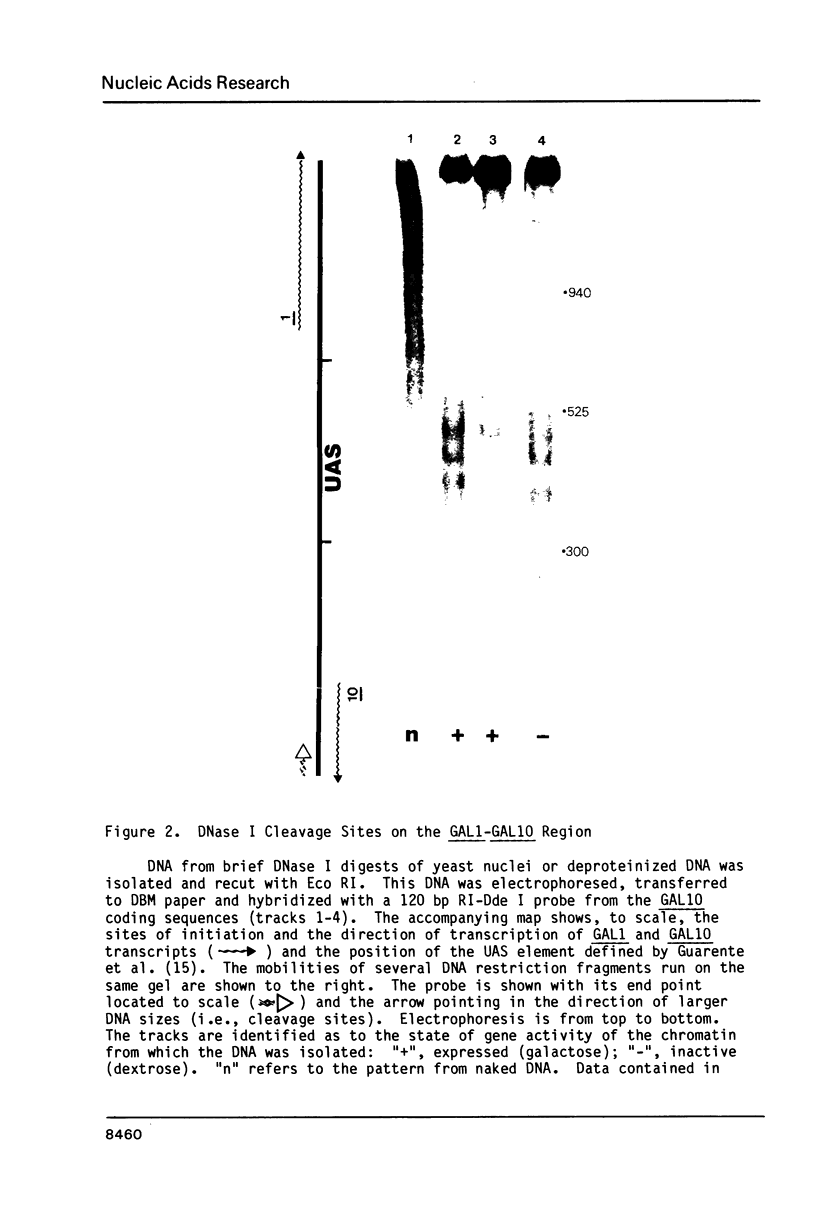
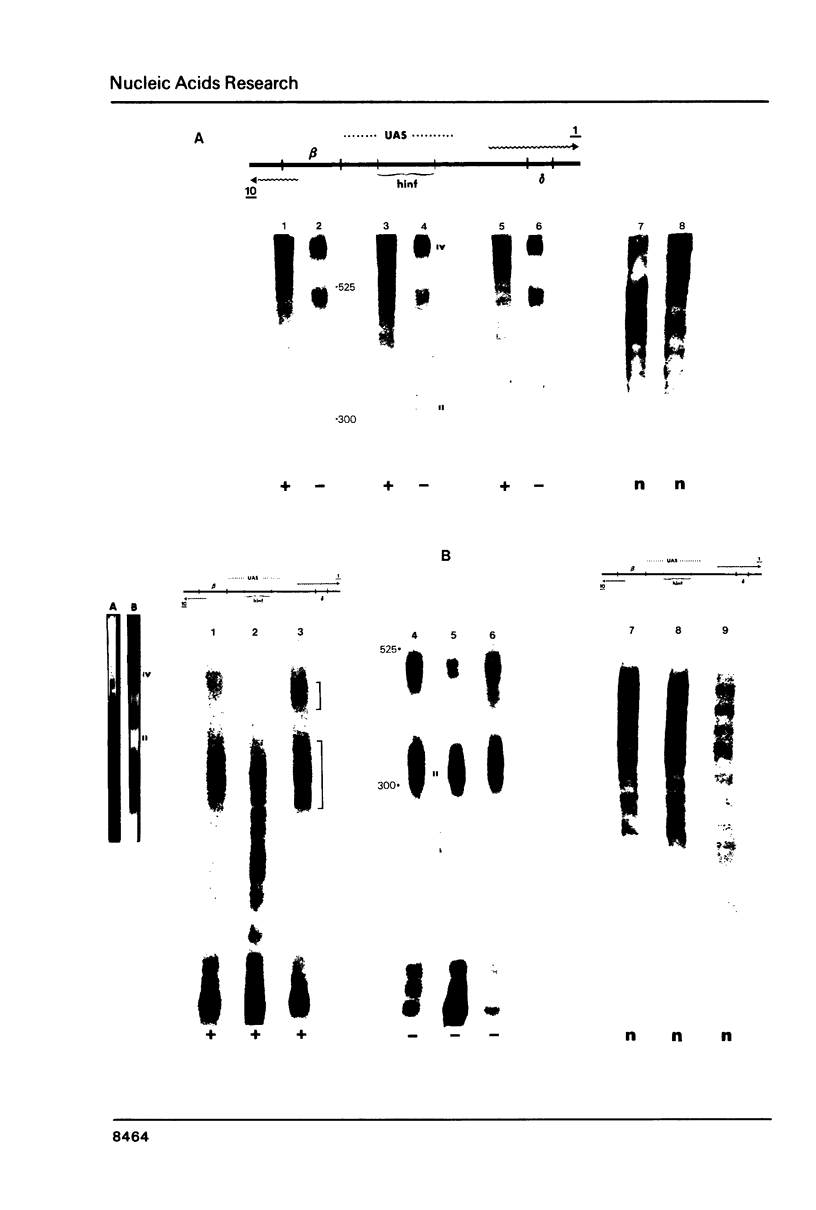
A defined, "far upstream" promoter element, the Upstream Activator Sequence (UAS), which mediates the galactose dependent induction of expression of the GAL10 gene in yeast, is the locus of an anomalous, mainly expression independent chromatin structure. The UAS chromatin shows three symmetrical DNase I hypersensitive sites in brief digests, a loss of the 10 bp DNase I ladder pattern in more extensive digests and an enhanced staphylococcal nuclease sensitivity. This anomalous structure is confined to a small region of the UAS. The surrounding chromatin, including the TATA box regions shows a more typical, but expression dependent nucleoprotein, probably nucleosomal, organization. Such an arrangement may be a common feature of eukaryotic genes.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R. Galactose regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The enzymes encoded by the GAL7, 10, 1 cluster are co-ordinately controlled and separately translated. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 15;131(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Chromatin structure, DNA structure. Nature. 1982 Dec 2;300(5891):402–403. doi: 10.1038/300402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M. Repair of overlapping DNA termini. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):63–64. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. E., Broach J. R., Rowe L. B. Regulation of the galactose pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: induction of uridyl transferase mRNA and dependency on GAL4 gene function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2878–2882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpov V. L., Preobrazhenskaya O. V., Mirzabekov A. D. Chromatin structure of hsp 70 genes, activated by heat shock: selective removal of histones from the coding region and their absence from the 5' region. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Wang J. C. Mapping the topography of DNA wrapped around gyrase by nucleolytic and chemical probing of complexes of unique DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Sr DNases and their use in the studies of primary structure of nucleic acids. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:165–220. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A., Noll M. Chromatin fine structure of active and repressed genes. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):198–203. doi: 10.1038/289198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D. A protected region upstream and limited nucleosomal positioning downstream of the transcription initiation region of the yeast 35S ribosomal gene. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4527–4534. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D. Chromatin structure differs between coding and upstream flanking sequences of the yeast 35S ribosomal genes. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):927–934. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Klug A. Sequence-dependent variation in the conformation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):745–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedospasov S. A., Georgiev G. P. Non-random cleavage of SV40 DNA in the compact minichromosome and free in solution by micrococcal nuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y., Matsumoto K., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Interaction of super-repressible and dominant constitutive mutations for the synthesis of galactose pathway enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):137–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00268810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Hopper J. E. Constitutive synthesis of the GAL4 protein, a galactose pathway regulator in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Helical periodicity of DNA determined by enzyme digestion. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):573–578. doi: 10.1038/286573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A., Galas D. J. The interaction of RNA polymerase and lac repressor with the lac control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):111–137. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. Isolation of galactose-inducible DNA sequences from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by differential plaque filter hybridization. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. The organization and transcription of the galactose gene cluster of Saccharomyces. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):285–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwag E. J., Dahlberg A. E. Electrophoretic transfer of DNA, RNA and protein onto diazobenzyloxymethyl (DBM) - paper. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):299–317. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wong Y. C., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]