Abstract
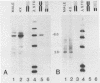
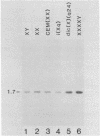
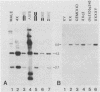
Fluorescence activated sorting of chromosomes from 49,XXXXY human lymphoblasts has been used to obtain DNA enriched for the human X. This DNA was cloned in lambda phage Charon 21A to obtain a library of approximately 60,000 pfu. Phage inserts free of human highly repeated DNA sequences are localized to different regions of the human X by two independent hybridization analyses. The first utilized comparative hybridization to rodent-human hybrid cell DNA samples containing all or known portions of the human X, while the second was based on hybridization dosage to DNA samples from human cell lines differing in the number of X chromosomes or X chromosome segments. Of five unique sequence inserts tested, three were X chromosome specific and were localized to regions Xpter leads to Xcen, Xql leads to Xq22 and Xq24 leads to Xqter, respectively. The library presented here represents a highly enriched source of human X chromosome-specific DNA sequences.
Full text
PDF







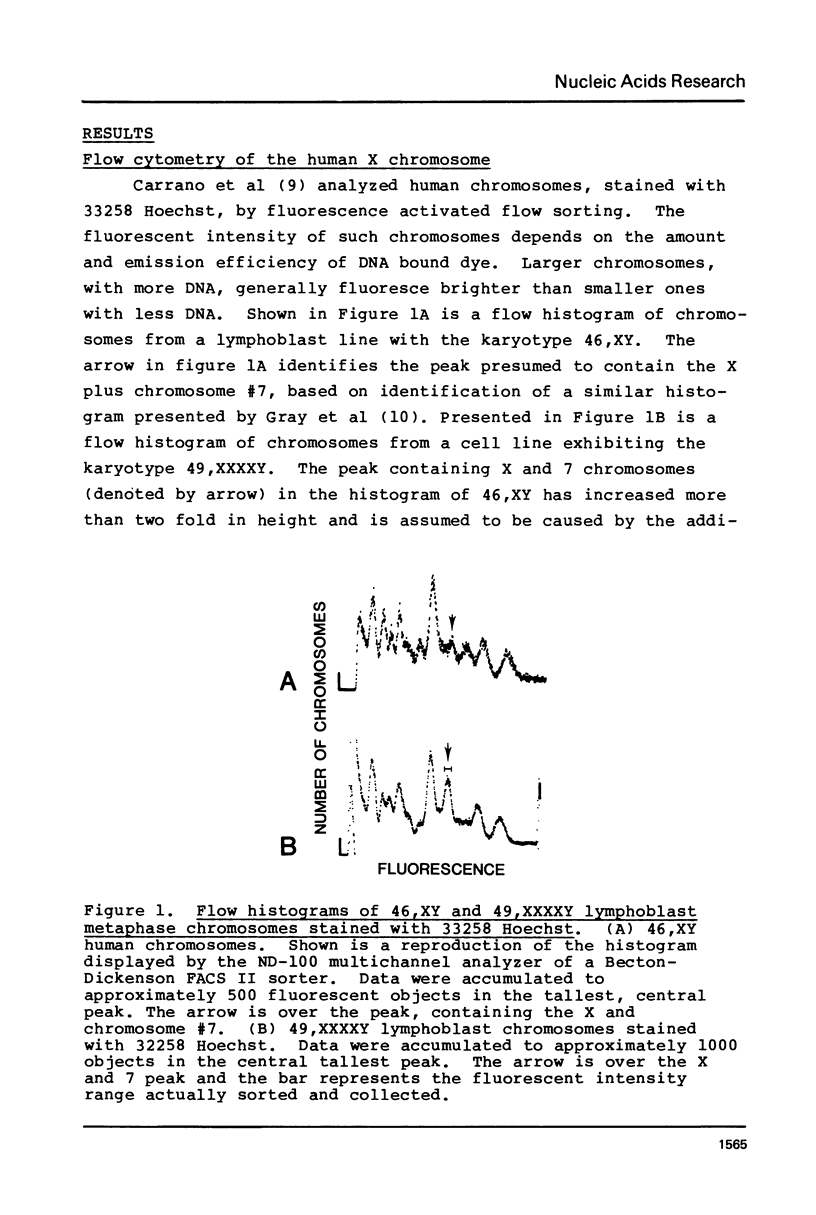













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATTANACH B. M. A chemically-induced variegated-type position effect in the mouse. Z Vererbungsl. 1961;92:165–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00890283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrano A. V., Gray J. W., Langlois R. G., Burkhart-Schultz K. J., Van Dilla M. A. Measurement and purification of human chromosomes by flow cytometry and sorting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1382–1384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Lindsten J., Lomakka G., Moller A., Zech L. The use of fluorescence techniques for the recognition of mammalian chromosomes and chromosome regions. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1972;11:1–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Young B. D., Elles R. G., Hill M. E., Williamson R. Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):374–376. doi: 10.1038/293374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disteche C. M., Carrano A. V., Ashworth L. K., Burkhart-Schultz K., Latt S. A. Flow sorting of the mouse Cattanach X chromosome, T (X; 7) 1 Ct, in an active or inactive state. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1981;29(4):189–197. doi: 10.1159/000131569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Keys C., VarsanyiBreiner A., Kao F. T., Jones C., Puck T. T., Housman D. Isolation and localization of DNA segments from specific human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuściński J., Skoczylas B. Simple and rapid fluorimetric method for DNA microassay. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):252–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuściński J., Skoczylas B. Simple and rapid fluorimetric method for DNA microassay. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):252–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishan A., Raychaudhuri R., Flowers A. Karyotype studies on human leukemic lymphoblasts in vitro and as serial transplants in neonatal syrian hamsters. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Dec;43(6):1203–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:372–373. doi: 10.1038/190372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Barell E. F., Dougherty C. P., Lazarus H. Patterns of late replication in X chromosomes of human lymphoid cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1981 Mar;3(2):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(81)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Willard H. F., Gerald P. S. BrdU-33258 Hoechst analysis of DNA replication in human lymphocytes with supernumerary or structurally abnormal X chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1976 Aug 17;57(2):135–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00292912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto F. J., Oldiges H., Göhde W., Barlogie B., Schumann J. Flow cytogenetics of uncloned and cloned Chinese hamster cells. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(1):52–56. doi: 10.1159/000131464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Willard H. F., Smith K. D. Isolation and characterization of cloned human DNA fragments carrying reiterated sequences common to both autosomes and the X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1853–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Mareni C. E., Migeon B. R. Isolation and characterization of cloned DNA sequences that hybridize to the human X chromosome. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]