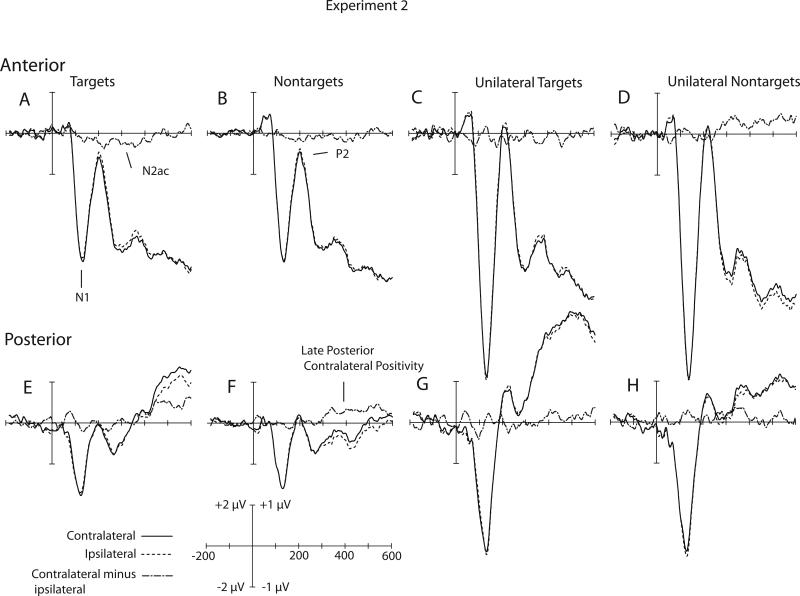
Figure 3.
Grand average of contralateral ipsilateral and contralateral minus ipsilateral waveforms for Experiment 2. A) Bilaterally presented Targets at anterior electrodes. B) Bilaterally presented nontargets at anterior electrodes. C) Unilaterally presented targets at anterior electrodes. D) Unilaterally presented nontargets at anterior electrodes. E) Bilaterally presented targets at posterior electrodes. F) Bilaterally presented nontargets at posterior electrodes. G) Unilaterally presented targets at posterior electrodes. H) Unilaterally presented nontargets at posterior electrodes. Anterior waveforms are collapsed across electrode sites F1/2, F3/4, F5/6, F7/8, FC1/2, FC3/4, FC5/6, FT7/8, C1/2, C3/4, C5/6, T7/T8. Posterior waveforms are collapsed across electrode sites. P1/2, P3/4, P5/6, P7/8, P9/10, PO3/4, PO7/8, O1/2. For visual clarity, the waveforms shown here were filtered offline with a low-pass Gaussian filter with a half-amplitude cutoff at 50 Hz. The raw contralateral and ipsilateral waveforms use the 2.0 μV scale. The contralateral-minus-ipsilateral difference waveforms use the 1.0 μV scale.