Abstract
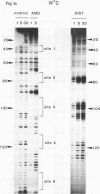
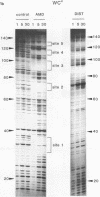
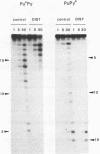
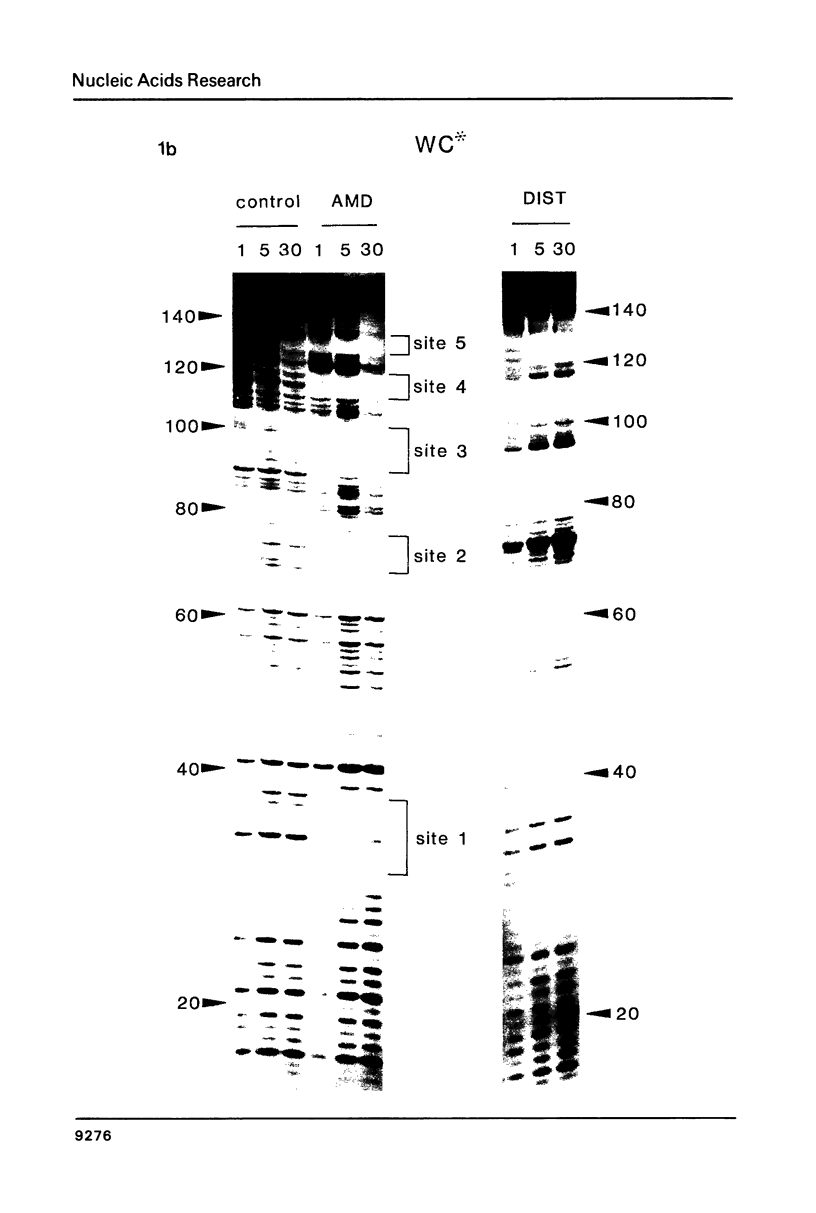
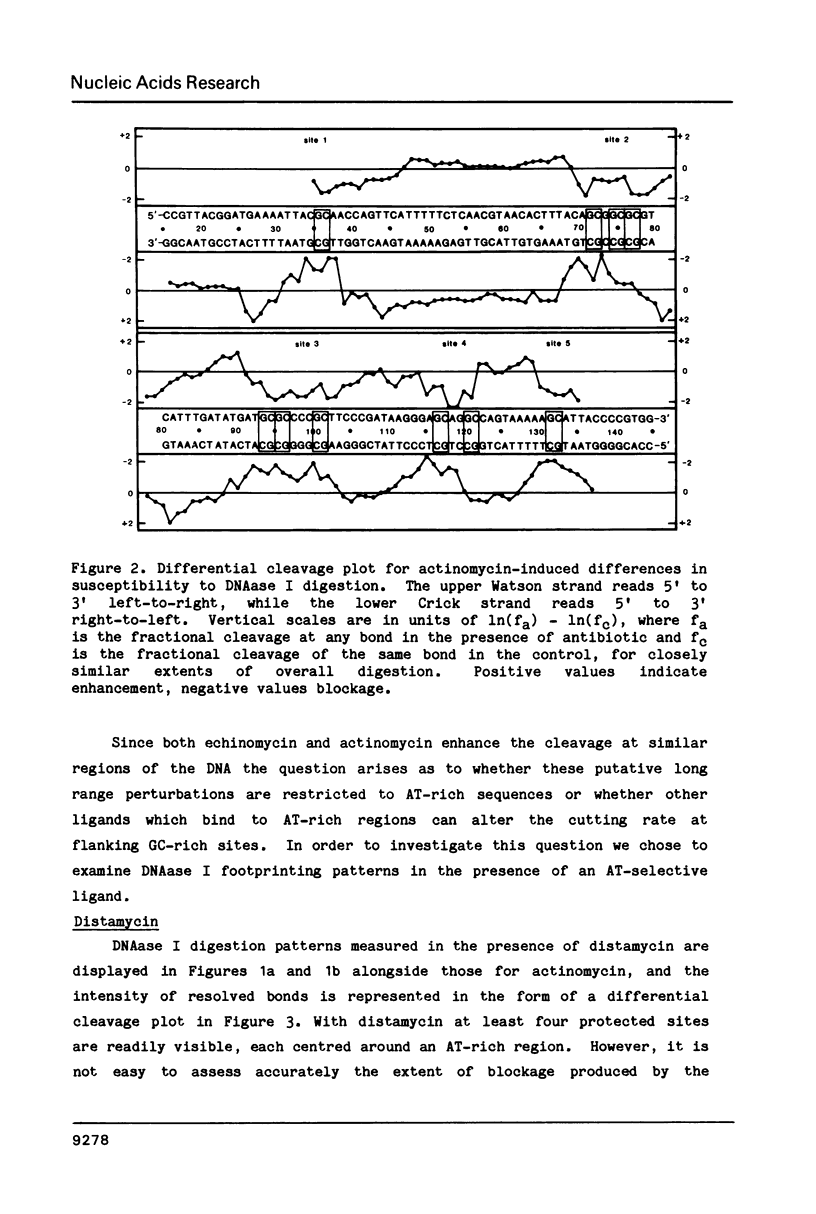
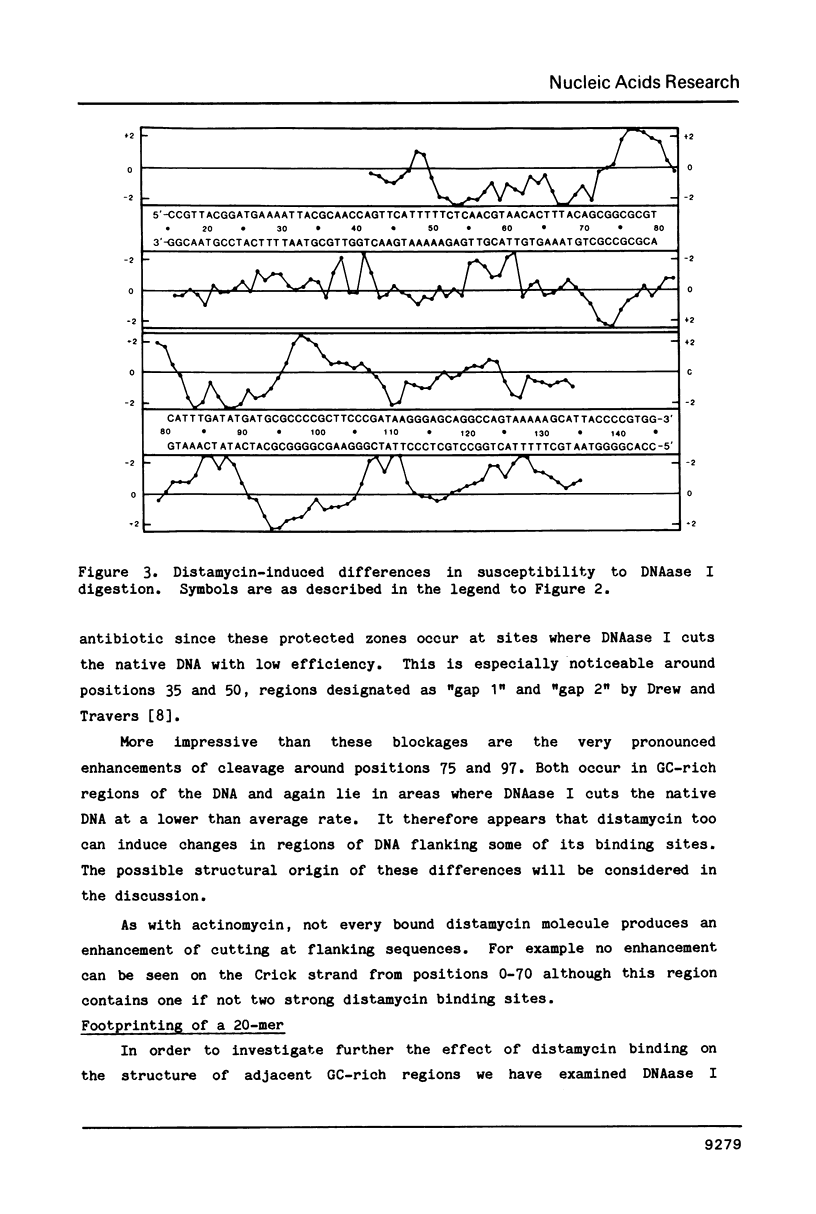
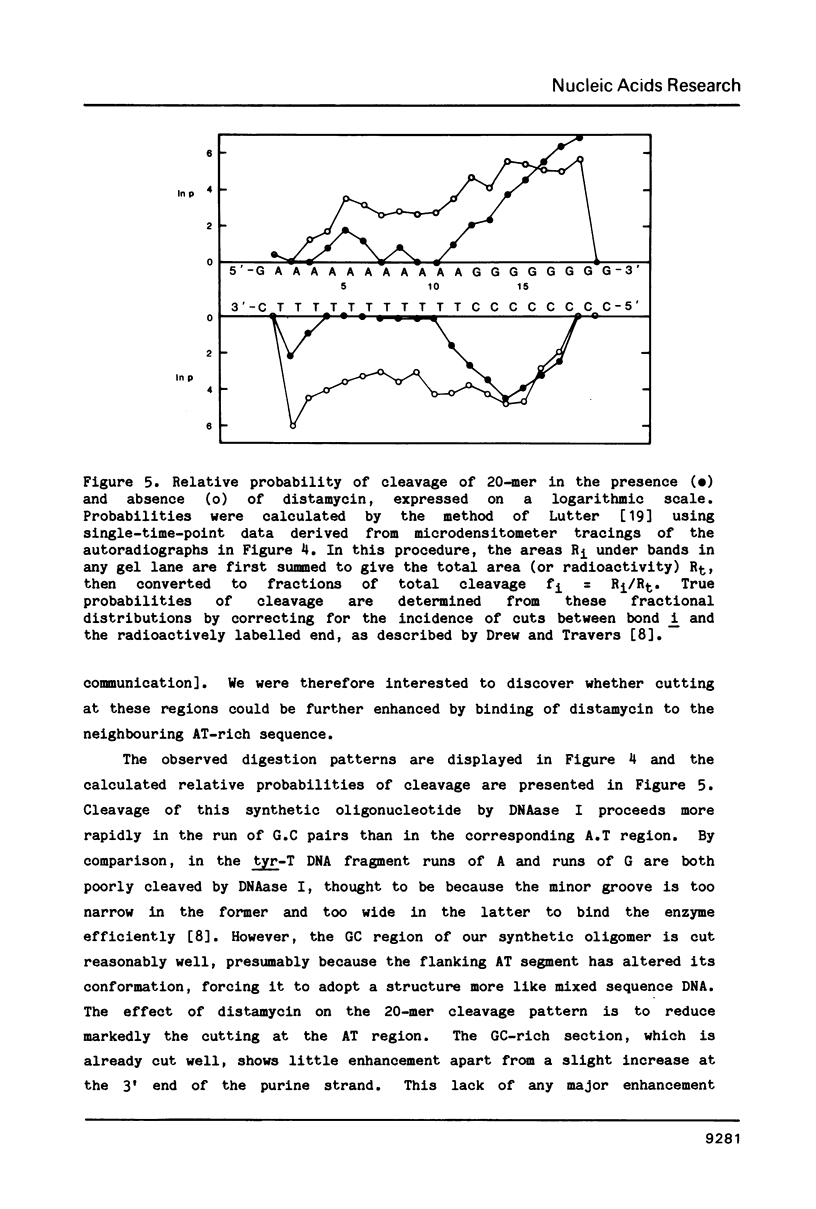
The technique of DNAase I footprinting has been used to investigate preferred binding sites for actinomycin D and distamycin on a 160-base-pair DNA fragment from E. coli containing the tyr T promoter sequence. Only sites containing the dinucleotide step GpC are protected by binding of actinomycin, and all such sites are protected. Distamycin recognizes four major regions rich in A + T residues. Both antibiotics induce enhanced rates of cleavage at certain regions flanking their binding sites. These effects are not restricted to any particular base sequence since they are produced in runs of A and T by actinomycin and in GC-rich sequences by distamycin. The observed increases in susceptibility to nuclease attack are attributed to DNA structural variations induced in the vicinity of the ligand binding site, most probably involving changes in the width of the helical minor groove.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Olsen R. K., Waring M. J. Equilibrium and kinetic studies on the binding of des-N-tetramethyltriostin A to DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 29;696(3):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90063-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Wakelin L. P., Waring M. J. Kinetics of the interaction between echinomycin and deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5768–5779. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. Kinetics of dissociation of quinoxaline antibiotics from DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 27;654(2):279–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. J., Dabrowiak J. C., Vournakis J. N. Sequence specificity of actinomycin D and Netropsin binding to pBR322 DNA analyzed by protection from DNase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Drew H. R., Waring M. J. Sequence-specific binding of echinomycin to DNA: evidence for conformational changes affecting flanking sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4865–4879. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scamrov A. V., Beabealashvilli R. S. Binding of actinomycin D to DNA revealed by DNase I footprinting. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snounou G., Malcom A. D. Production of positively supercoiled DNA by netropsin. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):211–216. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. The stereochemistry of actinomycin binding to DNA and its implications in molecular biology. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1973;13:153–190. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. M., Dervan P. B. Echinomycin binding sites on DNA. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1122–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.6089341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Dervan P. B. Chromomycin, mithramycin, and olivomycin binding sites on heterogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid. Footprinting with (methidiumpropyl-EDTA)iron(II). Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2373–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Dervan P. B. Methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II) and DNase I footprinting report different small molecule binding site sizes on DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5555–5567. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Ughetto G., Quigley G. J., Hakoshima T., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A. The molecular structure of a DNA-triostin A complex. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1115–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.6474168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. DNA modification and cancer. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:159–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J., Wakelin L. P. Echinomycin: a bifunctional intercalating antibiotic. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):653–657. doi: 10.1038/252653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. Variation of the supercoils in closed circular DNA by binding of antibiotics and drugs: evidence for molecular models involving intercalation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):247–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]