Abstract
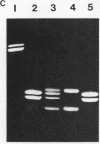
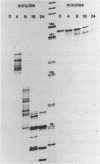
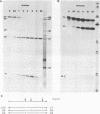
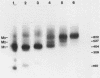
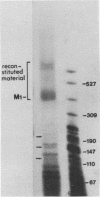
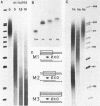
Reconstitution of mononucleosomes from DNA and core histones was carried out to study the positioning of histone octamers on the DNA. Using random DNA molecules in the 200 to 250 bp size range we found that the reconstitution products consisted of a mixture of three different types of particles that could be separated by low ionic strength gel electrophoresis. In one particle, DNA was complexed with histones along its entire length indicating the binding of more than one histone octamer. The second particle contained only one histone core that was always associated, however, with the terminal 145 bp of the DNA regardless of its sequence which can be ascribed to a DNA end effect. Only the third particle consisted of histone octamers bound at internal positions of the DNA and is therefore the only particle suitable for investigating the influence of the DNA sequence on the positioning of the histone cores. A defined 154 bp pBR 322 restriction fragment that contains three BspRI restriction sites was also reconstituted with core histones. The accessibility of these sites to BspRI was measured in order to delineate the utility of restriction nucleases as probes for the structure of chromatin. Two sites located close to the center of the DNA were less susceptible by at least a factor of 1000 as compared to free DNA while the susceptibility of the third site in the terminal section of the DNA decreased about 50 fold after reconstitution.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright S. C., Wiseman J. M., Lange R. A., Garrard W. T. Subunit structures of different electrophoretic forms of nucleosomes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3673–3684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck H., Abler S., Zhang X. Y., Fritton H., Igo-Kemenes T. Positioning of nucleosomes in satellite I-containing chromatin of rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 15;176(1):131–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90385-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V., Gralla J., Martinson H. G. DNA sequence directs placement of histone cores on restriction fragments during nucleosome formation. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1068–1074. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Jr, Isenberg I. A histone cross-complexing pattern. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 19;13(24):4992–4997. doi: 10.1021/bi00721a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Igo-Kemenes T., Pfeiffer W., Zachau H. G. Specific cleavage of chromatin by restriction nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3213–3226. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Miller F., Klobeck G., Zachau H. G. Deoxyribonuclease II as a probe for chromatin structure. II. Mode of cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 15;144(3):329–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Deoxyribonuclease II as a probe for chromatin structure. I. Location of cleavage sites. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 15;144(3):305–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss A., Sain B., Csordás-Tòth E., Venetianer P. A new sequence-specific endonuclease (Bsp) from Bacillus sphaericus. Gene. 1977 Jul;1(5-6):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Earnshaw W. C. Nucleosome assembly. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):763–767. doi: 10.1038/286763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer W., Horz W., Igo-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Restriction nucleases as probes of chromatin structure. Nature. 1975 Dec 4;258(5534):450–452. doi: 10.1038/258450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunell A., Kornberg R. D. Variable center to center distance of nucleosomes in chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 25;154(3):515–523. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunell A. Nucleosome reconstitution on plasmid-inserted poly(dA) . poly(dT). EMBO J. 1982;1(2):173–179. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. Nucleosome cores reconstituted from poly (dA-dT) and the octamer of histones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1805–1816. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D., Weintraub H. Nucleosomal DNA is digested to repeats of 10 bases by exonuclease III. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shick V. V., Belyavsky A. V., Bavykin S. G., Mirzabekov A. D. Primary organization of the nucleosome core particles. Sequential arrangement of histones along DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):491–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. H., Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. An octamer of histones H3 and H4 forms a compact complex with DNA of nucleosome size. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4805–4818. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. H., Felsenfeld G. A new procedure for purifying histone pairs H2A + H2B and H3 + H4 from chromatin using hydroxylapatite. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):689–696. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Künzler P. Cromatin and core particles formed from the inner histones and synthetic polydeoxyribonucleotides of defined sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1387–1415. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Stafford D. W. Structural features of a phased nucleosome core particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):51–55. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockley P. G., Thomas J. O. A nucleosome-like particle containing an octamer of the arginine-rich histones H3 and H4. FEBS Lett. 1979 Mar 1;99(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80264-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Prunell A. Nucleosome spacing in rat liver chromatin. A study with exonuclease III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2275–2293. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E. Compact oligomers and nucleosome phasing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3583–3587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E. Nucleosome reconstitution: effect of DNA length on nuclesome structure. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2871–2880. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Oudet P., Chambon P. Preferential in vitro assembly of nucleosome cores on some AT-rich regions of SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):705–713. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weischet W. O., Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E., Klump H. Thermal denaturation of nucleosomal core particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):139–160. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Fittler F., Hörz W. Eight different highly specific nucleosome phases on alpha-satellite DNA in the African green monkey. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4287–4306. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Hörz W. Analysis of highly purified satellite DNA containing chromatin from the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1481–1494. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Hörz W. Nucleosomes are positioned on mouse satellite DNA in multiple highly specific frames that are correlated with a diverged subrepeat of nine base-pairs. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 15;176(1):105–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90384-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]