Abstract
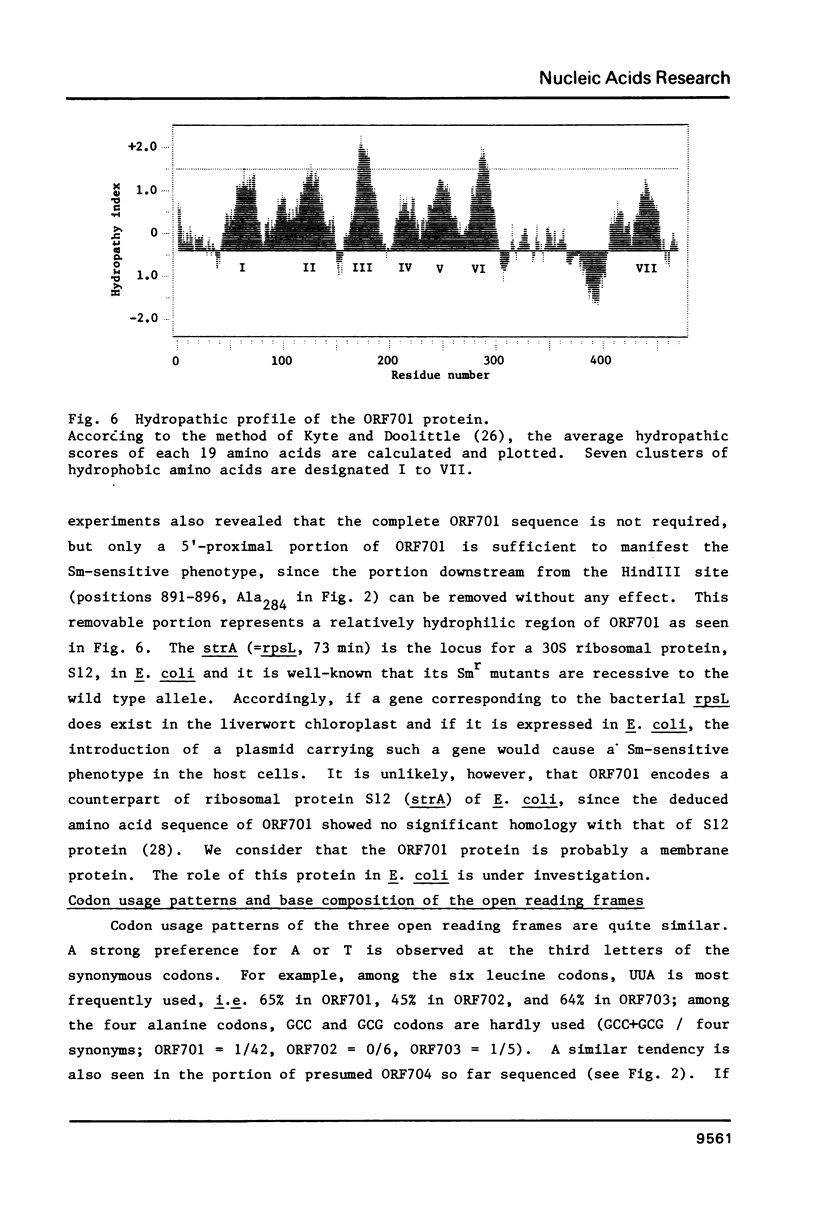
The nucleotide sequence of a region of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast DNA was determined. On this DNA sequence (3.38kb), three open reading frames (ORFs) and three putative tRNA genes were detected in the following order: -ORF701-tRNASer(UGA)-ORF702-tRNAGly(GCC)-initiator tRNAMet(CAU)-ORF703-. The ORF703 is composed of 100 codons in which those for lysine (15%) and arginine (11%) are abundant, and could be accounted for as a counterpart of E. coli ribosomal protein S14 since they share 45% homology in the amino acid sequences. The ORF701 appears to code for a membrane protein, showing a periodic appearance of seven clusters of hydrophobic amino acids. Although the mechanisms remain unknown, the ORF701 causes a streptomycin-sensitive phenotype in resistant mutants of E. coli. The ORFs and tRNA genes are separated from each other by extremely AT-rich spacers containing sequences of dyad symmetry. The third letter positions of the codons in the ORFs are also rich in A and T residues.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartsch M., Kimura M., Subramanian A. R. Purification, primary structure, and homology relationships of a chloroplast ribosomal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6871–6875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerretti D. P., Dean D., Davis G. R., Bedwell D. M., Nomura M. The spc ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: sequence and cotranscription of the ribosomal protein genes and a protein export gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2599–2616. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deno H., Kato A., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Nucleotide sequences of tobacco chloroplast genes for elongator tRNAMet and tRNAVal (UAC): the tRNAVal (UAC) gene contains a long intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7511–7520. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deno H., Sugiura M. Chloroplast tRNA gene contains a long intron in the D stem: Nucleotide sequences of tobacco chloroplast genes for tRNA (UCC) and tRNA (UCU). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):405–408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deno H., Sugiura M. The nucleotide sequences of tRNASer (GCU) and tRNAGln (UUG) genes from tobacco chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8407–8414. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Yaguchi M., Wittmann-Liebold B. Primary stucture of protein S12 from the small Escherichia coli ribosomal subunit. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):12–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):r1–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. J., Vold B. S. Sequence analysis of a cluster of twenty-one tRNA genes in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5763–5774. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi H., Yamao F., Sakano H., Ozeki H. Identification of transfer RNA suppressors in Escherichia coli. I. Amber suppressor su+2, an anticodon mutant of tRNA2Gln. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90380-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskunas S. R., Fallon A. M., Nomura M. Identification and organization of ribosomal protein genes of Escherichia coli carried by lambdafus2 transducing phage. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7323–7336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karabin G. D., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast transfer RNA transcription units. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a tRNAThr-tRNAGly-tRNAMet-tRNASer-tRNAGln gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5512–5518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J., Herrmann R. G. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the P680 chlorophyll alpha apoprotein of the photosystem II reaction center from spinach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2837–2850. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Nomura N., Morita M., Sugisaki H., Sugimoto K., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of small ColE1 derivatives: structure of the regions essential for autonomous replication and colicin E1 immunity. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 4;172(2):151–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00268276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. N., Rogers S. G. Plasmid pKC7: a vector containing ten restriction endonuclease sites suitable for cloning DNA segments. Gene. 1979 Sep;7(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz A. A., Krebbers E. T., Schwarz Z., Gubbins E. J., Bogorad L. Nucleotide sequences of five maize chloroplast transfer RNA genes and their flanking regions. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5503–5511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streisinger G., Okada Y., Emrich J., Newton J., Tsugita A., Terzaghi E., Inouye M. Frameshift mutations and the genetic code. This paper is dedicated to Professor Theodosius Dobzhansky on the occasion of his 66th birthday. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R., Steinmetz A., Bogorad L. Maize chloroplast DNA encodes a protein sequence homologous to the bacterial ribosome assembly protein S4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5277–5286. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Sugiura M. A putative gene of tobacco chloroplast coding for ribosomal protein similar to E. coli ribosomal protein S19. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1913–1918. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawrousek E. F., Hansen J. N. Structure and organization of a cluster of sic tRNA genes in the space between tandem ribosomal RNA gene sets in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bohnert H. J., Whitfeld P. R., Bottomley W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the M(r) 32,000 thylakoid membrane protein from Spinacia oleracea and Nicotiana debneyi predicts a totally conserved primary translation product of M(r) 38,950. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7699–7703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



