Abstract
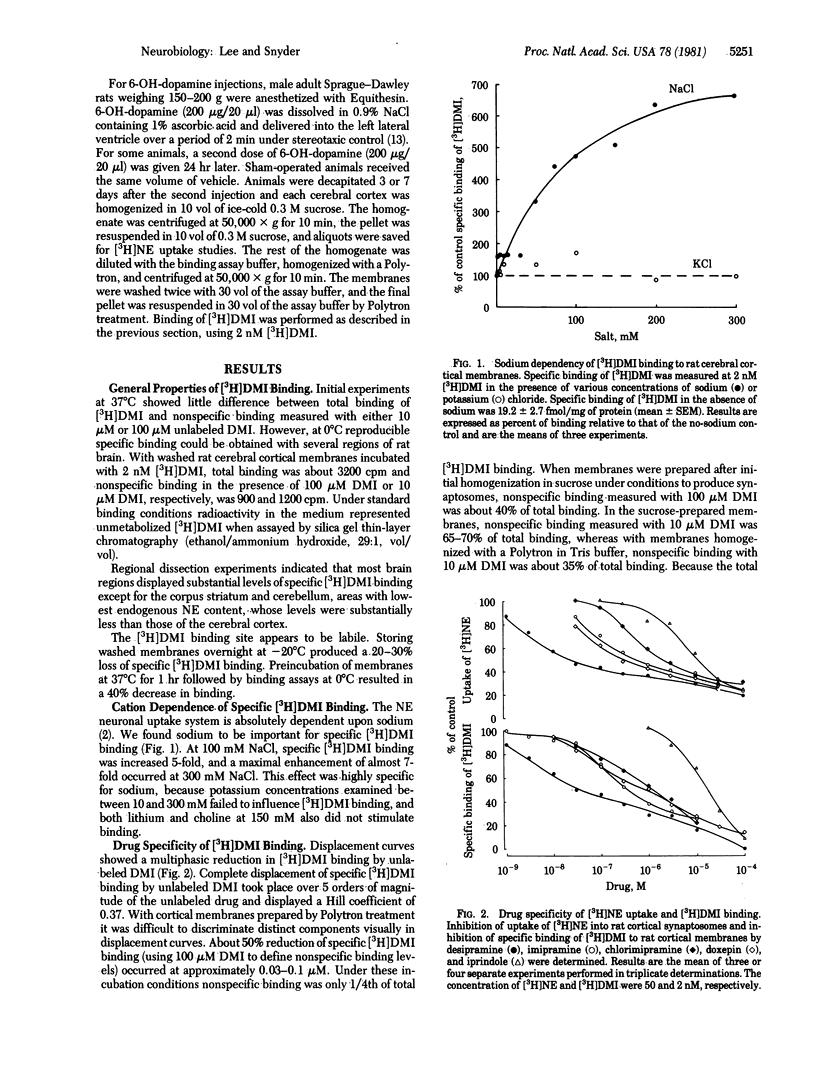
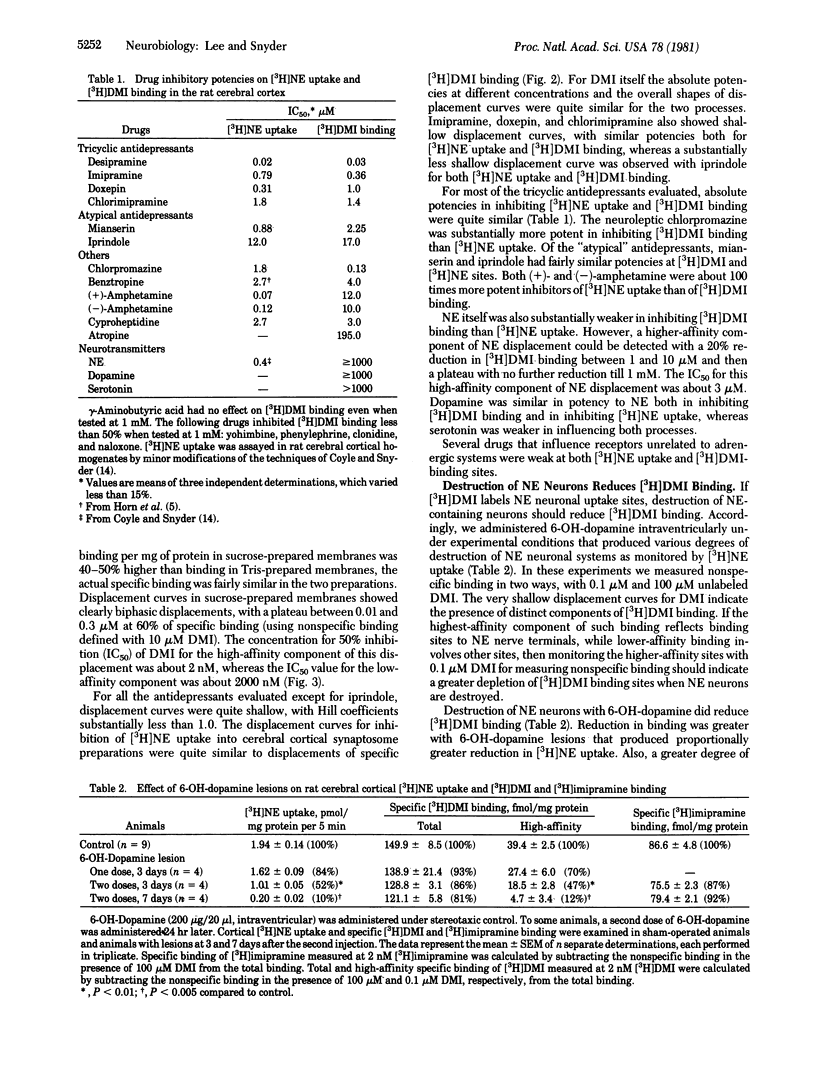
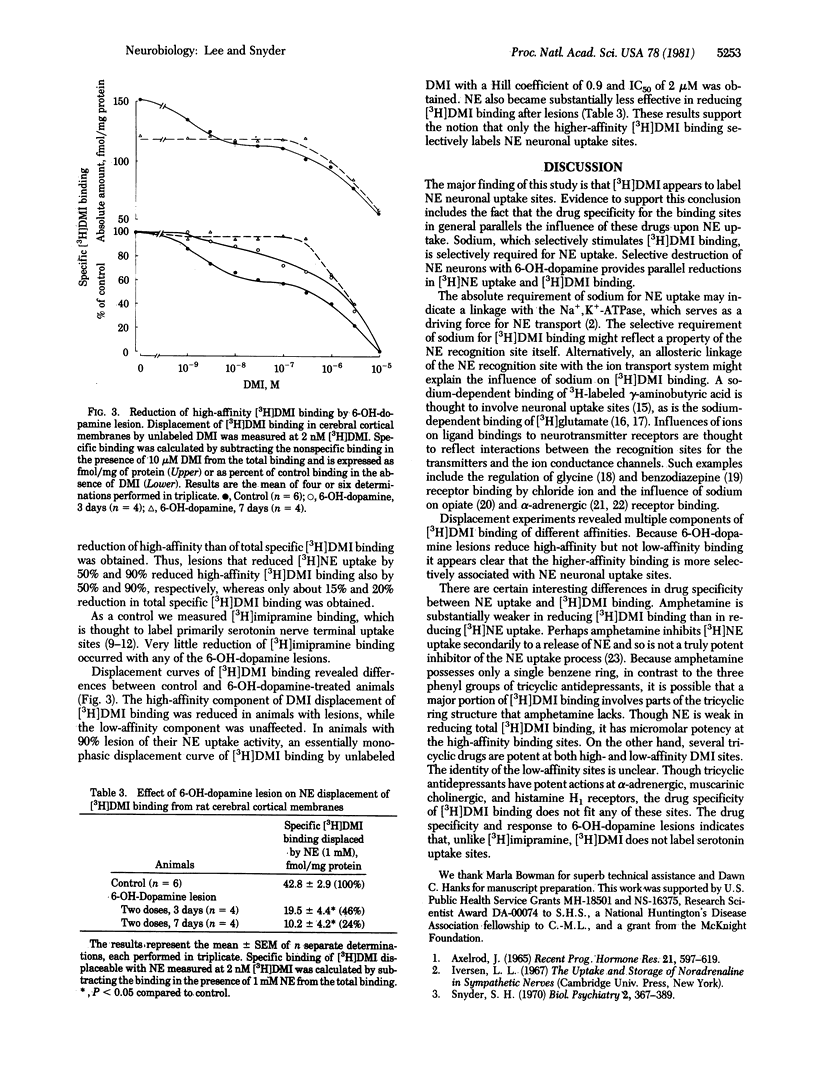
Neuronal uptake recognition sites in norepinephrine neurons have been labeled with the antidepressant [3H]desipramine. A high-affinity component of [3H]desipramine binding to rat cerebral cortex membranes is abolished selectively by 6-hydroxydopamine lesions, which destroy central catecholamine neurons. The high-affinity [3H]desipramine binding has a nanomolar affinity constant for desipramine and is inhibited by tricyclic antidepressants with potencies that correlate with their ability to inhibit the neuronal uptake of norepinephrine. [3H]Desipramine binding to the uptake sites is markedly stimulated by sodium, with potassium, lithium, and choline being much less effective. The ability to monitor norepinephrine neuronal uptake "receptors" in simple binding studies should permit a differential analysis of drug influences on the norepinephrine recognition site and the translocation mechanism. The regulation of [3H]desipramine binding by sodium may help clarify how sodium influences neurotransmitter uptake.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELROD J. THE METABOLISM, STORAGE, AND RELEASE OF CATECHOLAMINES. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1965;21:597–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Lynch G. Two glutamate binding sites in rat hippocampal membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug 1;57(2-3):283–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Rodbard D., Pert C. B. Is the benzodiazepine receptor coupled to a chloride anion channel? Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):315–317. doi: 10.1038/277315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Snyder S. H. Catecholamine uptake by synaptosomes in homogenates of rat brain: stereospecificity in different areas. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Dec;170(2):221–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding in rat brain synaptic membrane fractions. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):81–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Presek P. Alpha noradrenergic receptors in brain membranes: sodium, magnesium and guanyl nucleotides modulate agonist binding. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;306(1):67–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00515595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., U'Prichard D. C., Sheehan P., Snyder S. H. alpha-Noradrenergic receptors in the brain: differential effects of sodium on binding of [3H]agonists and [3H]antagonists. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 27;140(2):378–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90472-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R. E., Orlansky H., Mytilineou C., Cohen G. Amphetamine: evaluation of d- and l-isomers as releasing agents and uptake inhibitors for 3H-dopamine and 3H-norepinephrine in slices of rat neostriatum and cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Jul;194(1):47–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn A. S., Coyle J. T., Snyder S. H. Catecholamine uptake by synaptosomes from rat brain. Structure-activity relationships of drugs with differential effects on dopamine and norepinephrine neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;7(1):66–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z., Moret C., Raisman R., Dubocovich M. L., Briley M. High-affinity [3H]imipramine binding in rat hypothalamus: association with uptake of serotonin but not of norepinephrine. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1133–1135. doi: 10.1126/science.7444441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M., Raisman R., Briley M., Langer S. Z. Regional distribution of [3H]imipramine binding in rat brain. Brain Res. 1981 Apr 6;210(1-2):493–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90933-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehavi M., Paul S. M., Skolnick P., Goodwin F. K. Demonstration of specific high affinity binding sites for [3H] imipramine in human brain. Life Sci. 1980 Jun 30;26(26):2273–2279. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. B., Renyi A. L. Tricyclic antidepressant agents. II. Effect of oral administration on the uptake of 3-H-noradrenaline and 14-C-5-hydroxytryptamine in slices of the midbrain-hypothalamus region of the rat. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1975;36(Suppl 5):395–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1975.tb00807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut J. J., Kety S. S. Biogenic amines and emotion. Science. 1967 Apr 7;156(3771):21–37. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3771.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Goodman R. R. Multiple neurotransmitter receptors. J Neurochem. 1980 Jul;35(1):5–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb12483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Putative neurotransmitters in the brain: selective neuronal uptake, subcellular localization, and interactions with centrally acting drugs. Biol Psychiatry. 1970 Oct;2(4):367–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talvenheimo J., Nelson P. J., Rudnick G. Mechanism of imipramine inhibition of platelet 5-hydroxytryptamine transport. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4631–4635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., McGeer E. G. A comparison of sodium-dependent glutamate binding with high-affinity glutamate uptake in rat striatum. Brain Res. 1980 Feb 17;184(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90589-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Snyder S. H. The glycine synaptic receptor: evidence that strychnine binding is associated with the ionic conductance mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4002–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


