Abstract
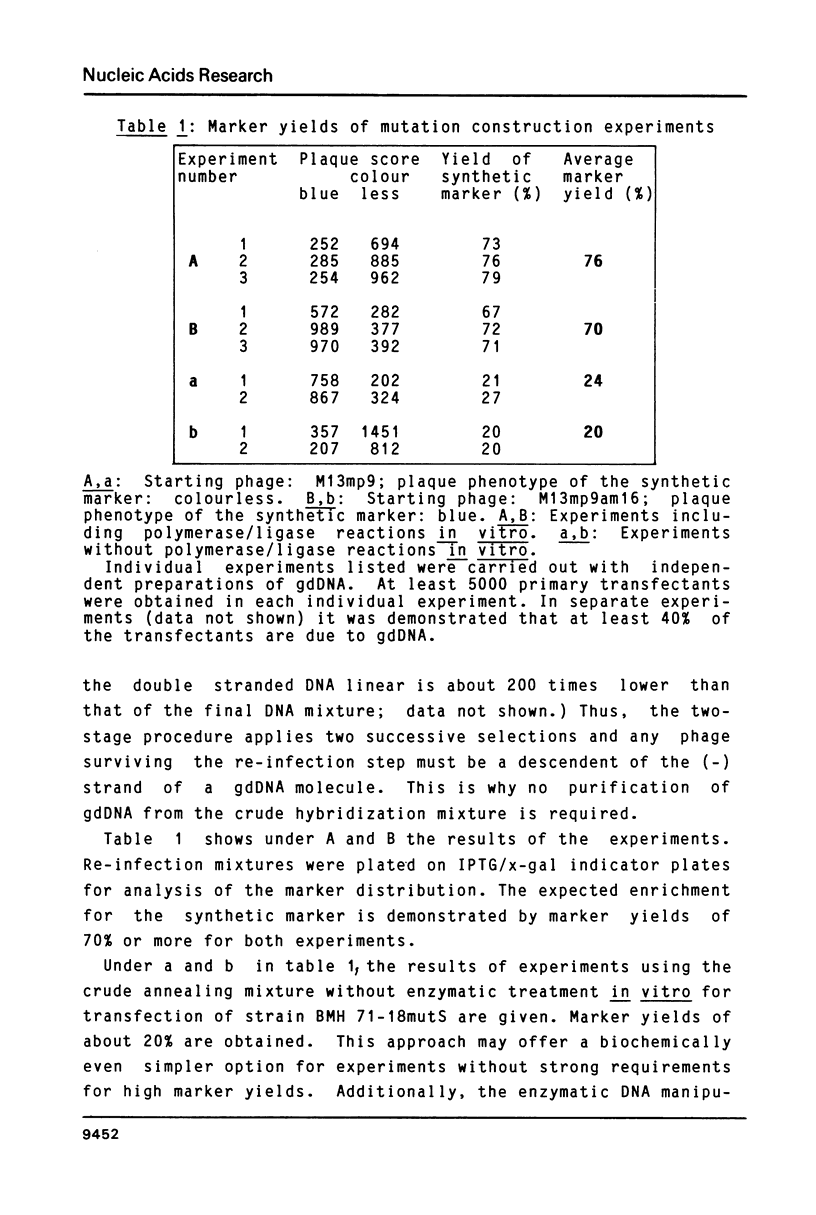
A simple and efficient method is described to introduce structurally pre-determined mutations into recombinant genomes of filamentous phage M13. The method rests on gapped duplex DNA (gdDNA) molecules of the phage M13 genome as the key intermediate. In this gdDNA, the (+) and the (shorter) (-) strand carry different genetic markers in such a way, that a rigorous selection can be applied for phage carrying the markers of the (-) strand. For introduction of the mutation, a synthetic oligonucleotide with partial homology to a target site within the single stranded DNA region is annealed to the gdDNA. The oligonucleotide subsequently becomes part of the (-) strand by enzymatic DNA gap filling and sealing. This physical linkage is preserved at the genetic level after transfection of a recipient E.coli strain deficient in DNA mismatch correction, so that the synthetic marker can be selected from the phage progeny independent from its potential phenotype. It is demonstrated that by this method mutants can be constructed with marker yields in excess of 70%.
Full text
PDF

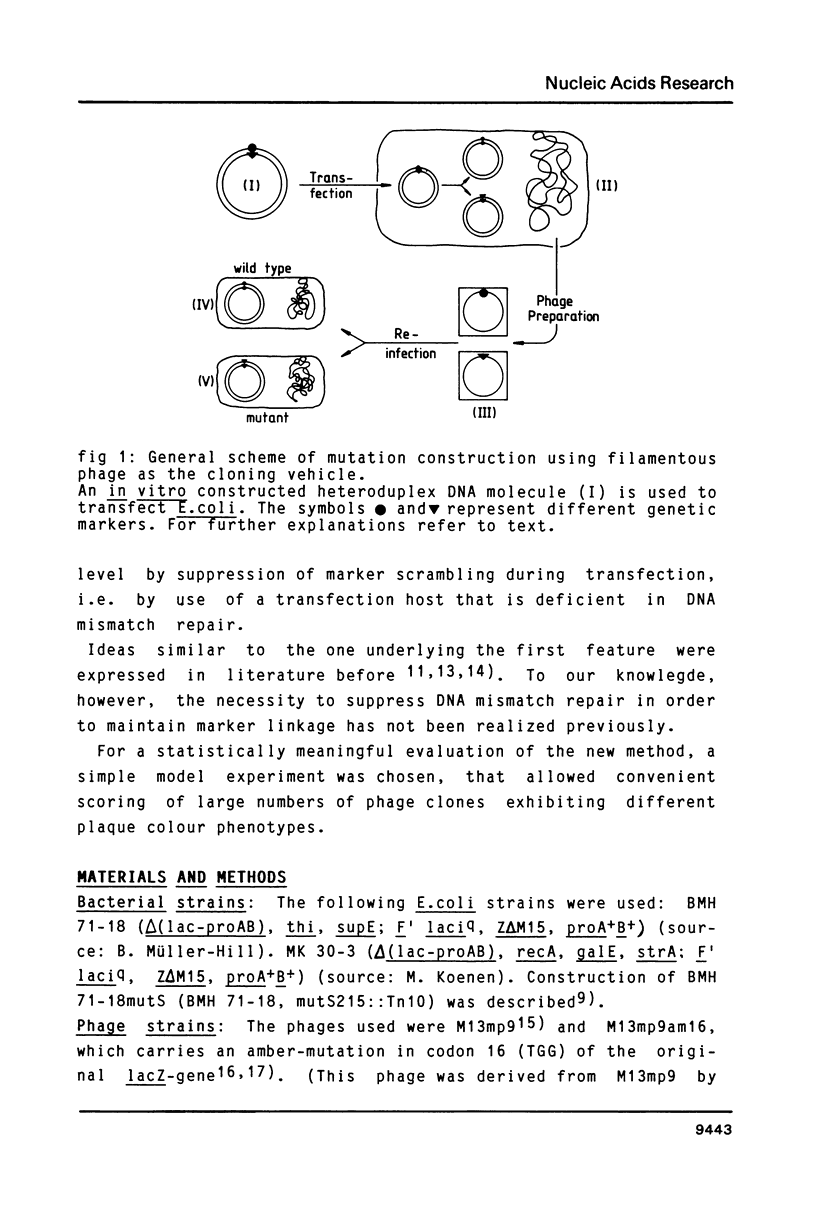












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baas P. D., Teertstra W. R., van Mansfeld A. D., Jansz H. S., van der Marel G. A., Veeneman G. H., van Boom J. H. Construction of viable and lethal mutations in the origin of bacteriophage 'phi' X174 using synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):615–639. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. J., Winter G., Wilkinson A. J., Fersht A. R. The use of double mutants to detect structural changes in the active site of the tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (Bacillus stearothermophilus). Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):835–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courage-Tebbe U., Kemper B. Construction of gapped circular DNA from phage M13 by in vitro hybridization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 26;697(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman B. W., Radman M. Escherichia coli mutator mutants deficient in methylation-instructed DNA mismatch correction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1063–1067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn B., Messing J. Methylation of single-stranded DNA in vitro introduces new restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):375–377. doi: 10.1038/272375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosse F., Krauss G. Replication of M13mp7 single-stranded DNA in vitro by the 9-S DNA polymerase alpha from calf thymus. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):109–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidecker G., Messing J., Gronenborn B. A versatile primer for DNA sequencing in the M13mp2 cloning system. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Takeuchi K., Hori H., Hirose T., Inayama S., Suzuki Y. Contact points between transcription machinery and the fibroin gene promoter deduced by functional tests of single-base substitution mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1394–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalnins A., Otto K., Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):593–597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer B., Kramer W., Fritz H. J. Different base/base mismatches are corrected with different efficiencies by the methyl-directed DNA mismatch-repair system of E. coli. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Schughart K., Fritz H. J. Directed mutagenesis of DNA cloned in filamentous phage: influence of hemimethylated GATC sites on marker recovery from restriction fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6475–6485. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley K. E., Villarejo M. R., Fowler A. V., Zamenhof P. J., Zabin I. Molecular basis of beta-galactosidase alpha-complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1254–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmenout A., Remaut E., van Boom J., Fiers W. Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis: selection of mutants by hemimethylation of GATC-sequences. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):126–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00332734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B., Hans Hopschneider P. Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osinga K. A., Van der Bliek A. M., Van der Horst G., Groot Koerkamp M. J., Tabak H. F., Veeneman G. H., Van Boom J. H. In vitro site-directed mutagenesis with synthetic DNA oligonucleotides yields unexpected deletions and insertions at high frequency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8595–8608. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pukkila P. J., Peterson J., Herman G., Modrich P., Meselson M. Effects of high levels of DNA adenine methylation on methyl-directed mismatch repair in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1983 Aug;104(4):571–582. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.4.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E. C., Kamel F. Reversion of frameshift mutations by mutator genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):994–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.994-1001.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboni C., Cortese R., Ciliberto G., Cesareni G. A general method to select for M13 clones carrying base pair substitution mutants constructed in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4229–4239. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wezenbeek P. M., Hulsebos T. J., Schoenmakers J. G. Nucleotide sequence of the filamentous bacteriophage M13 DNA genome: comparison with phage fd. Gene. 1980 Oct;11(1-2):129–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



